 According to their economic, social and political characteristics, countries can be classified differently. An emerging country is one that is developing or has industrialized in recent times .
According to their economic, social and political characteristics, countries can be classified differently. An emerging country is one that is developing or has industrialized in recent times .
It is understood that an emerging country is emerging from underdevelopment thanks to a growing economy . This expansion allows it to lay the foundations for sustainable development through the construction of new infrastructure and other modifications.
An emerging country generally has natural resources that, thanks to foreign investments and international support, it begins to exploit on a large scale. It can also become an attractive financial market for capital .
Although there are no precise definitions, it is common for an emerging country to be considered to be in better conditions than an underdeveloped country, although it has not yet achieved the status of a developed country. Therefore, although it does not suffer from extreme poverty , it is not a rich nation.
Regarding the social situation of an emerging country, it is common for there to be wide differences between the various classes and for the increase in wealth to take time to be reflected in a better standard of living for all sectors.
It is important to mention that the notion of emerging country is also used by risk rating agencies . These companies , such as Moody's , Standard & Poor's and MSCI , analyze the payment capacity that countries have to meet their financial obligations. The greater the difficulty in paying debts, the greater the risk.
One of the fundamental points when qualifying the situation of a country is to understand the causes that have led to it, whether it is a developed country or an emerging one. That is, it is not enough to evaluate an isolated moment in its history, but to understand in depth issues such as the quality of life of its inhabitants, a broad context is necessary.
 Generally speaking, the debate about the reasons why some countries enjoy greater development than others seems endless. The majority attributes this difference to the consequences of European imperialism , which began in the 16th century and extended for a long time, giving rise to the creation of extractive colonies on other continents, thanks to which Europe was able to accumulate wealth and propel itself towards the Industrial Revolution.
Generally speaking, the debate about the reasons why some countries enjoy greater development than others seems endless. The majority attributes this difference to the consequences of European imperialism , which began in the 16th century and extended for a long time, giving rise to the creation of extractive colonies on other continents, thanks to which Europe was able to accumulate wealth and propel itself towards the Industrial Revolution.
On the other side of this story are the colonies, which did not benefit from this process but instead became in a precarious situation and were involved in a relationship of dependency that deprived them of their freedom .
Broadly speaking, we can say that emerging countries are not all the same, but rather they fall into this category if they meet some of the following conditions, which are not considered particularly worrying if development is growing:
* it still cannot sustain itself completely independently, that is, its economy is not self-sustaining;
* its unemployment rate is high;
* The relationship between the percentage of its population that is economically active and its gross domestic product ( GDP ) is quite poor.
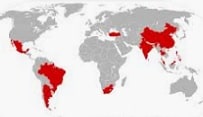
Within this framework, there is an international group called BRICS , which brings together a series of emerging economies, from whose names the initials are taken to form the acronym , since they are the following: Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa. We should not be fooled by the word "emerging", as if they were poor countries, since they are considered the most important worldwide within this category. This organization's main objectives are cooperation between these nations and their integration into the rest of the world.
