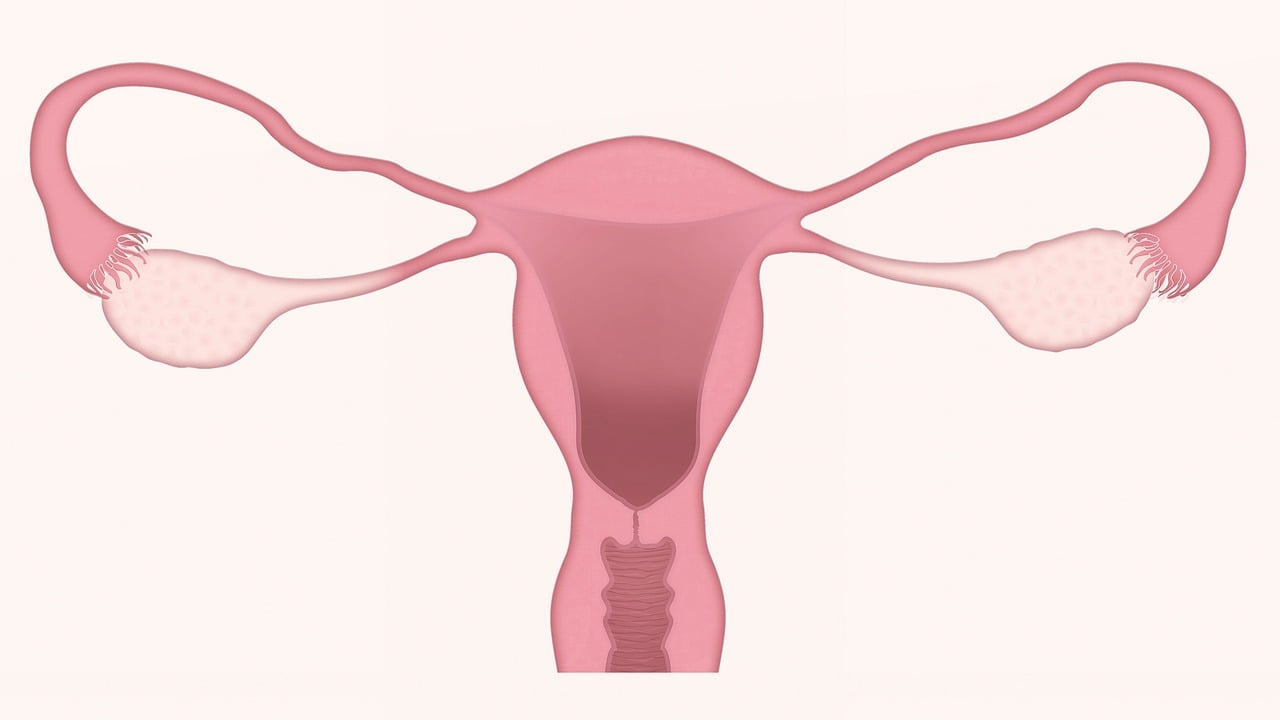
The female gonads are called ovaries.
The ovary is the female gonad that produces and secretes eggs and sex hormones (estrogens, androgens and others). It is the equivalent of male testicles.
The ovaries, whose shape resembles an almond, weigh 6-7 grams and have a grayish-white color. They are found on both sides of the uterus , to which they are fixed by ligaments and infundibulum. Two areas can be distinguished within the ovary (a term derived from the Latin ovarium ), called the ovarian cortex and medulla .
Parts of the ovary
The ovarian cortex is covered by a cuboidal epithelium that flattens over time . The cortex is composed of the stroma (the supporting tissue) and the ovarian parenchyma (with follicles in various stages of development).
The ovarian medulla , smaller than the cortex, has a greater number of elastic fibers and has veins, nervous lymphatic vessels, connective tissue and spiral arteries.
oophorectomy
The surgical process that involves the removal of one or both ovaries is known as oophorectomy . This surgery can be performed both conventionally and through laparoscopy in the abdomen .
The ovaries are usually removed if there is a tumor. If only one of the ovaries is affected, the woman can continue producing eggs and hormones with the remaining ovary. On the other hand, if both ovaries are removed, the woman enters a surgical menopause .
When doctors detect benign ovarian cysts , there is a possibility that only the cyst will be removed, leaving the ovary fully functioning and allowing the woman to continue her normal reproductive capacity.
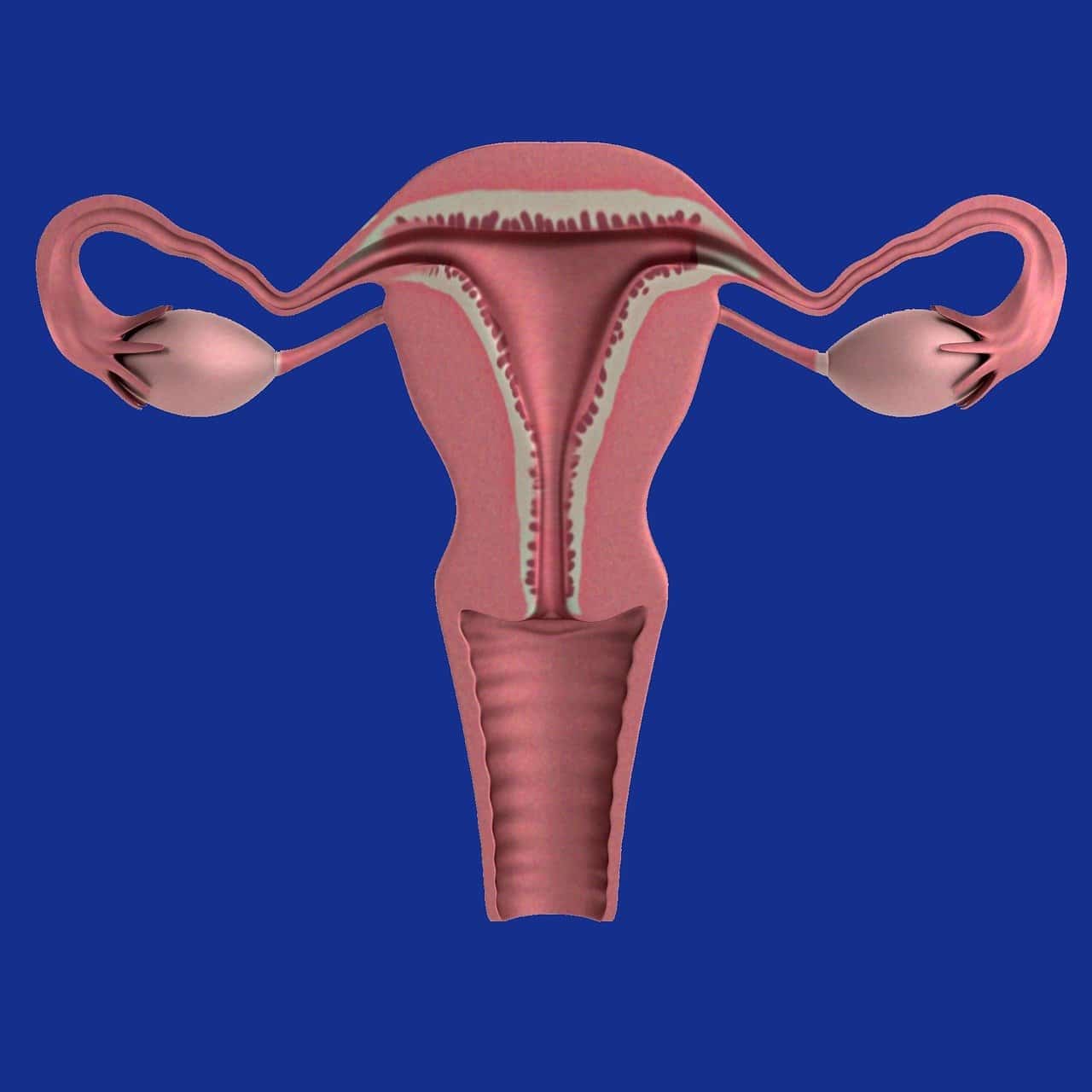
The ovary is responsible for the production and segregation of eggs and sex hormones.
ovarian cancer
Ovarian cancer , which manifests as a malignant tumor in one or both ovaries, has the highest mortality rate. Regarding diagnostic methods, none have proven to be sufficiently effective to detect this type of cancer in the initial stage of its evolution.
This disease only generates its first symptoms when it begins to spread. This is when the affected person may begin to show a series of symptoms that, it is worth clarifying, respond to a wide variety of disorders; You usually suffer from discomfort in the abdomen, weight loss, bleeding outside of menstruation days, digestion problems, vomiting, nausea and diarrhea.
When a doctor believes that one of his patients has a tumor in an ovary, among his resources for a correct evaluation is ultrasound, given that healthy tissues generate echoes different from those produced by carcinogens .
Another possibility is to perform a blood test to look for CA-125 , a substance that usually originates in the cells of this type of cancer; However, since CA-125 is also found in some healthy women, the results of this test cannot be considered decisive. As the last step for diagnosis, a biopsy is performed to remove a sample of the cancerous tissue and examine it with the help of a microscope .
Regarding treatment , this depends on the evolutionary stage of the cancer, the age of the patient and their general clinical history. Especially in the early stages, surgery is usually used to remove the affected ovaries, as well as the fallopian tubes and the uterus itself. When cancer is detected late, chemotherapy is added to the surgical intervention, both orally and intravenously.
Finally, the controversial bone marrow transplant represents hope for future ovarian cancer patients, and several centers are already practicing chemotherapy that includes the administration of stem cells. It is worth mentioning that this treatment is very dangerous, especially because obtaining the cells weakens the patient and makes her more vulnerable to contracting infections.
