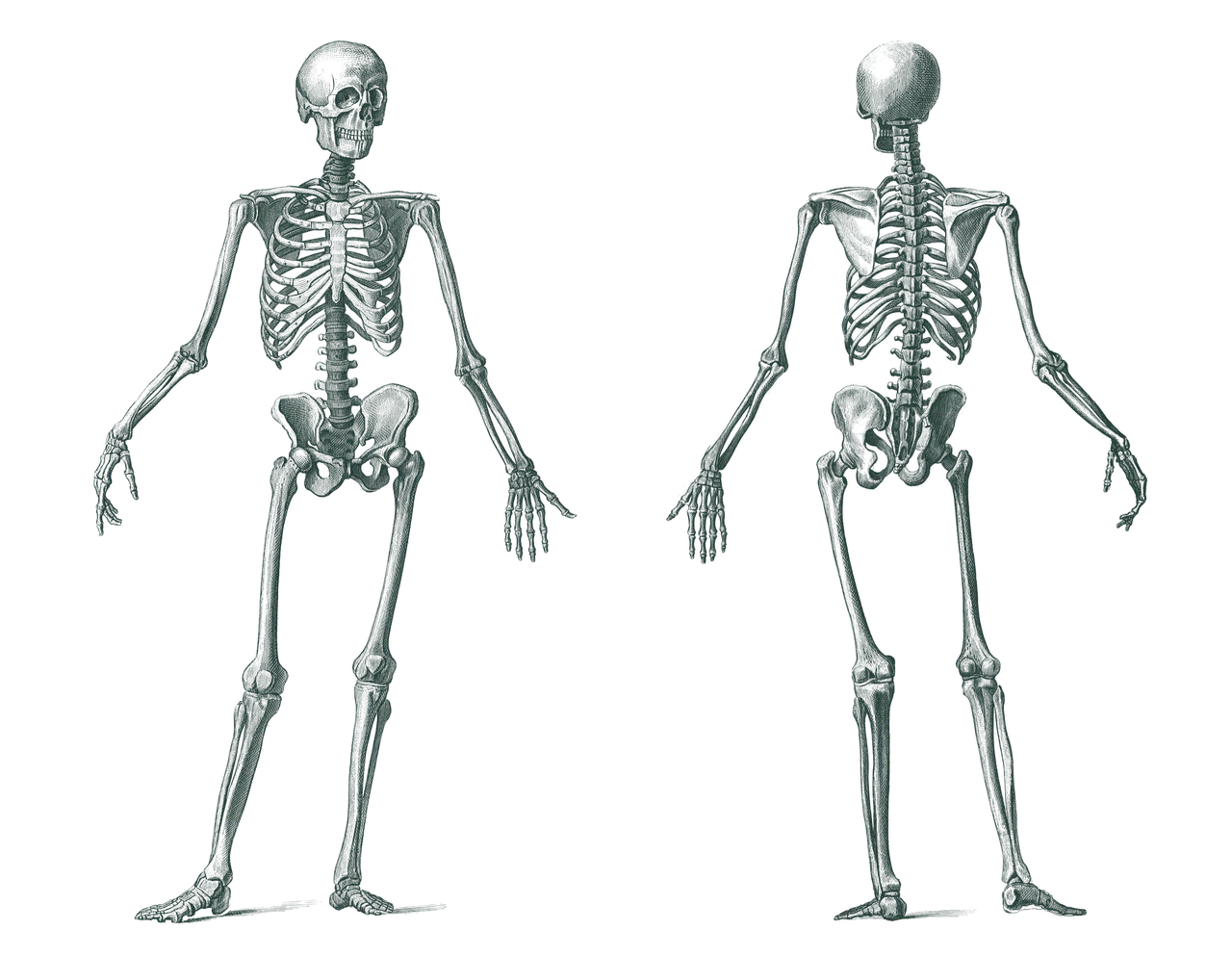
The idea of osseous refers to bones.
Bone is an adjective with etymological origin in the Latin osseus that names what belongs to or is linked to bones . A bone , for its part, is a very hard piece that makes up the skeleton of a class of living being (the so-called vertebrates ).
The most important component of bones is bone tissue , formed by various cells and an extracellular matrix subjected to calcification. Bone tissue gives the hardness and firmness that characterize bones. Three types of specialized cells make up bones: osteoclasts (which shed or resorb bone tissue), osteoblasts (drive the development of bone tissue), and osteocytes (the name osteoblasts receive when they reach maturity and change their function).
bone problems
It is likely that a person suffers a blow or impact that affects the bones. In this sense, a bone trauma is an injury that occurs in a bone. It may be an incomplete or complete fracture, depending on the severity. A bone fracture occurs when the bone loses continuity: if the bone that breaks produces a wound in the skin and comes to the surface, it is called an open fracture .
Bone cancer , on the other hand, is cancer that affects the bones. It is usually a cancer that arose in another region of the body and has spread to reach the bone. There is, however, primary bone cancer, which arises in the bone itself.
Bones and cartilage
Bones are solid structures that are mainly composed of bone tissue, and these make up the so-called skeletal system . Internal skeletons are rigid or semi-rigid structures that are found inside a body and move thanks to the action of a muscular system . In the case of humans and some mammals, these structures are ossified or mineralized and, therefore, are called bones.
Cartilages are also important components of the skeletal system as they complement its structure. The nose and ears of humans use cartilage in different ways. It is worth mentioning that some organisms do not have bone in their skeletons, but are composed exclusively of cartilage; Sharks are a clear example of this. To connect the bones with the rest of the rigid structures there are ligaments; The connection with the muscular system is achieved through tendons.
The bone elements fulfill a support function.
Functions of the skeletal system
The skeleton fulfills various functions of great importance, some of which are:
- Support : this system of bones or cartilage allows us to support ourselves and fix the rest of the parts of the body, but also to keep the muscles, ligaments and tendons in position, since these lack rigidity or solidity.
- Locomotion : although movement could not occur without the help of muscles, the skeletal system is an essential part of movement, since it serves to keep the body firm and structured.
- Hematopoiesis : the red marrow of long bones produces red blood cells and, to a lesser extent, lymphocytes and monocytes.
- Protection : given their solidity, the bones prevent the organs housed behind them from suffering significant damage when the body goes through situations such as a fall to the ground, a blow with another solid body or an attack from another living being. Some examples of this function are the brain, which takes refuge perfectly inside the skull; the lungs and heart, which receive protection from the ribs and spine; the eyes, which are located comfortably in the orbital cavities; the ear, housed in the temporal bone; the spinal cord, which acts within the vertebral column.
