A unicellular organism is made up of a single cell.
A unicellular organism is made up of just one cell . It should be noted that, within the context of biology , the group formed by the different organs of a living being is known as an organism . These bodies maintain a series of reciprocal links that are regulated by the laws of nature. Unicellular , for its part, refers to that which is composed of a single cell .
Before moving forward with the definition, it is necessary to know the etymological origin of the two words that make up the concept. Organism , which means "organs that give shape to a living being" , is the result of the sum of two Greek elements: the noun organon , which is synonymous with "instrument" ; and the suffix -ism , which indicates "activity" . Unicellular , for its part, has its origin in Latin. It translates as "of a cell" and is made up of two parts: unus , which is equivalent to "one" , and cellulla , which can be translated as "cell" .
If we take into account all the living beings that inhabit our planet, most of them are unicellular. All protozoa and bacteria , in fact, are part of this group. It is also important to note that, in their origin, organisms are always unicellular , since they develop from a single cell known as a zygote.
Characteristics of a unicellular organism
In addition to all of the above, it is also worth highlighting these other peculiarities of unicellular organisms:
- The circulation in them is carried out through what is known as cyclosis, which is the movement of the cytoplasm.
- They can basically be found in three different kingdoms: the protoctista kingdom, the fungi kingdom, and the monera kingdom .
- As a general rule, when talking about lists of single-celled organisms, those that are made establish the following sections: bacteria, fungi, the so-called archea, green algae, protists and plankton. The latter in turn is divided into zooplankton and phytoplankton.
- Unicellular algae are considered to be one of the most important living beings in the world. And they carry out a very important job at the level of photosynthesis, since they are capable of capturing a large amount of solar energy and, therefore, producing a high percentage of oxygen.
Organisms with more than one cell are called multicellular . Since they have different specialized cells, they are more complex organisms than unicellular ones. Multicellular organisms have tissues, organs, apparatus and systems , something that unicellular organisms lack.
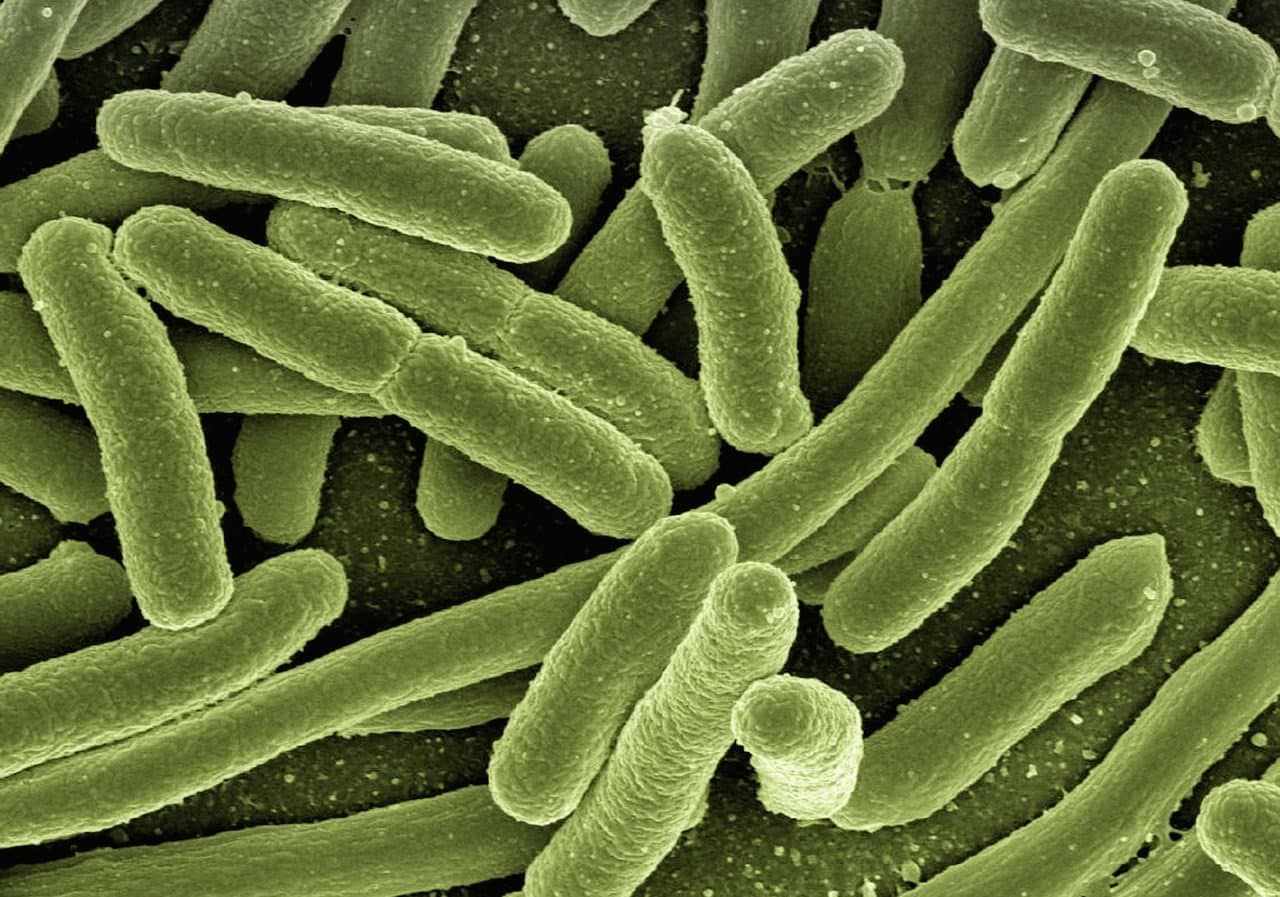
Bacteria are single-celled organisms.
Classification according to type
It should be noted that, despite this simplicity, unicellular organisms can be divided into two types: eukaryotes and prokaryotes , depending on the type of cell they house. Unicellular eukaryotic organisms have a cell that has a real nucleus. Prokaryotes, on the other hand, lack an established cell nucleus, which means that their DNA is distributed throughout the cytoplasm.
It is possible to place protozoa such as amoebas within the group of single-celled eukaryotic organisms, while bacteria such as salmonella are part of the single-celled prokaryotic organisms.
