
The path traveled by a body in space due to the gravitational action exerted by the stars is called an orbit.
Orbit is the path that a body travels in space due to the gravitational action exerted by the stars. The German scientist Johannes Kepler ( 1571 – 1630 ) was the one who analyzed, for the first time, orbits based on mathematical calculations. Kepler postulated that the orbits of the planets in the Solar System are elliptical and highlighted that the sun is not the center of these orbits, but one of their foci.
Kepler also stated that the orbital speed of a planet is not constant since it depends on the distance from the sun and found a universal relationship between the properties of the orbits of all planets that revolve around the sun.
Newton and orbits
The Englishman Isaac Newton ( 1643 – 1727 ) made other very important contributions to understanding the functioning of orbits. His law of universal gravitation and his laws of motion state that the sum of forces is equal to the mass multiplied by its acceleration, while gravity is proportional to mass and inversely proportional to the square of the distance.
In this case, it must be established that when it comes to studying and analyzing an orbit, a series of elements that are fundamental in it must be taken into account. We are referring, therefore, to issues such as eccentricity, inclination, the perihelion argument, the mean anomaly, the semi-minor axis, the length of the ascending node or the true anomaly.
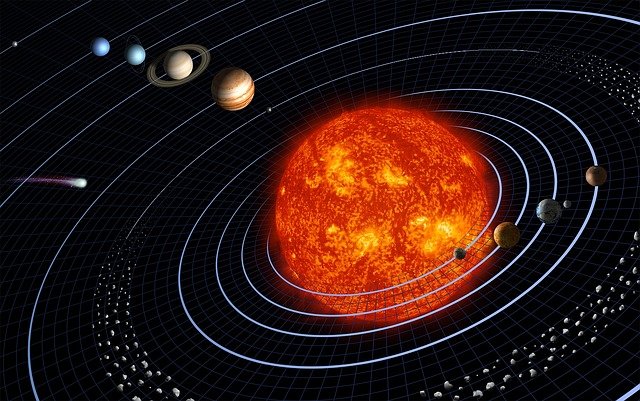
The planets in the Solar System develop elliptical orbits.
Classification according to type
There is a great variety of orbits based on the different criteria used to classify them. Thus, for example, if we use what would be the central body as a starting point, we would find four fundamental types of orbits: lunar, terrestrial, solar and Martian.
However, if the criterion to be used is the set of characteristics, we would have to talk about what are elliptical, inclined, circular, cemetery, ecliptic, synchronous, semi-synchronous orbits...
Orbit in physics and anatomy
For physics , an orbit is the path taken by a particle subjected to electromagnetic fields in particle accelerators and the path taken by an electron around the nucleus of an atom .
In the field of anatomy, the orbits are the cavities that are found on both sides of the face to house the eyeballs . It usually has a depth of between 42 and 50 millimeters, with a width of 40 millimeters at the base and a height of 35 millimeters.
The term in adverbial phrases
In addition to all of the above, we cannot ignore the existence of a large number of verbal phrases that we use in our daily lives and that make use of the term orbit that we are now analyzing. This would be the case of the expression "being in orbit." It means that a person is involved in a specific matter or is conveniently informed about it.
On the other hand, we have the verbal phrase "put into orbit" which has two meanings. Firstly, it means that a person is experiencing a stage of popularity and secondly, that they have been launched into space on a specific satellite.
