Before entering fully into the meaning of the term seismic wave, we are going to proceed to know the etymological origin of the two words that give it shape:
-First of all, we must explain that wave derives from Latin. Specifically, from "unda", which can be translated as " swirl " or as "wave".
-Secondly, it is necessary to know that seismic comes from Greek. In its case, it means "related to earthquakes" and is the result of the sum of two lexical components: the noun "seimos", which is synonymous with "shaking", and the suffix "-ica", which is used to indicate "relating to."
To define a seismic wave , it is necessary to take into account several concepts. First you have to know that the lithosphere is the outer layer of planet Earth . This is the rigid superficial crust, made up of tectonic plates.
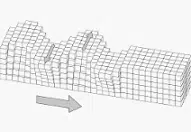 Tectonic plates move over a layer known as the asthenosphere . This plate movement is due to changes in the Earth's mantle.
Tectonic plates move over a layer known as the asthenosphere . This plate movement is due to changes in the Earth's mantle.
When two plates are in contact, friction forces are generated at their boundaries that "link" them and cause significant stress in the materials. If the efforts exceed the resistance, a violent rupture occurs that releases the accumulated energy and causes a tremor (an earthquake ).
This energy is released in the form of waves : seismic waves . Each seismic wave, therefore, is produced by the propagation of energy through the Earth and causes the ground to tremble.
Seismic waves radiate in all directions from the hypocenter (the point where, inside the Earth's crust, the earthquake originates). Internal seismic waves are those that propagate within the planet.
The primary wave is the fastest internal wave, which expands and compresses rocks in the same direction as its path . The secondary wave moves at a lower speed and produces a lateral deformation of the rocks with respect to its path.
When an earthquake occurs, the primary wave is the first thing that is felt through a vibration of the walls of buildings. Seconds later the secondary wave arrives, causing the vertical and horizontal displacement of the terrain.
In addition to the types of seismic waves mentioned, we must know that there are also so-called surface waves, which are slower than internal waves and are produced by the surface of the earth, air and water. These can be of three kinds:
-Rayleigh waves are those that are characterized because they cause a retrograde elliptical movement of the ground. They are also known as ground roll waves.
-Free waves or free oscillations. We can establish these surface seismic waves that cause the entire Earth to vibrate. They appear when earthquakes of enormous intensity occur.
-Love waves, which are named after the British mathematician Augustus Edward Hough Love. They are a little faster than Rayleigh waves and are characterized by the fact that they give rise to a horizontal shear movement on the surface.
