The first thing we have to establish is that occipital derives from Latin. Specifically, its etymological origin is found in the Latin word “occiput, occipitis”, which can be translated as “nape”. A word that is the result of the sum of the following lexical components:
-The prefix “ob-”, which can be translated as “against” or “confrontation”.
-The noun “caput”, which is synonymous with “head”.
This is what is called what is linked to the occiput : the sector of the head where it comes into contact with the vertebrae of the neck .
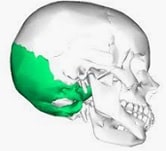 The occipital bone gives shape to the bottom, middle and back of the skull . With a somewhat rhomboidal structure, it contributes to the formation of the vault and cranial base.
The occipital bone gives shape to the bottom, middle and back of the skull . With a somewhat rhomboidal structure, it contributes to the formation of the vault and cranial base.
Convex backwards and downwards and concave forwards and upwards, the occipital bone has two faces : one endocranial and one exocranial. The endocranial or anterosuperior face maintains a relationship with the brain mass, while the exocranial or posteroinferior face has the occipital foramen in its lower sector.
A protuberance that can be found on the occipital bone is known as an occipital bun . This lump was common in the skull of Homo neanderthalensis and other ancestors of Homo sapiens , but is uncommon in modern man .
The occipital lobe , meanwhile, is one of the six functional sectors recognized in the brain . This is the posterior area of said organ and its function is to produce the images that we see.
Thanks to the occipital lobe, it is possible to process and interpret what is seen. It is also essential to discriminate colors and movements and recognize space .
The occipital muscle , on the other hand, is located in the back region of the head. It covers the epicranium and, in turn, is covered by skin .
The occipital angle , finally, is located in the interval of the occipital condyles. It has sides that pass through the lower limit of the orbit and the vertex of the head.
In the same way, we cannot ignore the fact that there is what is called occipital neuralgia. This is also known as Arnold's neuralgia, which is a headache in the form of a stab or cramp in the occipital area. Specifically, it can reach up to the highest part of the aforementioned head.
Sometimes, this neuralgia can be confused with a simple migraine and can occur for different reasons. Specifically, among the most frequent causes of this are cervical trauma, due to an accident or a blow, and even a strong contracture in the muscles that surround the occipital area.
When you suffer from this headache, the doctor usually establishes a treatment that is based on the use of anti-inflammatory medications. However, you can also resort to muscle relaxants. Not to mention that there are some drugs that do precisely prevent the aforementioned occipital neuralgia.
