
Obstetrics is the branch of medicine dedicated to the care of pregnancy, childbirth and the postpartum period.
Obstetrics is the branch of medicine that cares for pregnancy , childbirth and the puerperium (the period from childbirth until the woman returns to the state she had before pregnancy). The term comes from the Latin obstetricĭa .
Obstetricians are responsible not only for the physical condition of the mother and her baby, but also take care of the psychological and social factors linked to motherhood . It should be noted that, in some countries, obstetrics is known as midwifery . The specialist in this health science, therefore, can also be called a midwife or midwife .
Obstetrics and prenatal controls
Prenatal check-ups carried out by obstetrics allow the health of the woman and her child to be taken care of so that the birth takes place normally. Throughout prenatal care, it is common for the obstetrician to instruct the mother (especially when she is a first-time mother) about responsible procreation and family planning .
In certain cases, the obstetrician may order induction of labor if he or she notices risks of maintaining the pregnancy. Induction can usually be done any time after 24 weeks of gestation, although giving birth to a premature baby also carries risks to your health.
As for the birth itself, it can be done vaginally (which constitutes natural birth ) or by cesarean section (a surgical incision in the abdomen and uterus to extract the fetus). The obstetrician will work, in both cases, together with the gynecologist.
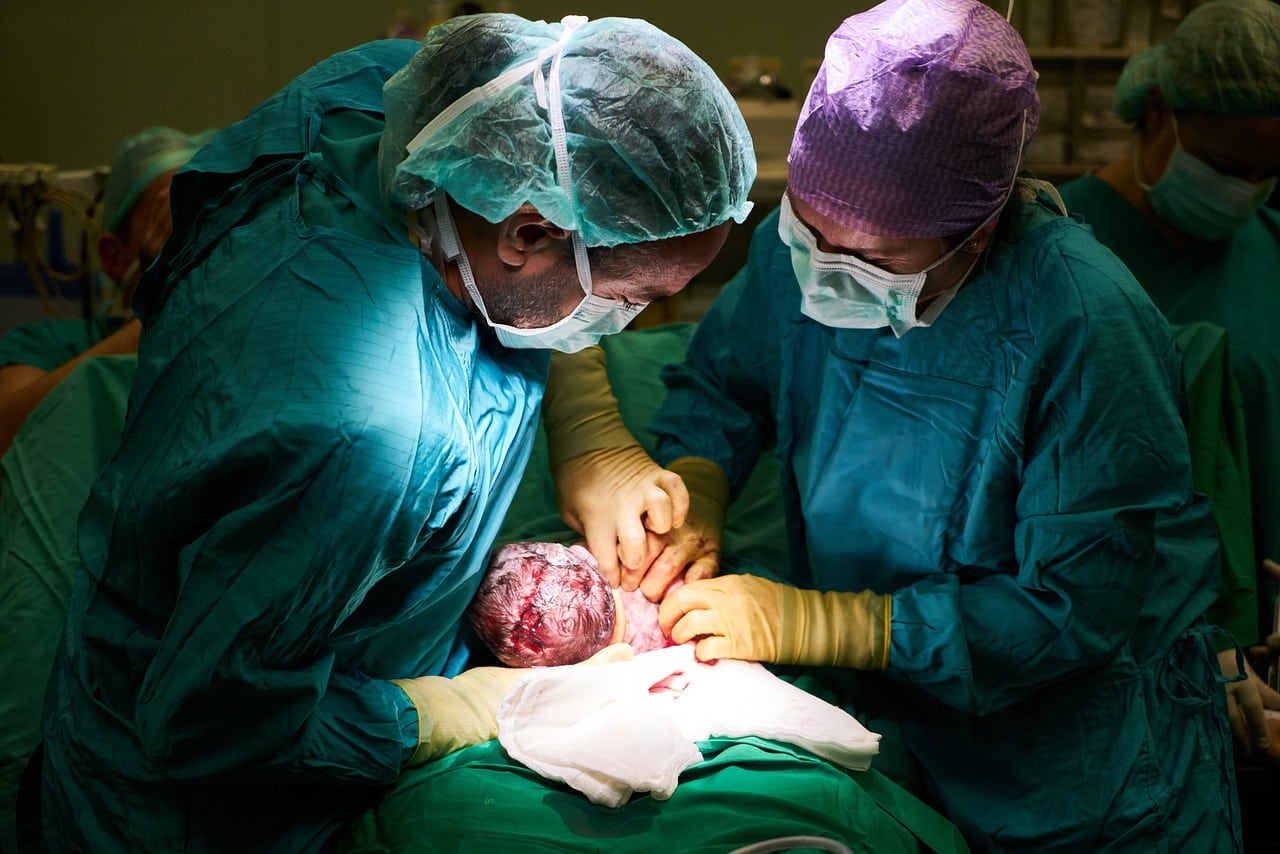
During a birth, the obstetrics specialist works together with a gynecologist.
Its social importance
Having said all this, it is clear that obstetrics has great importance in modern society, both for pregnant women and for each child who comes into this world in a hospital , since it is the professional area that is responsible for health. of future mothers throughout the entire process, from preconception to postconception, including the care of newborns.
It is precisely because of this importance that science has dedicated so many resources throughout history to make advances in this field. Before continuing, it is necessary to slightly clarify that there is a difference between obstetrics and gynecology : the latter is a subspecialty that is responsible for diseases of the uterus, vagina and ovaries. Experts assure that it is correct to say that every obstetrician is also a gynecologist, but that the same does not happen the other way around.
Obstetrics throughout history
In prehistoric times, women did not have all the support that obstetrics or other specialists currently provide, but had to face the entire pregnancy and even childbirth on their own. In fact, it is believed that when the time came to give birth, she approached the water to be able to wash herself and her baby . Regarding the pain, he had to endure it silently so as not to alert predators. His position also did not resemble the current one, instead he was squatting.
In the Ebers papyrus , one of the oldest scientific documents preserved in medicine, you can read that the births of Ancient Egypt were led by groups of women who had already given birth to, who offered their advice to the new ones. mothers and were also prescribed medications to treat different disorders in the uterus and vagina.
In Ancient Greece , on the other hand, it was also women who cared for women in labor, although with an authority that brought them closer to current obstetrics. The first school of obstetrics emerged only in the 16th century , in France ; At that time, men had already achieved exclusivity in the field of surgery .
