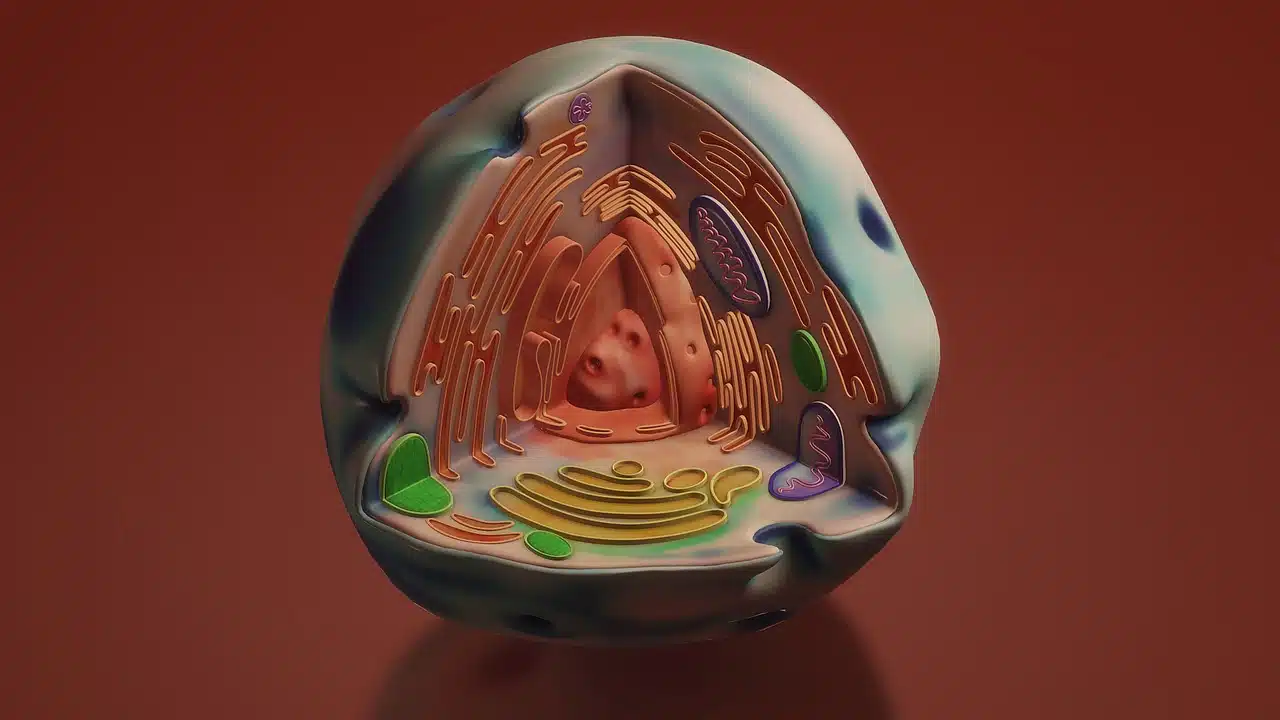

Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus.
The core is the main or essential component of something , to which other elements are added or coupled to form a whole or a set. The term comes from the Latin nucleus .
Also known as core is the dimension or central issue of a thing , whether physical or symbolic. For example: "The core of the issue is income redistribution" , "Let's get to the core of the problem: how many people are trapped?" , «To sustain the structure, its core must be shored up» .
Core, on the other hand, is the molar area of those fruits that have a hard shell and the stone or stone of the fruits. In another sense, the group or society of individuals who come together because they have something in common ( "The Buenos Aires nucleus demonstrated against the adjustment" ) and the group of houses and buildings with their inhabitants ( "The nucleus of Buenos Aires") is known as a nucleus. urban area experiences a marked increase in unemployment» ).
The syntactic nucleus , meanwhile, is a linguistic concept that allows us to name the term or morpheme that is responsible for determining the characteristics of the grammar and syntax of the phrase .
Core in biology
In cell biology , the nucleus is the part of eukaryotic cells that houses a large amount of genetic information. It is organized in chromosomes and accompanied by proteins .
This cell nucleus is responsible for exercising control over the activities of the cells and maintaining the integrity of the genes. It should be noted that, in a locus (a fixed position) of DNA , the gene is a unit of information that allows the coding of RNA or proteins.
The nuclear envelope (or nuclear envelope ) is the most important structure of the nucleus. It is a double membrane that separates the organelle from the cytoplasm and, by having nuclear pores, makes it possible to regulate genetic expression.
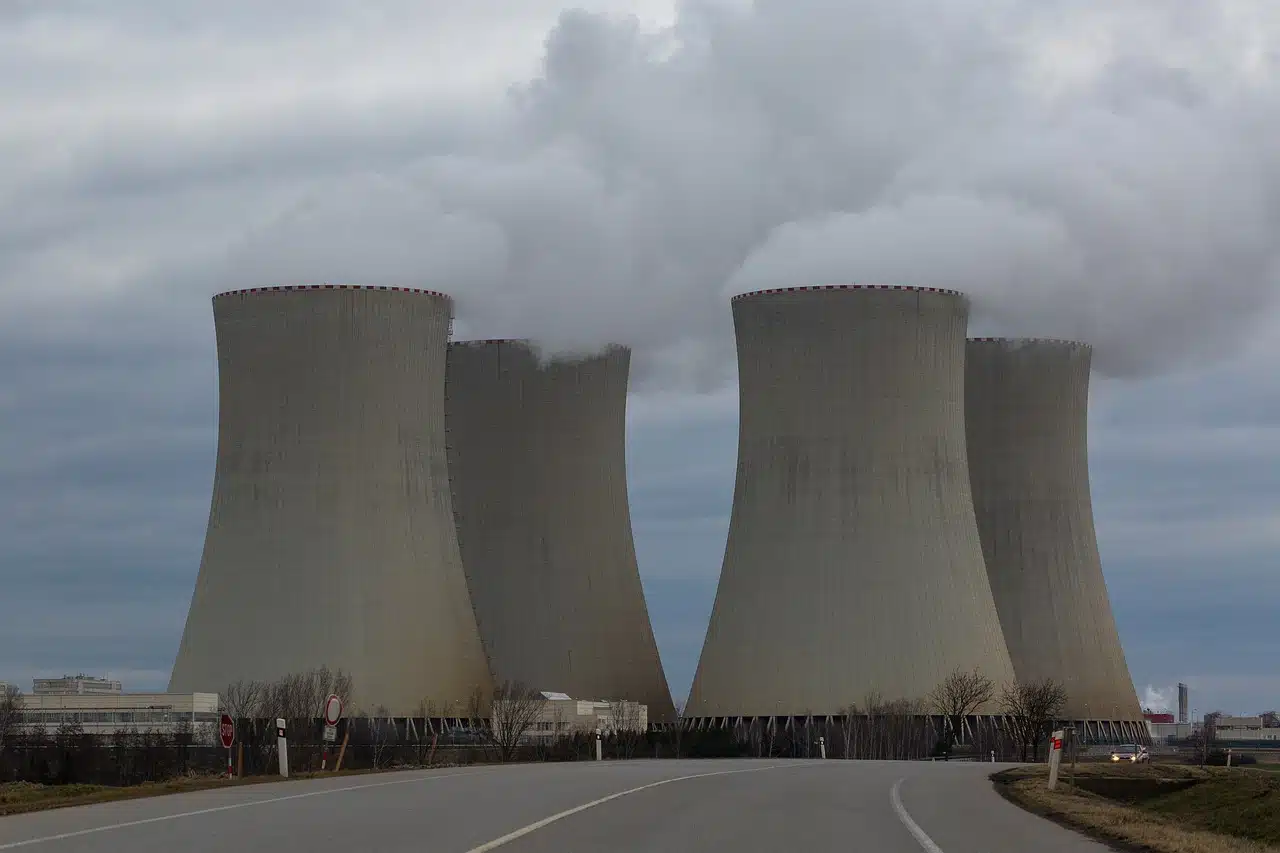

Uranium is the most widely used nuclear fuel in the production of nuclear energy.
The term in physics
In physics , the atomic nucleus is the center of an atom . It is made up of neutrons and protons that develop what is known as a strong nuclear force .
Endowed with a positive electrical charge, the nucleus has a certain number of protons that determines the atomic number of the chemical element in question. The chemical elements are arranged in the periodic table according to their atomic number.
Nuclear physics is the specialty focused on the analysis of the nucleus. It is interesting to mention, on the other hand, that nuclear energy is energy released within the framework of a spontaneous or artificially provoked nuclear reaction .
To generate electrical energy from nuclear energy, a nuclear power plant is required. This industrial facility has at least one nuclear reactor , which is the device that makes it possible to generate a controlled nuclear chain reaction .
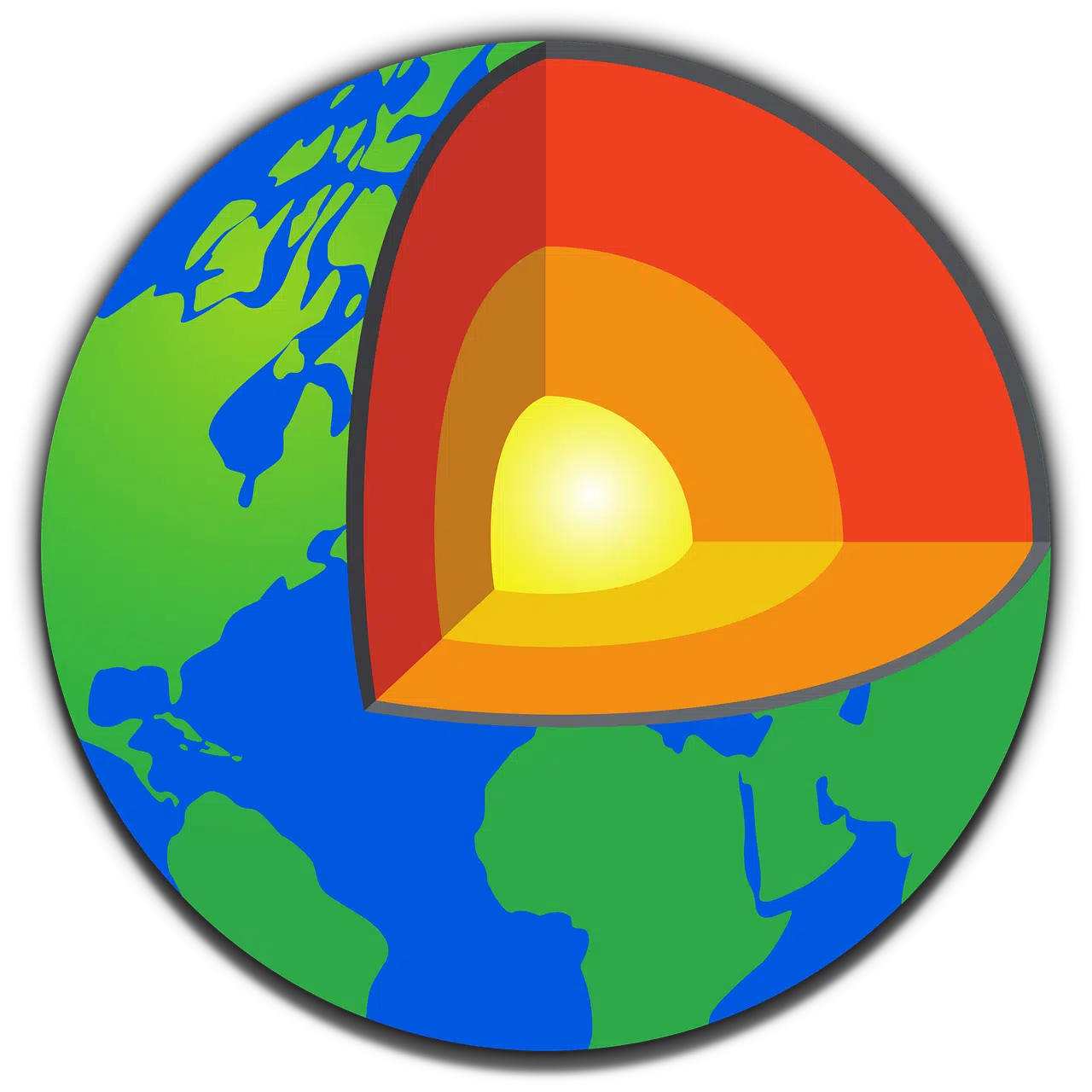
The Earth's core is one of the layers of the Earth.
Core in geology
For geology , the innermost layers of a planet form its core. These layers can be solid or present in a liquid state when melted. The Earth's core , for example, has iron as its main component.
The radius of the Earth's core has a radius of around 3,500 kilometers . In this way, the Earth's core represents 32% of the planet's total mass. In this core it is possible to recognize two different layers: a solid inner core and a liquid outer core, separated by a limit known as the Lehmann discontinuity (since it was discovered by the seismologist Inge Lehmann in 1936 ).
In the case of the sun, the core constitutes its central region, which represents one fifth of its total radius, around 139 thousand kilometers. It is in this same area where the thermonuclear reactions that generate all the energy produced by this star take place. It is made up of 49 percent hydrogen, 49 percent helium and the rest is divided between catalyst components. The temperature of the solar core, whose balance is achieved through the energy generated by its own transformations, is around 15 million kelvins (a unit whose absolute zero is the point at which all thermal activity stops).
The kernel
We can note, finally, that in computing the kernel (also known as kernel ) is the main part of the operating system .
Likewise, processors in computers and other devices, such as consoles and tablets, usually have more than one core, which multiplies their theoretical performance. Given the characteristics of electrical circuits, the maximum speed has found a ceiling that it has not managed to surpass considerably in recent years. To compensate for this impossibility due to the type of technology used, the presence of several brains that divide the tasks seems to have been the most intelligent response.
However, not all developers have chosen to optimize their applications to take advantage of this advantage. The same phenomenon occurs with respect to 64-bit processors. As a result, it is often observed that the efficiency of a program does not vary according to the number of cores; There may even be the case of inversely proportional performance .
A good example of the correct use of multiple cores is Blender , the most famous open source 3D editor in the world. When rendering (in this case, the process by which each of the numerous frames that make up a movie is created) an animation with this tool, the difference between the use of one processor or another is so clear that it is difficult to imagine a more graphic example. - The speed at which the image sequence is exported is directly proportional to the number of cores.
