Immense clouds of dust and gas make up nebulae, where planetary systems and stars usually emerge.
A planetary nebula is something that forms in interstellar space based on interstellar dust and gas from the exhaustion of a star's fuel . When it, now without hydrogen at its disposal and appealing to the reserve of helium , cannot resist the weight of its own mass, it becomes a red giant and expels that envelope in a gaseous state commonly defined as a planetary nebula that captivates with its brightness. .
These phenomena are of great interest to astronomers and astrophysicists since, by returning heavy metals and others resulting from stellar nucleosynthesis , they are relevant to the formation and evolution of galaxies . In some of these areas, in addition, the birth of stars occurs as a result of the aggregation of matter and condensation .
In order to be able to analyze them with precision (since they cannot be seen with the naked eye) and record images of them, experts use powerful space telescopes , among which Hubble and Spitzer can be mentioned.
Formation and evolution of a planetary nebula
It is interesting and enriching to learn about the formation and evolution of a planetary nebula .
In this framework it is necessary to focus on the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram and carefully observe stellar evolution . By identifying a star in the main sequence and monitoring it, it will be detected that, if it is a luminous astronomical object with a solar mass of less than ten whose nuclear fuel has run out, a white dwarf emerges that will end up generating a planetary nebula . Of course, others, due to their characteristics, will be classified as red giants , a stage where luminosity decreases and the star contracts. There is red clumping in the case of figures with high metallicity or a horizontal branch period if they are stars with low metallicity . A giant asymptotic branch is also detected throughout this process.
In these processes there is stellar instability given the temperature changes experienced by the helium fusion reaction and the considerable release of energy . There is, in this scenario, an expansion and cooling of the layer made up of helium as well as very intense pulsations. The gases that end up being ejected form a cloud that surrounds each core of the stars and which, after a displacement of the atmosphere and its ionization (a phenomenon that makes it shine), acquires the name of planetary nebula .
In this situation, the gases that were expelled move away very quickly from the central star , which in principle increases temperature and contracts but its luminosity does not alter (it is in this instance that the hydrogen present in the outer layer of the core burns). ). Then, as the outer mantle is consumed, the star cools and the ultraviolet radiation that is radiated is not enough to achieve ionization of the separated gas. After a recombination of the gas cloud that puts an end to the so-called plasma state and makes it invisible, the planetary nebula ceases to exist.
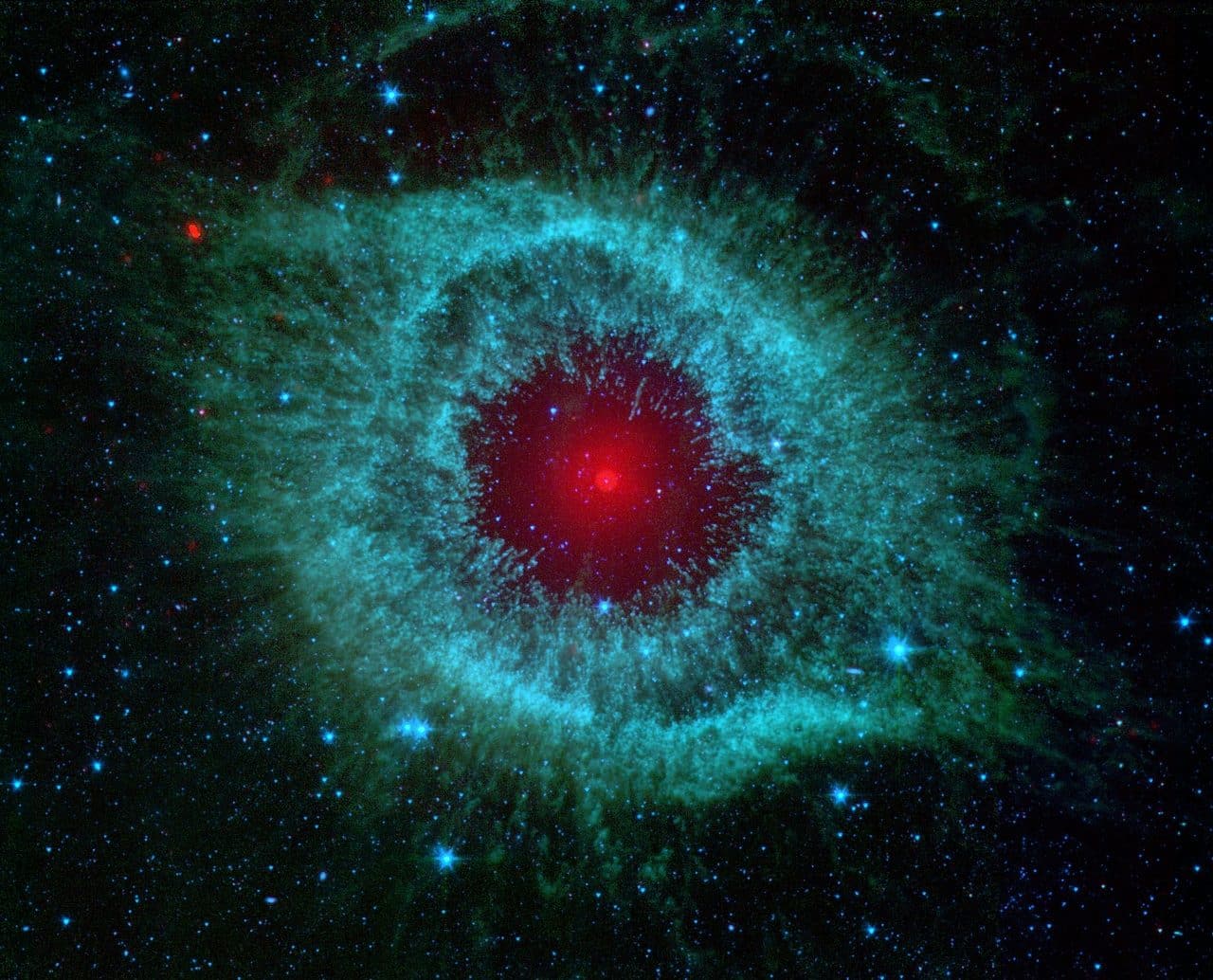

In the constellation of Aquarius, the Helix (or God's Eye) nebula has been discovered, whose physical features resemble the Dumbbell Nebula and its appearance resembles the Ring Nebula.
Examples
It is worth collecting information on planetary nebulae that have become popular internationally to have specific references or specific examples of these celestial objects available.
In the constellation of Lyra , to indicate a specific case, the Ring Nebula has been detected. Thanks to the James Webb space telescope , some time ago extraordinary images were obtained of what is also called, in honor of the French-born astronomer Charles Messier , Messier 57 . Associated with this scientist is also the Dumbbell nebula (or Messier object 27 ) which is located in the Vulpecula constellation .
Meanwhile, the Medusa Nebula and NGC 2392 , generally recognized as the Eskimo Nebula , have been identified in the constellation of Gemini .
About three thousand light years from Earth , a type of reflection nebula similar to the Egg Nebula has been detected within the constellation Cygnus .
The Crab Nebula (generated based on a supernova and seen in detail using the James Webb telescope ), the Saturn Nebula (corresponding to the constellation of Aquarius and with an identity that accounts for the similarity between the appearance of the nebula and the planet of the same name), the Smiling Cat Nebula (or Sh2-284 , located in the constellation of Monoceros ) and the Ant Nebula (a bipolar nebula located in the constellation of Norma ) are other options to consider when wanting Learn more about planetary nebulae .
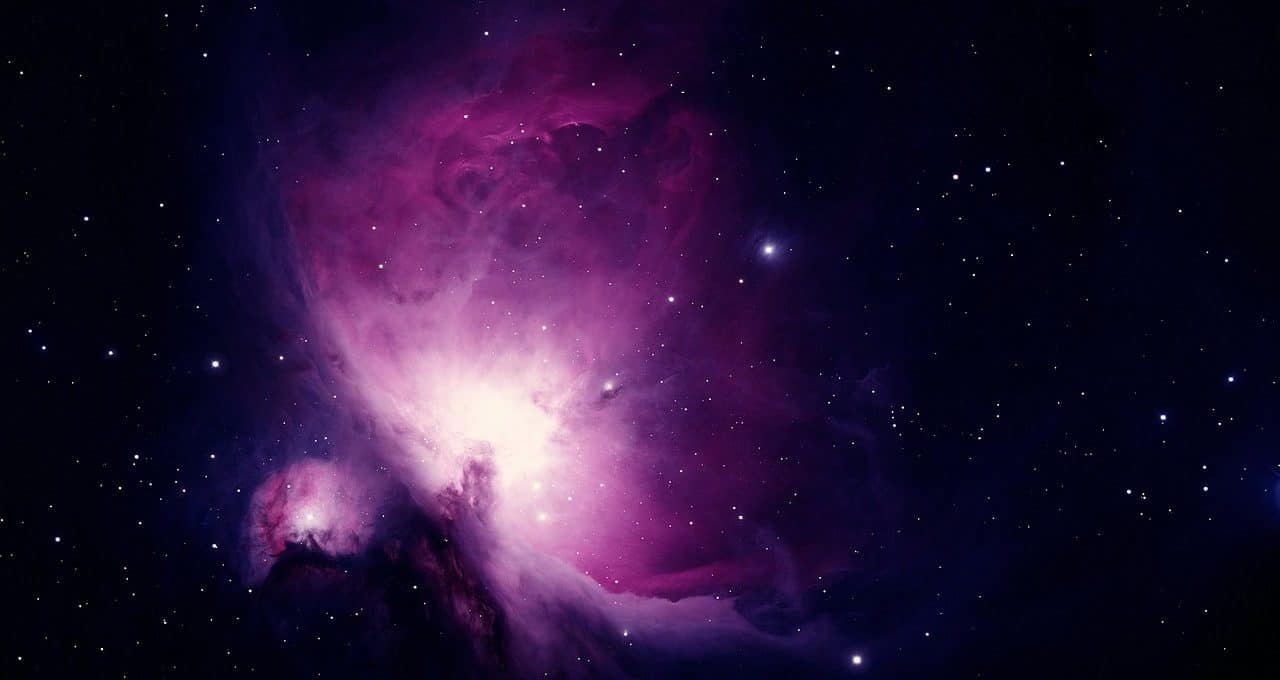

In Orion's belt there is a diffuse (very bright) nebula made of dust and gas named Messier 42 or Orion Nebula.
Types of planetary nebulae
There are multiple types of planetary nebulae .
Depending on their format or appearance, for example, they are classified as bipolar nebulae (structured with a pair of lobes and axial symmetry, such as the Butterfly Wings and Homunculus nebulae), spiral nebulae (such as Andromeda ) and nebulae. spherical (such as the Abell 39 ).
There are also irregular nebulae , others that are quadrupole and some that exhibit a marked annular shape, to add more details that reveal the great range that exists in the field of nebulae , a group where even the emission nebula coexists, the absorption nebula (or dark nebula ) and the reflection nebula .
