 The notion of motility comes from the English word motility . The term refers to the ability to move : move to leave one place and move to a different one.
The notion of motility comes from the English word motility . The term refers to the ability to move : move to leave one place and move to a different one.
In the field of medicine , motility specifically refers to the ability to develop coordinated movements with a certain degree of complexity . In this framework, the concept is linked to motor skills .
For biology , motility is the ability to move independently and spontaneously . That which has motility, therefore, can move.
Cell motility is key so that organs and tissues can form. Cells are able to respond to environmental stimuli, moving through contractile, vibratile or other types of movements.
Sperm , for example, are cells that have motility. These male gametes have a flagellum that provides them with mobility and allows them to “swim” freely to fertilize an egg.
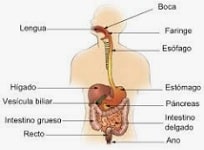
The idea of gastrointestinal motility , on the other hand, refers to the action that the digestive system develops so that the food that is introduced into the mouth ends up arriving, once digestion has been carried out, to the anus for expulsion. Thanks to the activity carried out by certain cells, the chyme or bolus moves.
Several organs intervene in a coordinated manner in gastrointestinal motility. When the passage of food through the intestine occurs late or too quickly, it is called a motility disorder . It should be noted that there are drugs that help regularize functions.
Various studies suggest that gastrointestinal motility disorders affect a significant percentage of the population, although the numbers vary from one country to another; At the beginning of 2020, for example, in Mexico they were talking about 35 percent. Some of the most common causes of this health problem are stress, so common in modern life, poor eating habits and anxiety.
 All of this reminds us that our body is a whole, and that is why we must take care of ourselves, knowing that a lack of attention to one aspect of our life can trigger problems in others, even those that seem less related. Gastrointestinal motility disorders have their own names, such as: functional dyspepsia, gastroparesis, and reflux disease . Statistical data indicate that they occur twice as frequently in women than in men, and that the age range goes from 20 to 70 years old.
All of this reminds us that our body is a whole, and that is why we must take care of ourselves, knowing that a lack of attention to one aspect of our life can trigger problems in others, even those that seem less related. Gastrointestinal motility disorders have their own names, such as: functional dyspepsia, gastroparesis, and reflux disease . Statistical data indicate that they occur twice as frequently in women than in men, and that the age range goes from 20 to 70 years old.
The one that stands out from the previous list is dyspepsia , which affects 15 percent of the population and has a list of quite annoying symptoms : nausea, flatulence, a feeling of heaviness, burning and pain in the upper abdomen; As if that were not enough, they usually appear after meals. Furthermore, symptoms increase when you suffer from stress or anxiety. In patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease , dyspepsia appears in an average of 65 percent.
If we look at the aforementioned symptoms with a little distance, we will notice that in addition to the physical discomfort they cause in patients, there is the humiliation that some of them can cause in a work or student environment. For this reason, this type of gastrointestinal motility disorder affects several aspects of life.
People who suffer from diabetes mellitus and are overweight are prone to gastroparesis , another intestinal motility disorder that slows down and prevents proper emptying of the stomach . It shares symptoms with dyspepsia and adds abnormal levels of blood glucose. There are medications made specifically to treat these and other related problems, but it is important to complement them with emotional health care.
