
Morphosyntax is the part of grammar that integrates morphology and syntax.
Morphosyntax is the area of grammar that is responsible for the integration of syntax and morphology . As you can see, to understand the concept it is necessary to first pay attention to other terms.
Grammar, syntax and morphology
We said that morphosyntax is part of grammar : this is the name given to the sector of linguistics dedicated to the analysis of the elements of language, including its organization and form.
Syntax , on the other hand, studies how the combination of words is carried out and the groups that they develop for the expression of meanings. The constituent components and structure of words, meanwhile, are investigated by morphology .
Rules and relationships
Returning to the idea of morphosyntax, it is a field of study that is oriented towards the constitution, relationships and combinations of words . The term also refers to the rules that make it possible to construct sentences that make sense and are not ambiguous.
When a morphosyntactic observation is carried out, the indexations and hierarchies of the syntactic constituents are examined and the agreement links in the sentence are inspected.
The analysis carried out by morphosyntax begins by studying each of the words to categorize and typify them . This way it is possible to know with which prepositions , nouns , adjectives , verbs , etc. count the sentence. Syntactic analysis is then carried out to determine how the groupings are specified in phrases and what the functions of the words are. In this way the subject , the predicate and the complements of the sentences are obtained and the relationships they maintain between them are established.
The importance of this analysis is considerable for the correct use of the language, particularly if we want to access topics of great complexity, beyond the everyday sentences that we repeat without thinking, such as "good morning", "how much does it cost?" or "I haven't slept at all." When we want to go beyond this basic language, we need tools that allow us to organize our ideas, prioritize them and then organize them into sentences that keep the desired message intact, so that the interlocutor can interpret it and give us a coherent response.
Example of morphosyntax
We have already talked about the steps we must follow when carrying out a morphosyntactic analysis , but without taking it to an example it can be a bit overwhelming, since this work is generally required of us in school, but when we reach the adulthood we stop applying it. Let's see, therefore, a simple sentence that serves as a reference: "Marcela made a model for her brother."
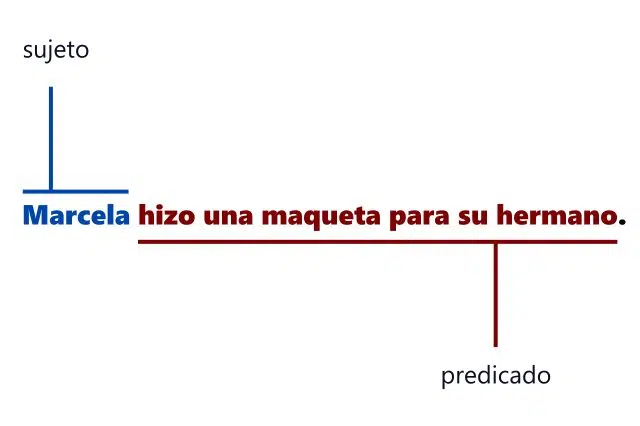
First step of syntactic analysis
The first analysis that we must do is the morphological one, after which we will understand that Marcela is a noun , more precisely a proper name; did is a verb (conjugated in the third person singular of the simple past perfect tense of the indicative mood); model and mother are two other nouns; one is an adjective that serves to indicate unity; para is a preposition used to express the purpose of an action ; his is a possessive adjective.
Having studied the form of the sentence, it is time for syntactic analysis, which we can begin in a general way by distinguishing its two largest parts: the subject ("Marcela") and the predicate ("he made a model for his brother"). . In the first, given that it is made up of a single word, we do not hesitate to describe "Marcela" as the nucleus. In the predicate, however, the nucleus is "did." We continue with a model , which is a direct complement , since it can be replaced by "the" ("he made it"); For his brother , finally, it is an indirect object , since it can be replaced by "le" ("he made him a model") or, if we combine both objects , by "se" ("he made it for him").
