Although it had limitations and some concepts were corrected, Dalton's atomic model left an indelible mark on the history of Chemistry.
Dalton's atomic model is a presentation that, between 1803 and 1807 (or 1808, depending on the source consulted), was made by the British scientist John Dalton . For this expert, the proposal that has remained in history as the first of the atomic models that had scientific support, was an atomic theory .
Thanks to this work, it was possible to respond to the reaction in fixed proportions at a stoichiometric level by the chemical compounds (an aspect contemplated in the so-called law of defined proportions ). It has also served to understand why the proportions associated with the reaction of a pair of substances that make up at least two different compounds are translated into whole numbers (base content of the law of multiple proportions ).
This contribution maintains that matter is made up of atoms (which, in one of his postulates, Dalton presents as "minimal particles" impossible to divide and destroy), thus giving the guideline for the existence of a finite number of particles. essential.
From this model it follows that, if one of the specific chemical elements is taken into account, atoms will be detected that are identical to each other, sharing properties and atomic mass . By comparing atoms of different elements, then these aspects will vary and can be combined with the purpose of forming a chemical compound .
Limitations of Dalton's atomic model
Dalton's atomic model has shown limitations and inaccuracies. Part of these inconsistencies occurred due to Dalton 's belief about substances in a gaseous state, which he conceived as monatomic, and his lack of knowledge regarding atomic weights . He also maintained that the combination of atoms when it came to constituting "atoms of compounds" (as what was described in his time as what, over the years, was called a molecule ) always occurred in the lowest proportion.
Dalton 's proposal also does not recognize that a certain element has multiple isotopes and was not useful when offering an explanation of the periodic regularity manifested by the properties of a chemical element , something that was captured in the periodic table of the elements that he was able to launch. Dmitri Mendeleev . There is even no room in this model for research focused on cathode rays .
Almost all atoms have in their nucleus some particles known as protons whose charge is positive and others, without charge, which are defined as neutrons.
Beyond these issues, Dalton 's contributions were valuable and served as inspiration to further research, make findings, and add other postulates. Over time, Thomson's atomic model , Rutherford's atomic model , and Bohr's atomic model came to light. There were other outstanding representations in history , among which we cannot fail to mention Heisenberg's atomic model or Schrödinger's atomic model .
Weight laws
There is a set of laws, identified as weight laws , that refer to chemical reactions . These contents were of utmost importance to develop the atomic-molecular theory focused on matter.
One of them is called the law of conservation of mass , very well adapted to chemical reactions . This principle indicates that, within the framework of a chemical reaction involving an isolated system, the total mass remains constant. Thus it is possible to establish that the mass consumed by the reactants is equivalent to the mass of the products obtained in that process.
The law of definite proportions (or constants) is a relevant stoichiometric law since it indicates that, when at least two elements combine to generate a compound, the mass ratio remains constant.
This information would be incomplete if space is not given to Dalton's law or law of multiple proportions , whose content covers elements that make up more than one compound, contemplating the combination of masses and concluding that this relationship can be expressed by a quotient cited in whole numbers.
The law of reciprocal proportions , meanwhile, is a stoichiometric law centered on equivalent weight that revolutionized Chemistry by favoring the development of the notions of chemical formula and mole .
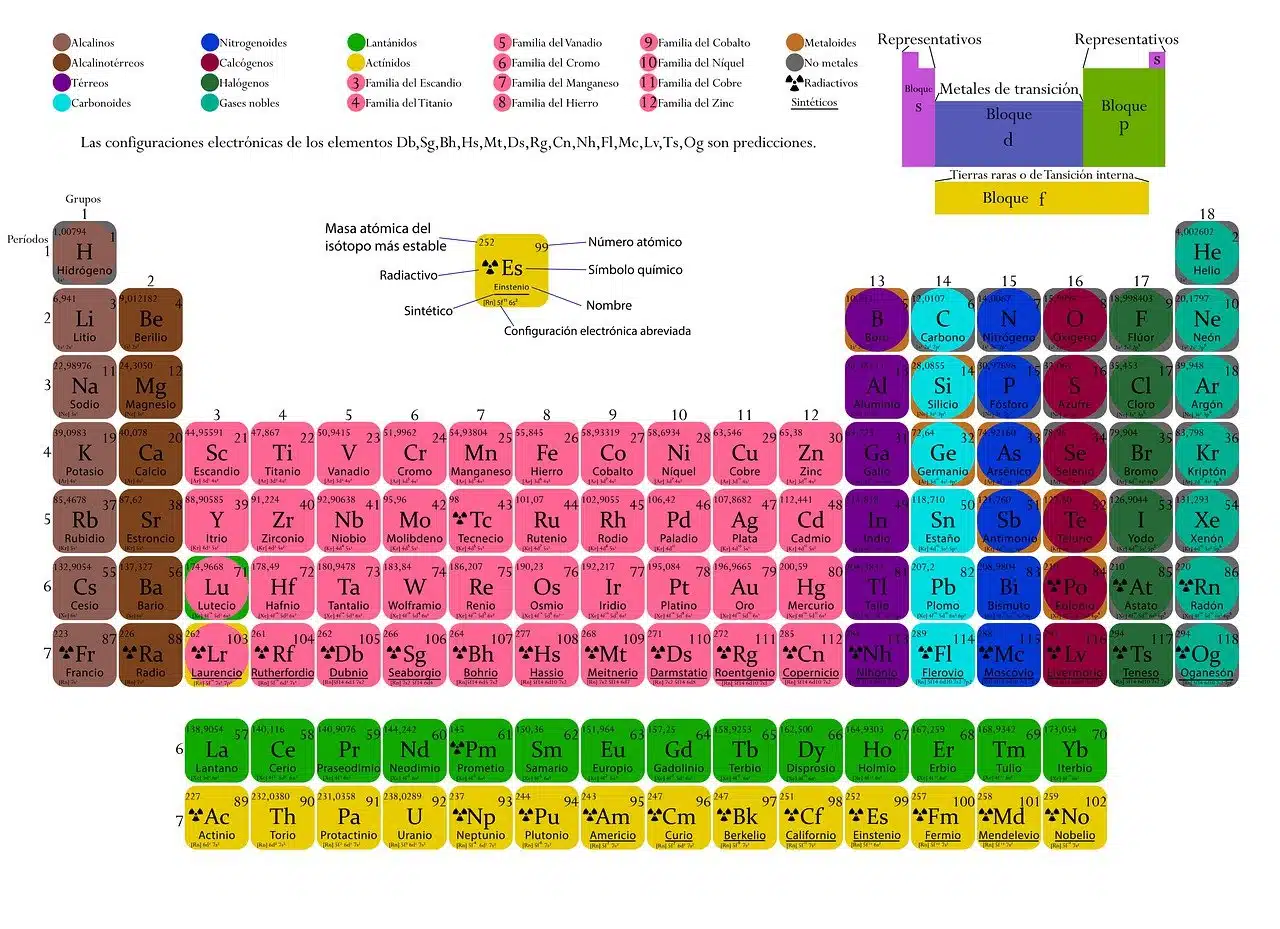
The chemical elements, depending on their properties, electronic configuration and atomic number, occupy a certain space within the periodic table.
Importance of Dalton's atomic model
Below we will emphasize the importance of Dalton's model .
At the time, it barely transcended, it was relevant because it became the first scientific base that added data about the internal structure of matter. Although it had errors that were corrected as the research progressed, Dalton 's contribution to the atomic level undoubtedly marked a before and after within the world of Chemistry . Based on Dalton's atomic theory , which was appreciated for its simplicity, its effectiveness and its advanced nature for the time, laws were promoted referring to chemical compounds , for example.
Although the initial content underwent modifications based on discoveries, Dalton's atomic model has never been overshadowed or forgotten. It evolved in this regard, knowledge about electrons was incorporated, knowledge in relation to the different types of existing chemical bonds was deepened and technological progress was made, but John Dalton 's legacy is still present and retains its value throughout the planet.
