The first step we are going to take in this definition of myasthenia is to know its etymological origin. Thus, we can determine that it derives from Greek, specifically it is the result of the sum of these lexical components:
-The term “mys, myos”, which can be translated as “muscle”.
-The word “asthenia”, which means “without strength”.
Muscle weakness is called myasthenia . A muscle, meanwhile, is an organ made up mostly of contractile fibers.
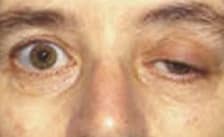 Myasthenia gravis , also called myasthenia gravis , is an autoimmune disease : that is, caused by a failure of the immune system. In this case, the immune system produces antibodies that block and modify the nerve signals that must reach the skeletal muscles.
Myasthenia gravis , also called myasthenia gravis , is an autoimmune disease : that is, caused by a failure of the immune system. In this case, the immune system produces antibodies that block and modify the nerve signals that must reach the skeletal muscles.
With myasthenia gravis, thus, the person suffers from the weakening of certain voluntary muscles . The disorder can affect the chewing and speaking muscles; to those who control the eyelids and eye movement; or those that are linked to breathing , for example.
Myasthenia gravis generally begins with a loss of strength that is reversed with rest. However, once the affected person resumes physical activity, it reappears. In this way, myasthenia gravis is present every time the subject is active .
In addition to the symptoms already mentioned, others that are associated with myasthenia gravis should not be overlooked. We are referring to both difficulties in pronouncing or articulating words, as well as fatigue in the legs and arms, and even difficulty in being able to gesture.
Likewise, it is interesting to know that myasthenia is more common in women and, specifically, in those between 20 and 40 years old. However, it is also common in men who have surpassed the age of 60.
A myasthenic crisis is a risk situation where muscle weakness is exacerbated. It may appear associated with respiratory failure that threatens the patient's life .
It is important to note that myasthenia gravis can be treated with drugs that reduce the production of abnormal antibodies and facilitate communication between nerves and muscles. The individual must also receive psychological support since the difficulty in executing daily actions is frustrating.
In addition to the one already mentioned, there are other types of myasthenia, among which the following stand out:
-Ocular myasthenia gravis. This is also known as ocular MG and is characterized because the weakness occurs in the extraocular muscles and also in the eyelids.
-Neonatal myasthenia, which occurs in newborns whose mothers have myasthenia. The usual thing is that this gradually disappears during the first year of the child's life.
-Congenital myasthenia, which also responds to the name of SMC. It must be established that it is a so-called rare disease and is inherited.
Congenital myasthenic syndromes , on the other hand, are a varied set of diseases of genetic origin. As in the case of myasthenia gravis, they are due to a disorder in neuromuscular transmission.
