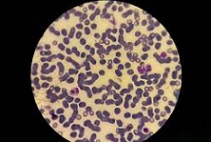
 Lymphocytes are a class of leukocytes : cells also known as white blood cells , which are responsible for the body's immune response. In the specific case of lymphocytes, they are lymphatic cells produced by the bone marrow and lymphoid tissue.
Lymphocytes are a class of leukocytes : cells also known as white blood cells , which are responsible for the body's immune response. In the specific case of lymphocytes, they are lymphatic cells produced by the bone marrow and lymphoid tissue.
Each lymphocyte has a large, spherical-shaped nucleus that is surrounded by a generally small amount of cytoplasm . In this cytoplasm, on the other hand, there are free ribosomes, mitochondria and the Golgi apparatus.
Lymphocytes regulate the specific or adaptive immune response . In this way, they react against antigens such as tumor cells or microorganisms. It is possible to differentiate between T lymphocytes , B lymphocytes and so-called NK cells .
The process of lymphocyte development is called lymphopoiesis . This procedure begins in a pluripotent hematopoietic stem cell.
When the level of lymphocytes is elevated compared to the reference values, it is a case of lymphocytosis . On the contrary, when the amount is lower, it is called lymphocytopenia . It should be noted that the value considered normal is between 20% and 40% lymphocytes in the total white blood cells: a higher percentage reflects lymphocytosis, while a lower percentage reveals lymphocytopenia.
To know the level of lymphocytes it is necessary to perform a blood test. The blood count is carried out in a laboratory and allows the diagnosis of different disorders. The alteration of normal lymphocyte numbers may be due to an infection or inflammation, for example.
That said, to discover a case of lymphocytosis or lymphocytopenia it is necessary to undergo a blood test. To do this, a doctor must request it and refer the patient to a clinic in which a team of specialized nurses performs the extraction and subsequent complete blood count.
More precisely, lymphocytosis occurs when the total number of lymphocytes exceeds 4,500 per cubic millimeter, although the reference value may be higher in some cases. To diagnose it in a child under one year of age, for example, a value greater than 7000 per cubic millimeter is sought, while for children older than one year the number to exceed is 9000 per cubic millimeter.
Lymphocytosis can be classified as follows:
* polyclonal : usually occurs as a result of inflammation or infection;
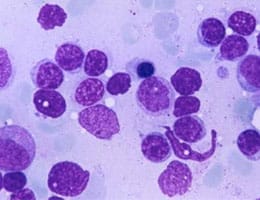 * monoclonal : usually reflects a proliferative disease , in which the number of lymphocytes increases as a result of a defect in the lymphoid population.
* monoclonal : usually reflects a proliferative disease , in which the number of lymphocytes increases as a result of a defect in the lymphoid population.
It is common for the doctor to order a repeat blood count if a possible case of leukocytosis is detected, to ensure that there has not been an error in the sample count.
With respect to lymphocytopenia, the disorders that can impact the decrease in lymphocytes are several; For example, it can occur due to an infection caused by a virus , such as HIV or the flu. The classification of this disorder gives us the following two types of lymphocytopenia:
* acute : takes place for a short period throughout the course of some diseases, but eventually resolves;
* chronic : its duration is much longer and it is not easy to estimate when -or if- it will be resolved.
Lymphocytopenia is not always accompanied by symptoms , but there are some that are associated with it, such as the following:
* enlargement of the lymph nodes and spleen, often due to cancer or HIV;
* fever, rhinorrhea and cough, which usually indicates a viral respiratory infection;
* reduction in the size of the lymph nodes , usually due to a disorder in the immune system.
