 The Greek words íschein (which translates as "stop" ) and haîma (which means "blood" ) allowed the construction of the term íschaimos , which refers to what "stops the blood." This notion reached scientific Latin as ischaemia , the etymological root of ischemia .
The Greek words íschein (which translates as "stop" ) and haîma (which means "blood" ) allowed the construction of the term íschaimos , which refers to what "stops the blood." This notion reached scientific Latin as ischaemia , the etymological root of ischemia .
In the field of medicine , ischemia is called the temporary or permanent decrease in blood supply to a sector of the body. This disorder is generated by an alteration that occurs in the arteries .
Let us remember that blood, which circulates through the veins and arteries, allows the distribution of nutrients and oxygen between the cells of the body, in addition to enabling the collection of metabolic waste. When cells begin to receive less blood, whether momentarily or sustained over time, they suffer stress that can lead to death and even cause tissue necrosis.
Ischemia, therefore, causes the cells to not obtain the energy they need to survive, since less blood reaches them (and, therefore, less oxygen). Tolerance to this decrease in oxygen varies according to the type of tissue.
Chronic ischemia is known as the drop in blood flow that develops gradually and progressively. This problem affects the extremities, especially the lower ones. Acute ischemia , on the other hand, comes on suddenly and can damage the extremities, the brain or the kidneys.
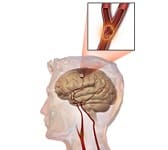
When blood flow to the brain decreases, cerebral ischemia occurs. This type of ischemia, which occurs more frequently among those who suffer from high blood pressure, diabetes or atherosclerosis or who are drug users, can cause anything from aphasia and paralysis to death.
Cardiac ischemia , also called myocardial ischemia , is another type of ischemia, which occurs when blood flow to the heart is reduced. The main consequence of this phenomenon is that the heart cannot receive the necessary amount of oxygen to function correctly.
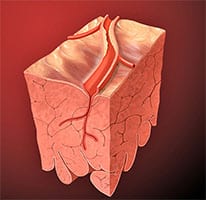 Generally, this reduction in blood flow occurs because the coronary arteries (that is, those of the heart) suffer from a blockage, either partial or total. Myocardial ischemia can cause damage to the heart muscle and negatively affect its pumping ability. If the obstruction occurs suddenly and is considerable, it can lead to a heart attack. In the rest of the cases, abnormal heart rhythms of varying severity may appear.
Generally, this reduction in blood flow occurs because the coronary arteries (that is, those of the heart) suffer from a blockage, either partial or total. Myocardial ischemia can cause damage to the heart muscle and negatively affect its pumping ability. If the obstruction occurs suddenly and is considerable, it can lead to a heart attack. In the rest of the cases, abnormal heart rhythms of varying severity may appear.
Regarding treatment, the main objective is to improve blood flow to the heart muscle and may consist of the consumption of certain medications, surgery or a procedure that opens the arteries in which the obstruction is located. The best way to prevent this problem is to lead a healthy life .
It is important to note that in some cases no symptoms are noticed, and then we must speak of asymptomatic ischemia . For the rest of the people, the most frequent are the following:
* chest pain or pressure (usually this occurs on the left side);
* pain in the jaw or neck;
* the heart beats too fast;
* difficulty breathing during physical activity ;
* vomiting or nausea;
* excessive sweating;
* tiredness above normal.
As soon as we notice chest pain, especially if it is intense or if it lasts more than a few minutes, we should make an appointment with our trusted doctor. Taking into account all the aforementioned characteristics of ischemia, it goes without saying that if we do not treat it in time it can have very serious consequences.
