If we want to discover the meaning of the term hyperplasia, it is necessary, first of all, to indicate its etymological origin. In this case, we can indicate that it is a word that derives from Greek, specifically it is the result of the sum of two lexical components of said language:
-The word “hyper”, which is synonymous with “excessive”.
-The adjective “plasía”, which can be translated as “formed” or “molded”.
Likewise, we have to indicate that this term was used for the first time in the 19th century. Specifically, it was in 1861 when “hyperplasia” was spoken of in English in a medical document in which it was indicated that it was a type of hypertrophy that is identified because a great multiplication of cells occurs. .
The term hyperplasia is used in the field of medicine and biology to refer to the exaggerated proliferation of normal cells in a tissue or organ. This multiplication of the number of cells causes an increase in the size of the tissue or organ in question.
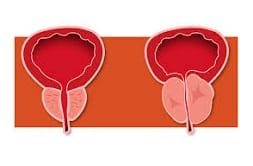 While hyperplasia involves an increase in the number of cells , hypertrophy involves a growth in cell size. In both cases, the consequence is excessive tissue development.
While hyperplasia involves an increase in the number of cells , hypertrophy involves a growth in cell size. In both cases, the consequence is excessive tissue development.
Hyperplasia is a process that takes place in the mammary glands when a woman is breastfeeding , for example. In the menstrual cycle, in turn, endometrial hyperplasia occurs, although this endometrial hyperplasia can also be due to some type of disorder.
Benign prostatic hyperplasia , on the other hand, is a condition suffered by many elderly people. It consists of an increase in the size of the prostate, which results in compression of the urethra. In this situation, the person may have difficulty urinating or there may be a reflux of urine that generates the need to excrete very frequently.
Blockage of urine flow from the bladder is the most common consequence of benign prostatic hyperplasia. However, it should not be overlooked that it can also cause other problems such as difficulties affecting the kidney or urinary tract.
In order to deal with this problem, the doctor who treats the patient will have to analyze his case, the state of this hyperplasia as well as his age and state of health in order to choose the most appropriate treatment. In this case, you must know that said treatment may consist of a specific medication, although you can also choose to undertake non-invasive therapy or even surgery.
Dentists, meanwhile, sometimes face hyperplasia of the mandibular condyle : the neck and head of the condyle grow, causing bite problems.
It should be noted that it is possible to differentiate between physiological hyperplasia and pathological hyperplasia . Physiological hyperplasia, in turn, can be hormonal or compensatory . These hyperplasias have different causes and effects .
The treatment of each hyperplasia will be linked to the characteristics of the disorder . It is possible to reverse it or mitigate its consequences with drugs or surgical interventions, to name two possibilities.
