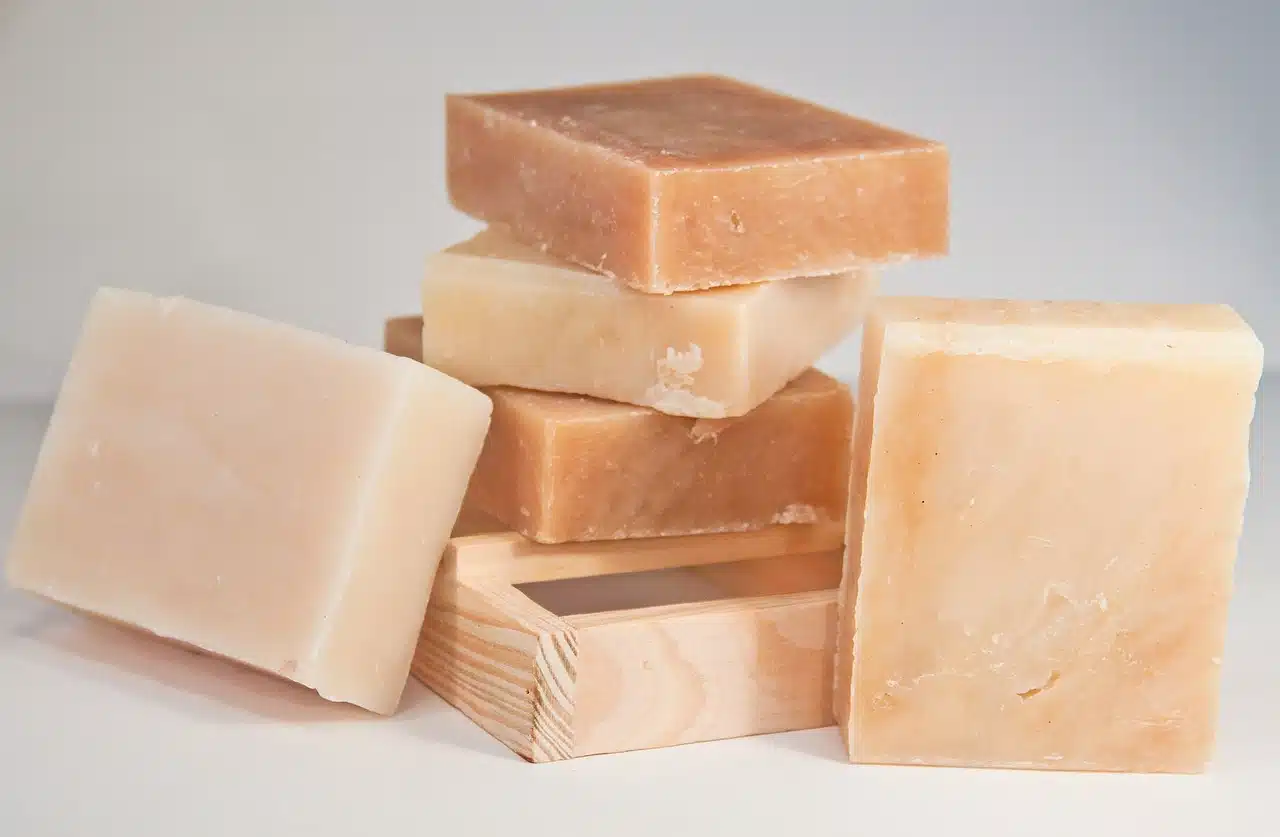

Saponification is the hydrolysis of an ester to obtain glycerin and soap.
Hydrolysis is a phenomenon that occurs when the division of a water molecule develops with the consequent breaking of one or more chemical bonds and the union of its atoms to the other substance that intervenes and decomposes. This type of chemical reaction is very common since water usually works as a solvent.
For hydrolysis to occur, the water molecule ( H2O ) must react with another macromolecule. Water, in this type of interactions, acts as a nucleophile since it gives up electrons and bonds, covalently, to another element.
What is hydrolysis
According to the dictionary of the Royal Spanish Academy ( RAE ), hydrolysis – also mentioned as hydrolysis – implies that a molecule unfolds due to the intervention of water .
Before moving forward, it is important to mention that the most basic unit of a substance that maintains its chemical properties is called a molecule . Molecules are made up of atoms : particles that cannot be divided by chemical procedures and that consist of electrons surrounding a nucleus.
In the case of water , each molecule is formed with one oxygen atom and two hydrogen atoms (that is why its chemical formula is H2O ). It should be noted that water is the primary component of living beings and the most abundant substance on the surface of our planet.
When a solute reacts with water, its molecules break apart. In other words: the incorporation of water triggers a chemical reaction that leads to the breaking of molecular bonds and the other substance decomposing into simpler elements.
There are other methods of separating compounds, such as electrolysis . In this process, which is carried out through electricity , an anion releases electrons at the anode and a cation collects the electrons at the cathode , which involves oxidation and reduction .
The hydrolysis of triglycerides requires the intervention of enzymes called lipases.
The opposite of a condensation reaction
Hydrolysis is the opposite of a condensation reaction in the framework of organic chemistry. While condensation involves the combination of two molecules to generate a product that is accompanied by the appearance of a water molecule, hydrolysis causes the breakdown of a chemical species through the inclusion of water.
Therefore, with hydrolysis a chemical reaction is carried out between a water molecule and an organic molecule that results in the breaking of at least one covalent bond to form two organic molecules. This pair of molecules has functional groups that incorporate the constituent atoms of that water molecule that dissolved.
At a general level, the hydrolysis equation is AB + H2O → AH + BOH . In this scheme, AB is the compound that in the first instance has two molecules; then, A and B are the molecules that have already separated, with a hydrogen ion ( H ) attached to one of them and the hydroxyl group ( OH ) attached to the other.

Reverse osmosis can be affected by membrane hydrolysis.
Polymer hydrolysis
We can analyze the hydrolysis of polymers to understand the process. Polymers are biological macromolecules that develop when several molecules of the same type and smaller ones join together.
What hydrolysis does, in these cases, is allow the decomposition of the polymers into monomers . At an organic level this is key since cells can absorb simpler molecules more easily.
In metabolism (which encompasses all the chemical reactions that are triggered in an organism), a distinction can be made between catabolic reactions and anabolic reactions . Catabolic reactions involve the release of energy and the breakdown of molecules, while anabolic reactions require energy and generate larger molecules.
Hydrolysis, in this framework, is a catabolic reaction. When water is incorporated, the covalent bonds that allow the polymer monomers to join are broken, causing the separation of the macromolecule.
The importance in digestion
Hydrolysis is of great importance in digestion . The lipids and proteins that we eat with food are macromolecules that, in the digestive process, must be broken down so that the body can take advantage of that energy. In this context, hydrolases intervene, which are enzymes that encourage catalysis to increase the reaction speed: that is why we speak of enzymatic hydrolysis .
Let's take the case of carbohydrates , which can be polysaccharides (such as cellulose ) or oligosaccharides (whose simplest members are disaccharides ). These polymers are composed of monosaccharides , which can be separated through hydrolysis. Proteins, meanwhile, are broken down into amino acids .
For the development of digestion, in short, digestive enzymes must intervene which, through hydrolysis, promote the breakdown of food macromolecules into simpler molecules.
Types of hydrolysis
Hydrolysis can be classified in different ways. An acid-base hydrolysis reaction occurs when water is split into a proton and a hydroxyl ion. The proton is instantly hydrated to form a hydronium ion.
Ester hydrolysis , adenosine triphophate (ATP) hydrolysis , and amide hydrolysis are other types of hydrolysis, in addition to the aforementioned enzymatic hydrolysis and polysaccharide hydrolysis.
