 The concept of hexahedron comes from the Latin word hexáhedron and refers to a solid that consists of six faces . The notion is used in the field of geometry.
The concept of hexahedron comes from the Latin word hexáhedron and refers to a solid that consists of six faces . The notion is used in the field of geometry.
In this context, a solid is a geometric body : that is, an object that has three dimensions (height, width and length). The faces are the various surfaces that make up these solids; In the case of the hexahedron, the object is formed with six faces.
Being developed with flat surfaces, the hexahedron is also a polyhedron . With greater precision we can say that it is a convex polyhedron , since any segment that joins two of its points will be contained within the polyhedron itself.
Another characteristic of hexahedrons is that their faces have five sides or less. When all the faces of the solid are congruent squares (their sides are equal), it is a regular hexahedron .
These regular hexahedrons are cubes : solids that are made up of six equal squares. It should be noted that cubes - and, therefore, regular hexahedrons - are Platonic solids , as all convex polyhedra are called whose faces are regular polygons that are equal to each other. This name is linked to Plato , the Ancient Greek philosopher who carried out the first studies on the matter.
 It is possible to recognize several kinds of hexahedrons, with different amounts of vertices and edges. From a topological point of view, only seven of them are easy to distinguish, but there are more. Of course, in all cases they are six-sided solids, since that is the distinctive property of these polyhedra. Let's see a brief description of some of the most common ones:
It is possible to recognize several kinds of hexahedrons, with different amounts of vertices and edges. From a topological point of view, only seven of them are easy to distinguish, but there are more. Of course, in all cases they are six-sided solids, since that is the distinctive property of these polyhedra. Let's see a brief description of some of the most common ones:
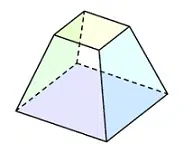
* The pentagonal-based pyramid has five three-sided faces and one five-sided face (the latter is its base), six vertices and ten edges. This differs from the image that we generally have of the pyramid, when we think of the Egyptian ones, for example, since they have a base with four sides and four faces with three sides each;
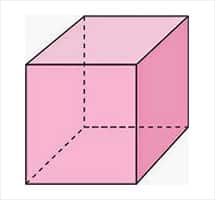
* The rectangular prism , also known as a cuboid , has six four-sided faces, eight vertices and twelve edges each. We are faced with a shape that we all know but that we do not usually call it this way or associate it with the concept of hexahedron, but rather we simply associate it with the concept of "box", another term that is accepted to refer to it in informal conversation or even in certain technical fields, such as three-dimensional graphic design;
* The cube is the most common of all hexahedrons, and is a three-dimensional solid object that is made up of six identical faces, each with four vertices and four sides. Starting from the two-dimensional universe, six squares are necessary to form a cube;
* The double tetrahedron has six three-sided faces, five vertices and nine edges each. The tetrahedron is a polyhedron whose faces are triangles . At first glance, it looks like a pyramid with one side missing. If all its faces are equilateral triangles, all equal to each other, then it is a regular tetrahedron ;
* The parallelepiped is a polyhedron with the same number of faces and vertices as the cube or rectangular prism, although each of its faces is a parallelogram , that is, a figure with four sides of which each pair of opposites are equal to each other but different from the others;
In addition to the types of hexahedrons just exposed, there are several more, although they are not always related to a specific name, but rather can be recognized based on their characteristics.
