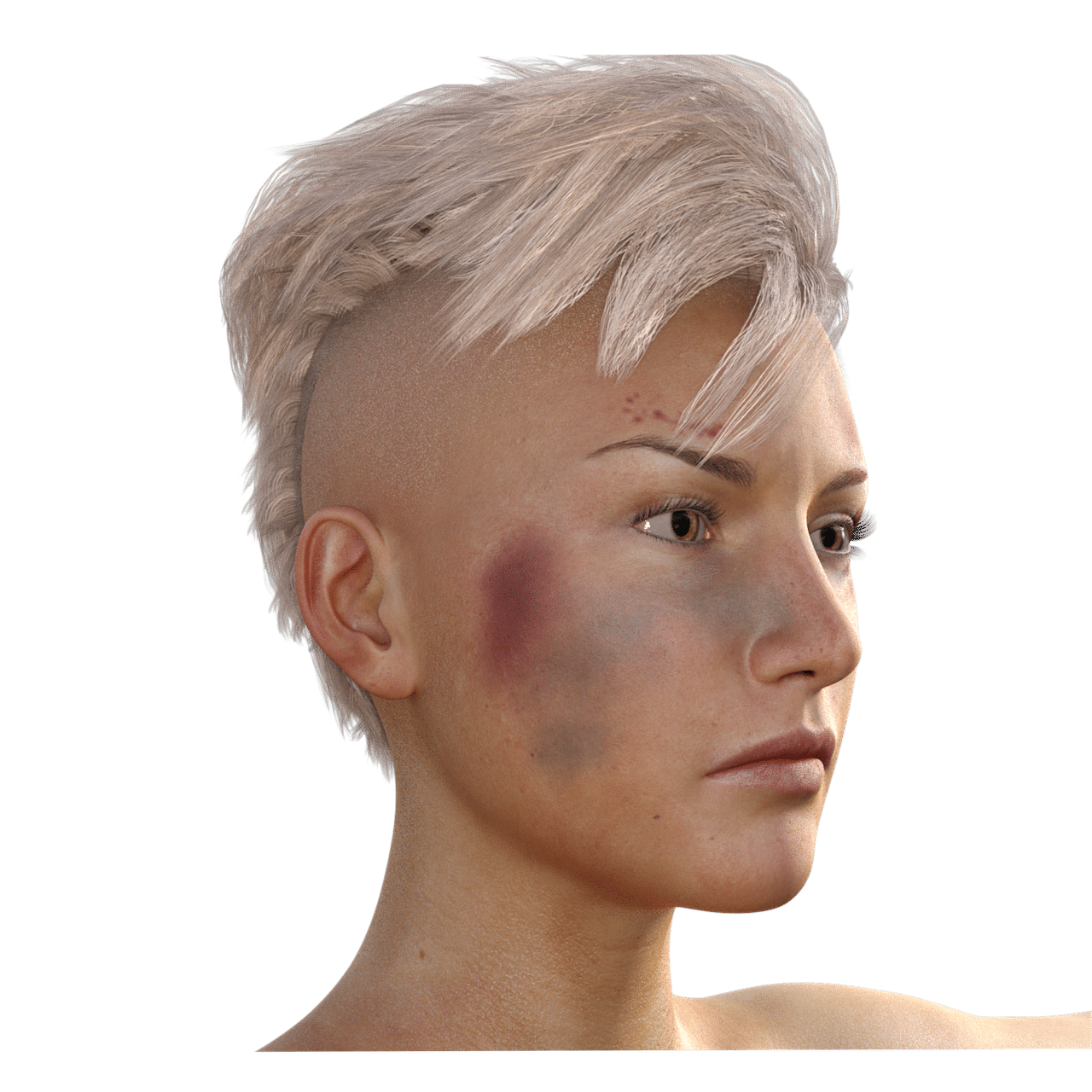

A hematoma is an accumulation of blood fluid that occurs from the rupture of a capillary vessel.
A hematoma is a mark that appears somewhere on the human body as a result of an accumulation of blood fluid caused by damage that has broken a capillary vessel. It is a bodily reaction to blows or a bruise that can turn the affected area purplish or bluish.
The hematoma, also known as bruise , bruise or bruise , constitutes an ecchymosis . This type of spots can appear on the skin or internal organs of the body for multiple reasons. When pigments and cells move through the connective tissue, the hematoma can change its position. To cite a specific case as an example, a bruise that appears on a knuckle can move to cover the entire finger over the course of a few days.
Classification of bruises
Hematomas can be classified into three large groups: subcutaneous (they are the mildest: they are found under the skin), intramuscular (they appear in the protuberant area of a muscle and can affect internal organs) or periosteal (they occur when the contusion affects to a bone).
The process until the appearance of a bruise detectable to the naked eye begins at the moment of the blow and can be expected from the immediate pain felt in the affected area. After a short time, inflammation occurs which then decreases naturally. Finally, the area involved changes color and goes through various states (pinkish, bluish, greenish-yellow) until it returns to its usual pigmentation.
There are several ointments for external application that allow the treatment of bruises. Using ice on the affected area is another option during the first days. If the pain is intense, the consumption of an analgesic can offer very positive results.
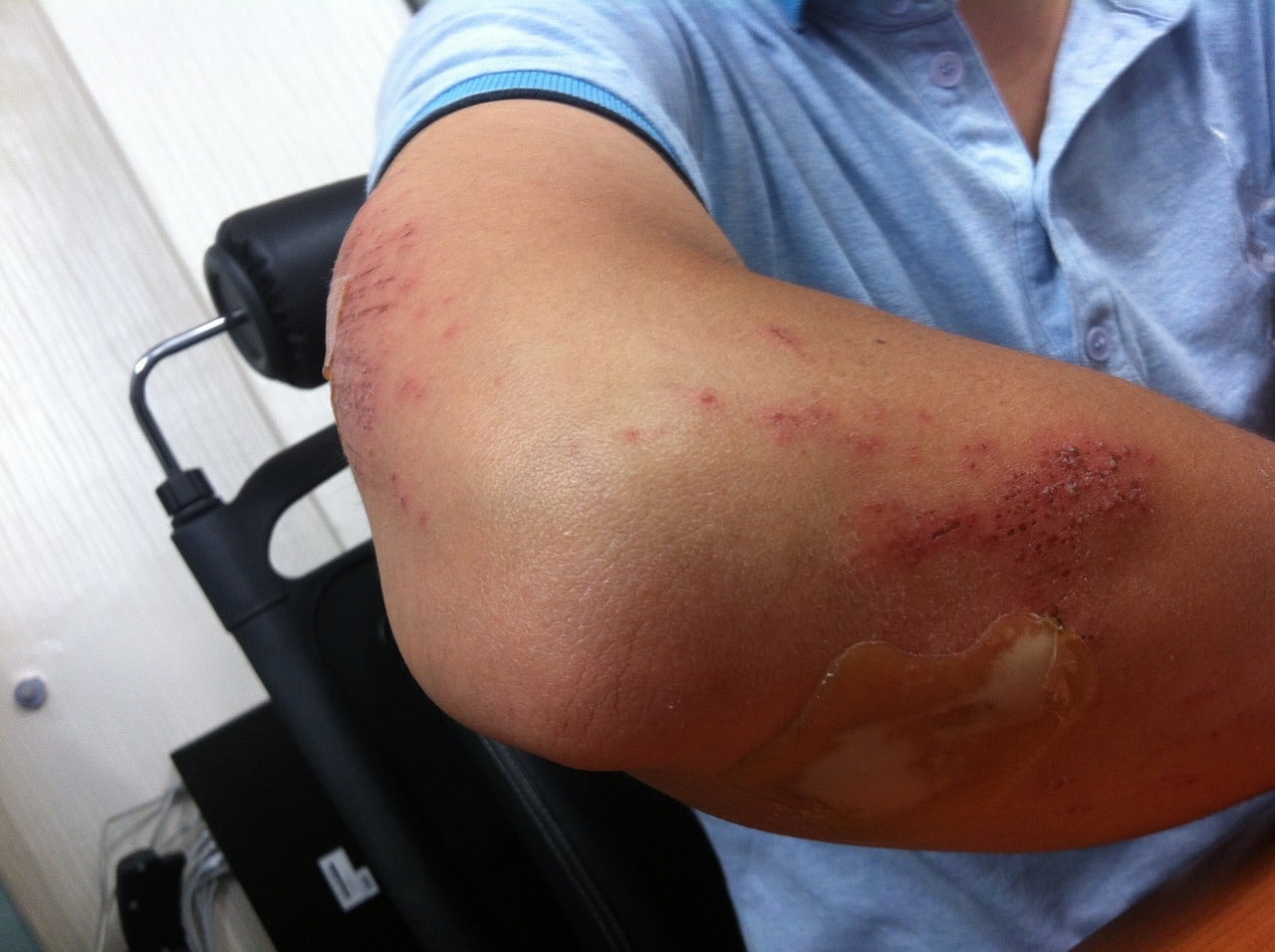
A hematoma is an ecchymosis: a subcutaneous lesion.
Its appearance during pregnancy
It is very common for a woman to experience blood loss during the first trimester of pregnancy; The causes can be problems of varying importance, one of the most frequent being intrauterine hematomas . These are also known as interdeciduotrophoblastic and occur when small accumulations of blood are generated within the endometrial cavity.
Although they tend to occur in many cases, the reasons why they occur are unknown. Generally, they do not cause pain in the abdomen; Blood loss, which does not always occur, is not the same in all cases and a medical consultation is recommended as soon as it is detected. In fact, when a hematoma of this type is discovered, the pregnancy is considered high risk and receives exhaustive periodic observation to analyze its evolution.
Fortunately, intrauterine hematomas do not interrupt pregnancy, and are generally reabsorbed and disappear spontaneously if adequate rest is given . Depending on the size, the time needed for removal and bleeding may vary. Its detection can be done using a control ultrasound and its volume is calculated by multiplying its extension by its width.
Types of intrauterine hematomas
Depending on their location, intrauterine hematomas can be called retroplacental , marginal , subchorionic (or retrochorionic ) or supracervical . They usually have a cuneiform or crescent-like appearance .
If they are large in size and their location is compromised, they are usually related to complications such as premature rupture of the water or placental abruption, issues that can lead to an abortion or early delivery, in the case of advanced pregnancies.
As in other types of disorders , complete rest is one of the most common indications that doctors usually give. However, in practice, it is almost impossible for a working-class woman to follow, especially considering that this is a problem present in the first months of pregnancy, when it is not yet easy to be absent from work.
