 The method that allows analyzing the measurement of the gases that are released during the development of a chemical reaction is called gasometry . The concept is frequently used in the field of medicine to refer to the analysis of the gases that are present in the blood .
The method that allows analyzing the measurement of the gases that are released during the development of a chemical reaction is called gasometry . The concept is frequently used in the field of medicine to refer to the analysis of the gases that are present in the blood .
In this case we speak of arterial gasometry . Using this technique , carbon dioxide and oxygen levels in the blood can be measured and studied, among other data of interest to the medical professional.
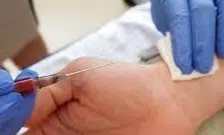
To perform arterial blood gas, a blood sample must first be obtained from the radial artery , brachial artery , or femoral artery . In certain cases, it is also possible to use a sample of a vein. Blood extraction is carried out by inserting a needle through the skin: once the sample is obtained, it is sent to a laboratory for the corresponding analysis.
Arterial gasometry allows the diagnosis and study of lung disorders and respiratory diseases in general . It also provides information about the metabolic state and the acid-base balance of the body .
An abnormal blood gas result can reveal lung disease, kidney problems, or an imbalance in metabolism. It can even be linked to any type of injury that alters normal breathing.
It is important to mention that arterial blood gas analysis is a very low risk study. Possible complications are bleeding, a bruise, or a blood flow problem at the puncture site. There is also the possibility of infection .
Medicine frequently resorts to gasometry because it is a non-invasive treatment for the patient (in fact the degree to which it invades the patient is really minimal) but it has the potential to provide a large volume of essential information about their condition. of health. For this reason, it is usually indicated routinely to detect alterations such as those mentioned in the previous paragraphs.
 Respiratory failure is one of the situations that can alter the body's metabolism and gas levels. Although it is possible to suspect that a patient is suffering from this type of disorder based on some of their symptoms , the only way to diagnose respiratory failure is through arterial blood gas analysis.
Respiratory failure is one of the situations that can alter the body's metabolism and gas levels. Although it is possible to suspect that a patient is suffering from this type of disorder based on some of their symptoms , the only way to diagnose respiratory failure is through arterial blood gas analysis.
Among the situations in which we can speak of respiratory failure are the following: COPD ( chronic obstructive pulmonary disease , which limits the passage of air to the lungs), asthma, acute lung edema and pulmonary fibrosis. As can be seen, they are not problems that we can or should take lightly, and that is why gasometry is so important.
Another situation that can be detected with the help of a gasometry is hyperventilation , which occurs when the patient breathes too quickly and agitatedly, which results in the expulsion of an excessive amount of carbon dioxide . Since the blood also needs this component, hyperventilation generates an alteration in the metabolism that affects the calcium and pH of the blood.
On the other hand, there is acidosis , which occurs when acid levels in the blood reach too high values. In this case, to know the blood pH it is possible to perform a gasometry in an artery or vein. In this framework we can talk about sepsis (lactic acid is generated and oxygen is not used) and diabetic ketoacidosis (it is not possible to use glucose and ketone bodies are generated).
