Nuclear physics allows us to learn more about the characteristics and distinctive features of atomic nuclei.
Nuclear physics is the name given to one of the branches of physics . It is a discipline that focuses on the interactions, properties and behavior of the atomic nucleus .
The history of nuclear physics began to be written and take on its own momentum when the French physicist Henri Becquerel discovered radioactivity (also known as radioactivity ). Later, the British Joseph John Thomson found electrons and, within that framework, the existence of a structure within atoms was confirmed. Over time, research and experts expanded the information on the matter, thus distinguishing classes of radioactive decay that involve alpha particles , beta particles and gamma rays , for example.
Otto Hahn, James Chadwick (recordado por haber detectado a los neutrons), Marie Curie,Enrico Fermi y Ernest Rutherford, a través de sus trabajos científicos, han sido fundamentales también para la evolución de la nuclear physics. Tampoco se puede dejar de mencionar que Arthur Stanley Eddington llegó a anticipar mediante un artículo centrado en la disposición estelar que en las estrellas tiene lugar un proceso bautizado como nuclear fusion.
Branches of nuclear physics
Although nuclear physics is considered a specialization within a larger category such as physics , it is possible to find divisions and combinations that diversify and expand the scope of this discipline.
Given the current challenges, the studies benefiting from cutting-edge technology and contemporary approaches, to indicate a specific case, it is possible to refer to modern nuclear physics . These include models (such as the so-called liquid drop model or the one identified as the nuclear shell model ) that become relevant when analyzing or tracking phenomena or features in heavy nuclei that encompass a hundred nucleons .
On the other hand, nuclear astrophysics is recognized as the result of a connection between scientific areas, a field in which nuclear physics and astrophysics are nourished and complemented.
And there is, in addition, a segmentation classified as high energy physics in which the focus is on how nuclear matter behaves in a context of energy systems typical of particle physics . Its main purpose is to observe how heavy ions collide (using the Large Hadron Collider and the relativistic heavy ion accelerator , specifically), as opposed to lighter atoms tackled in different particle accelerators . Low energy physics , on the other hand, is concerned with adding details about the structure and low energy reactions in the nucleus of atoms .

Nuclear physics contributes to nuclear medicine, art, geology and the process of creating nuclear weapons, for example.
Importance
Nuclear physics is important because it makes it possible for nuclear energy to be used in thermal power plants . It is also taken into account when developing nuclear weapons , whether fusion or nuclear fission .
It also has significant value for the field of archeology where, as in art , nuclear technology is a great ally when carrying out conservation work on pieces.
Nuclear medicine is another space that takes advantage of this discipline by obtaining internal images of an organism and being able, based on these studies, to provide an exact diagnosis and appropriate treatment. In this context, it is appropriate to mention the magnetic resonance imaging scan that many health professionals indicate when analyzing the state or condition of a patient.
There is a technique associated with nuclear physics (activation analysis), to add more references, that is used to investigate certain materials based on the tracking of elements that are found in small quantities.
As experiments linked to nuclear physics do not cease, surely in the coming decades the applications of this discipline will deepen and expand.
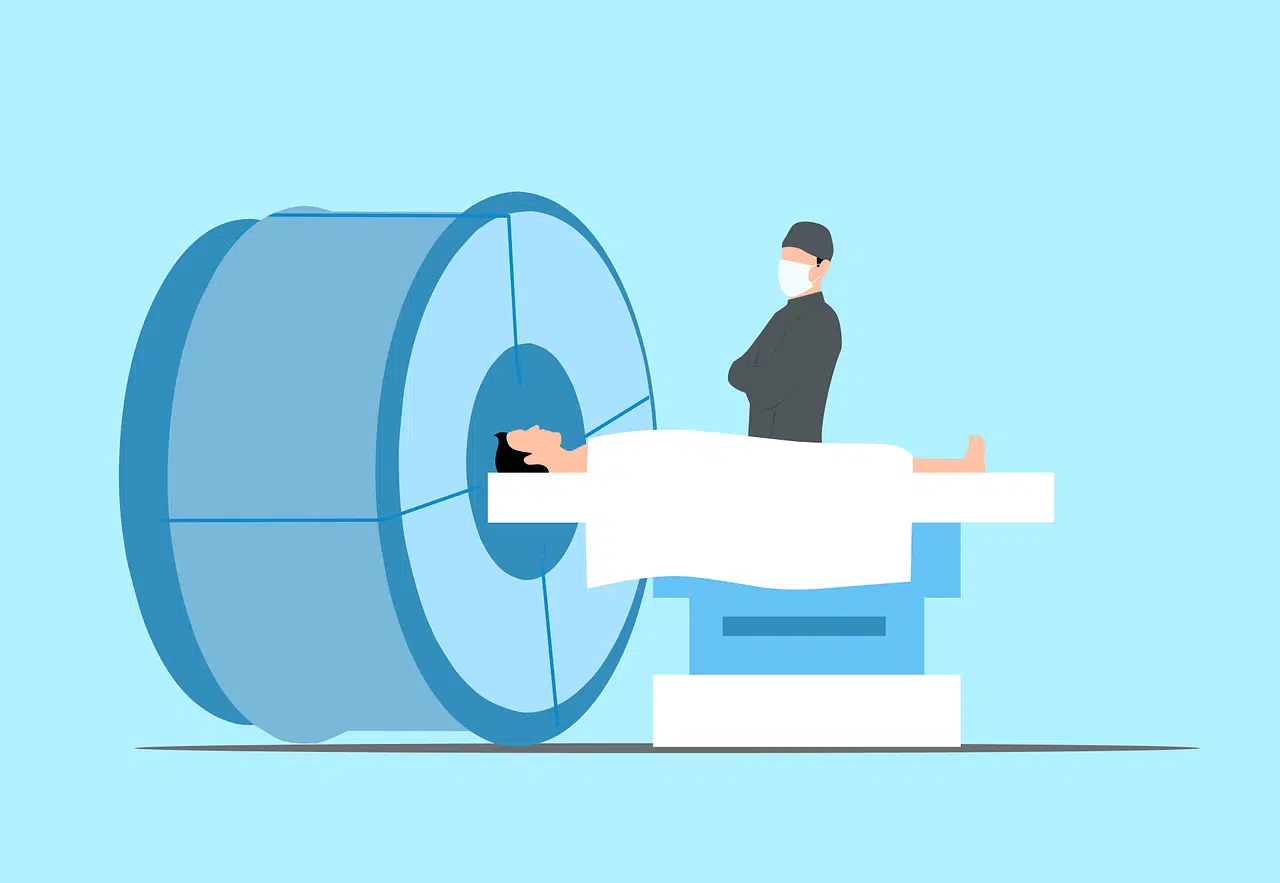
A computer, radio waves and a magnetic field come together in nuclear magnetic resonance imaging to obtain images of a human being's body to allow medical personnel to evaluate the patient's health status.
Examples of nuclear physics
In practice, numerous examples of nuclear physics frequently come to light.
Seasons ago, as noted when reviewing journalistic archives, experts from Lund University proposed a review of an old manifesto related to the eventual discovery of superheavy elements. According to this consideration, long-lived nuclei would generate a kind of "island" marked by stability . It is believed that there is a "magical" combination of neutrons and protons capable of ensuring the extension of the useful life of certain elements. The test, which lasted almost twenty days, consisted of the acceleration of atomic nuclei , an atomic nuclear fusion , the creation of flerovium , and the real-time observation of the radioactive decay of several nuclei .
According to other research works, nuclear physics can be combined with quantum physics to, according to forecasts, develop nuclear clocks capable of making more precise measurements of time compared to the operation of current atomic clocks .
