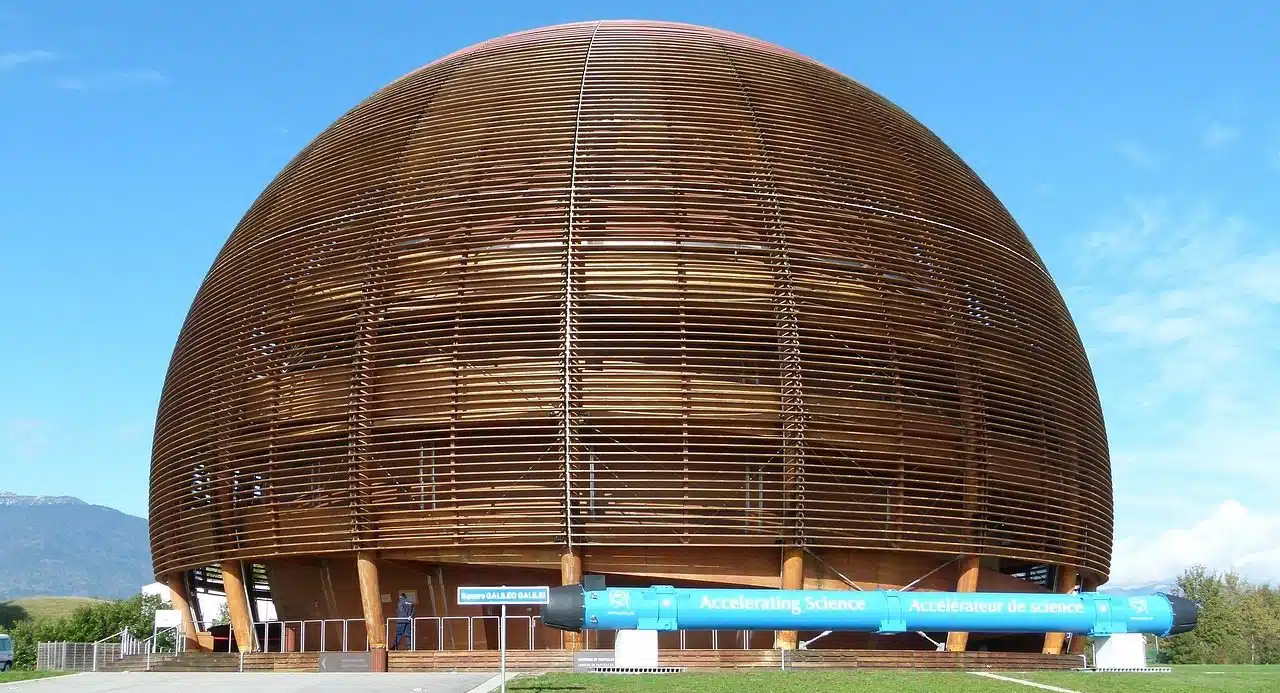

The European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN) has developed a huge and powerful particle accelerator known as the Large Hadron Collider.
Particle physics is the name of a discipline framed in physics whose object of study is the components of matter, also contemplating the analysis of the interactions that occur between them.
This scientific branch, also called high energy physics , is responsible for focusing on the distinctive features and behaviors of elementary particles , many of which can only be observed when using a particle accelerator . This is known as equipment that uses electromagnetic fields to drive particles that, after reaching a high level of energy , collide with other elements.
Today, experts appeal to the standard particle model (as called a quantum field theory that was developed in the early 1970s that recognizes more than ten pairs of particles together with their constituents as constituents of matter). respective antiparticles ) to segment the aforementioned elementary particles into two groups: that of the fermion and that of the boson . In the first case, the theory says, the set encompasses the quark and the lepton and, by presenting a half-integer particle spin , the elements are subordinated to the Pauli exclusion principle . The boson family, meanwhile, includes the gluon , the photon , the graviton (which is indicated, in most models related to quantum gravity , as a hypothetical elementary particle that influences the gravitational interaction ) and to the Higgs boson . The properties of fermions and bosons , experts on the subject consider, could have a point of contact based on a hypothetical symmetry designated as supersymmetry .
Applications of particle physics
Particle physics has been adding more and more applications thanks to scientific discoveries and technological innovation.
This branch that helps to know in depth and understand the immensity of the universe is fed back and complemented by astroparticle physics , an area where the focus is on investigating, for example, cosmic rays and neutrinos . Likewise, it is linked and enriched with knowledge of cosmology .
It has also contributed to perfecting medical diagnostic techniques and the development of useful therapies for the treatment of different pathologies; It has inspired and promoted cultural projects that promote the fusion of art and science , and has allowed the manufacture of electronic devices that use semiconductors, to list other achievements derived from the dedication to the progress of particle physics .
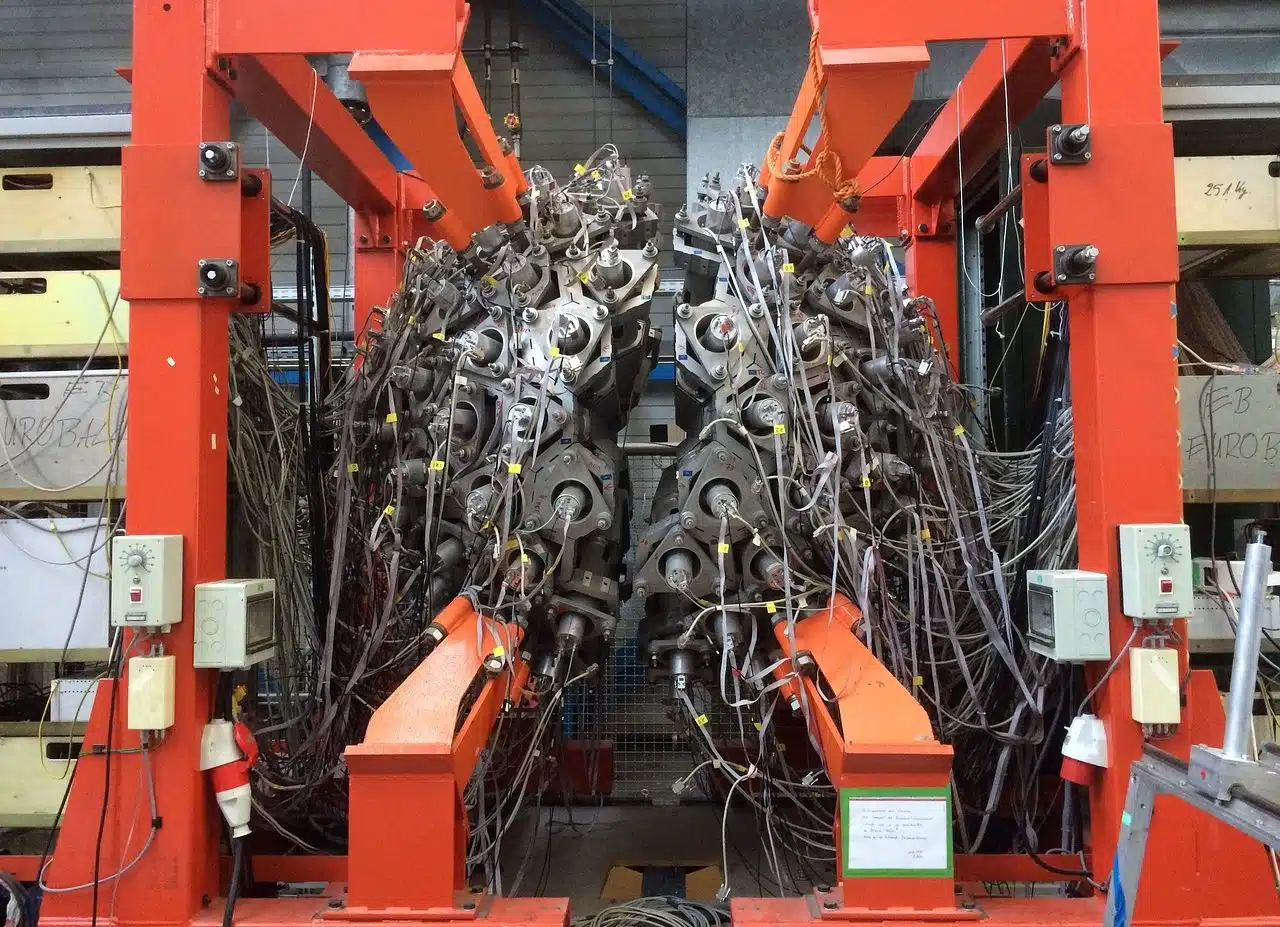
Particle physics experts use different types of particle accelerators to carry out their scientific research.
fundamental force
Among the concepts that need to be mastered to understand more about particle physics is the notion of fundamental force . This expression identifies each type of interaction that has subatomic particles as protagonists.
It is possible, in this framework, to differentiate between weak interaction (as a result of which the disintegration of particles occurs and a nuclear fission process begins), strong interaction (a powerful force that manages to maintain the union between neutrons and protons and that It is adequately explained by quantum chromodynamics ), gravitational interaction (focused on the phenomenon of gravitation ) and electromagnetic interaction (a set in which magnetic interaction and electrostatic interaction coexist).

Through particle physics it is possible to discover and understand phenomena and components related to the universe.
Centers specialized in particle physics
Research and experimentation focused on particle physics is carried out in specialized centers distributed in various nations.
One of the most recognized internationally is CERN (European Organization for Nuclear Research) , which was created in 1954 and managed to establish itself as an example of joint work since scientists from multiple countries collaborate in this space. There, to list some milestones, the discovery of the so-called W and Z bosons took place, while the physicist and engineer Georges Charpak managed to generate a multiwire proportional camera , a type of particle detector .
The Fermilab Laboratory installed in the United States also enjoys great prestige. The Tevatron , one of the most powerful particle accelerators on the planet, was installed there (the other is the Large Hadron Collider that powered CERN ). Thanks to this device, the top quark was discovered, identified decades after having identified the bottom quark .
Another accredited North American scientific research center is the SLAC Laboratory (Stanford Linear Accelerator Center) . Among the facilities and equipment that have enriched it over the years, we can mention the Stanford Linear Collider and a linear accelerator that was once the largest in the world.
In search of information about particle physics experiments, meanwhile, projects such as the Forward Search ExpeRiment (FASER) regain visibility, conceived to be able to analyze in detail interactions generated between high-energy neutrinos , the ALICE (A Large Ion Collider Experiment , intended for study of heavy ion encounters) and the Compact Muon Solenoid (CMS) emerged to expand knowledge in relation to forces in the universe and the essential composition of matter .
