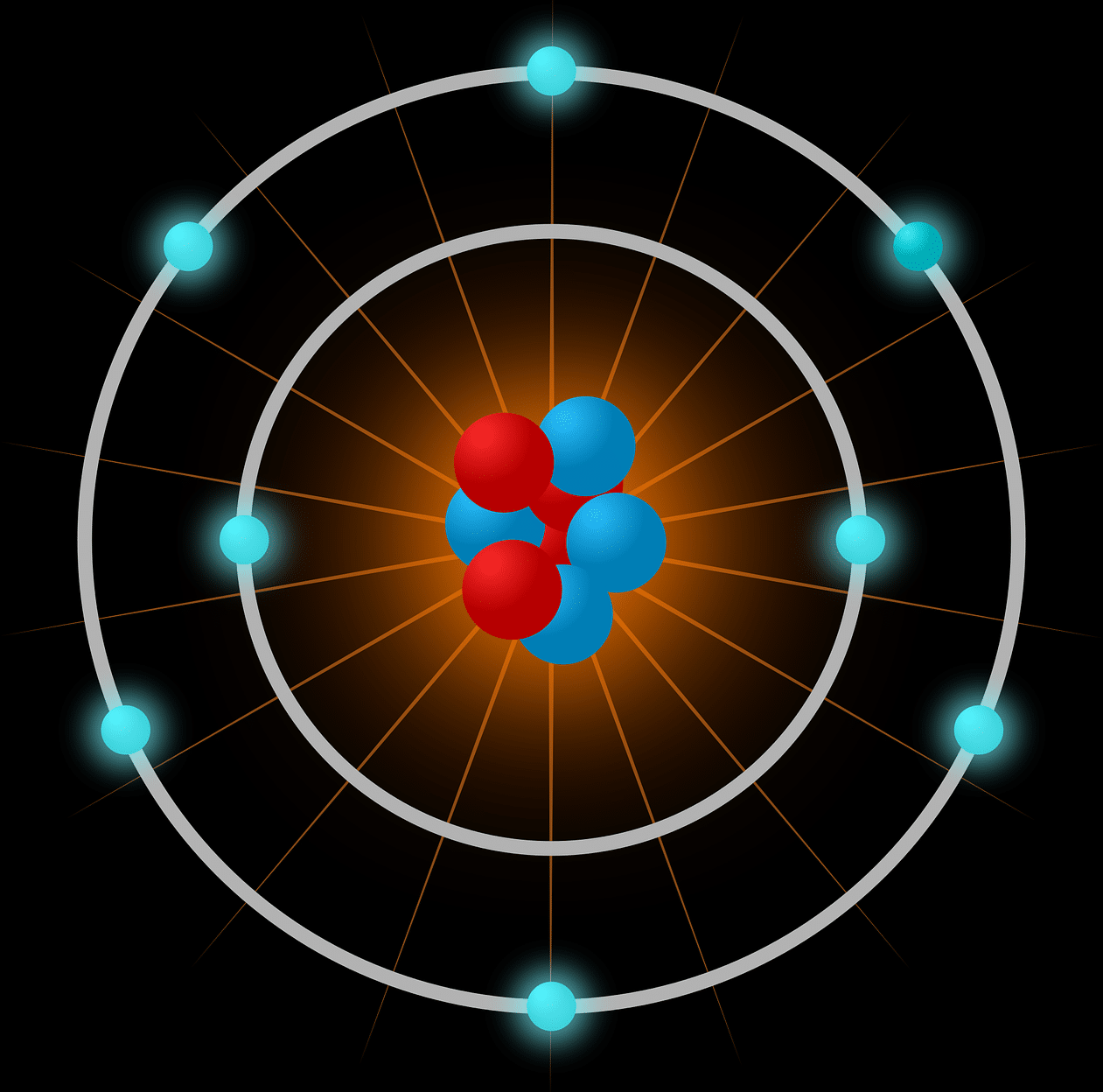
Using atomic physics, we can understand how atoms behave and what properties they have, for example.
Atomic physics is the name given to a specialty within physics that has allowed, with the passage of time, to know more and better about the universe . With information provided by this discipline that deals with the atomic structure as a whole, and having mastery of spectroscopy , one can, for example, observe and understand in depth what the interaction between matter and electromagnetic radiation is like.
In other words, atomic physics is a field of knowledge focused on the study of the behavior and characteristics of atoms , without losing sight of the electromagnetic force or the particularities of the atomic nucleus . As there are micro and macroscopic analyses, in this scientific branch not only traditional or classical procedures are taken into account but also quantum methods .
Experts dedicated to atomic and molecular physics , specifically, investigate the properties evidenced by matter from both an atomic and molecular perspective. It is valuable in this area to advance in the development of molecular simulation , the evolution of systems that make it possible to carry out extremely precise atomic calculations and in experimentation linked to various atomic processes using some source of ionizing radiation or particle accelerators .
Origin and evolution of atomic physics
It was necessary to discover that atoms are the smallest components that exist in matter and that the path of spectroscopy be increasingly explored so that the origin and evolution of atomic physics could begin to be written.
Knowing what and how spectral lines are and adding evidence about the importance of Bohr's atomic model were key to outlining the theoretical basis and field of application of atomic physics . It should be noted that given the magnitude of his scientific contributions, the Danish Niels Bohr was rewarded with a Nobel Prize in Physics and remembered throughout history as a determining figure for the advancement and strengthening of many branches of physics .
Both atomic physics , subatomic physics and molecular physics have been consolidated, perfected and modernized thanks to the work of numerous physicists of different nationalities and technological progress. Decisive for scientific growth in these areas were the emergence of the periodic table of elements , the double slit experiment , the recognition of the photoelectric effect and studies on wave-particle duality , for example.

Experts in atomic physics usually model atoms by thinking of them in isolation.
Basics
As can be seen from practice, atomic physics is based on three issues: the atomic structure , certain relevant atomic models and some guidelines or postulates of quantum mechanics that apply to the atom.
The gaze of specialists in this branch of physics therefore rests on the nucleus of the atom , the protons , the neutrons and the profile of each electron that appears attached to the atomic center.
The atomic models of Rutherford , Thomson and Bohr are also taken into consideration.
It is also necessary in this area to be aware of the content and usefulness of the Schrödinger equation that was proposed in 1925 by a talented physicist named Erwin Schrödinger and to know what the Heisenberg uncertainty principle indicates and what its consequences are.

Thanks to atomic physics it is possible to appreciate in depth and take better advantage of the information reflected in the periodic table of the elements.
Applications and scope of atomic physics
Atomic physics has multiple applications and scopes. It is important, to point out a specific case as a reference, in research and experimentation related to the phenomenon of nuclear fusion and when putting into practice techniques for cooling samples of either atoms or molecules by means of a laser field.
Technological advances and scientific challenges are increasingly revolutionizing the field of atomic physics , which could have a before and after with the generation of gamma ray lasers . In this regard, there are tests with high-speed electrons capable of interacting with a powerful laser field .
Analyze materials, improve technologies at the service of medicine and medical diagnosis to optimize the process and images of nuclear magnetic resonance (MRI) or positron emission tomography (PET) and take advantage of notions to perfect computing Quantum physics are other benefits that arise from atomic physics . This discipline is also essential to understand issues associated with high energy density plasma .
Much progress has already been made in the sector of atomic physics , achieving valuable discoveries and opening paths to continue connecting and complementing this area of study with other scientific specialties. However, there are still unknowns to be resolved, challenges to be overcome and unanswered questions about the mysteries of the universe and matter , for example. That is why, on a global scale, work in this discipline, which still has the potential to continue evolving and gaining precision, must continue to be stimulated and encouraged.
