Before entering fully into the meaning of the term fibrosis, we are going to know its etymological origin. Thus, we can determine that it is the result of the sum of two lexical components that derive from Latin:
-The noun "fiber", which has that same meaning.
-The suffix "-osis", which is used to indicate "pathological process."
Fibrosis is a pathological development of fibrous tissue . This abnormal formation is generated from chronic inflammation or a circulatory problem that causes an increase in collagen production.
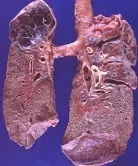 Due to fibrosis, the tissue structure increases in thickness as the connective or fibrous tissue grows. Depending on the organ affected, fibrosis can cause different symptoms, such as high blood pressure , dyspnea and others.
Due to fibrosis, the tissue structure increases in thickness as the connective or fibrous tissue grows. Depending on the organ affected, fibrosis can cause different symptoms, such as high blood pressure , dyspnea and others.
The diagnosis of fibrosis is made by analyzing tissue modifications. Once diagnosed, the treatment indicated by the doctor will be linked to the disease that underlies the appearance of fibrosis. Generally, the aim is to ensure that alterations in the tissue do not progress, since the changes that have already occurred cannot be reversed.
Pulmonary fibrosis , for example, involves the loss of the alveoli's ability to exchange gases due to tissue thickening and scarring. This fibrosis can be idiopathic (no known cause) or due to exposure to certain substances, rheumatoid arthritis, tuberculosis or lupus, among other reasons. Pulmonary fibrosis is characterized by breathing problems, chronic cough, fatigue , and loss of appetite and weight.
Cystic fibrosis , meanwhile, is a genetic disorder that primarily affects the lungs , although it also affects the functioning of the intestine, liver and pancreas . This disease includes fibrosis, the accumulation of mucus and multiple disorders that are potentially fatal.
In the same way, we cannot ignore the existence of what is known as muscle fibrosis. We can indicate that this basically consists of an interruption of the sliding that the muscles perform on themselves. What this brings with it, therefore, is that the natural, functional and primary muscle tissue of the organism is replaced by another that is defined as "anarchic."
Among the possible causes of muscle fibrosis are everything from surgery to chronic tendinitis to a break in muscle fibers, old age or muscle hypertrophy, among others.
Physiotherapy and even surgery are two of the main pillars of treatment that are usually established for patients suffering from muscle fibrosis. However, sometimes the use of drugs is also used.
It must be established, in addition to everything indicated, that on many occasions this type of fibrosis appears in people who suffer from Duchenne disease, which is a muscular dystrophy that is usually caused by a defective gene that affects what is the protein that exists in muscles.
Mediastinal fibrosis and endomyocardial fibrosis are other types of fibrosis that can affect a person.
