An important step that we are going to take to discover the meaning of the term phagocytosis is to know its etymological origin. In this case, we can state that it is a word that derives from Greek, since it is the result of the sum of several lexical components of said language:
-The word “phagos”, which means “eating”.
-The noun “kytos”, which is synonymous with “cell”.
-The suffix “-osis”, which is equivalent to “conversion” or “formation”.
The idea of phagocytosis is used in the field of biology . The term refers to a type of endocytosis : a procedure that allows a cell to introduce particles or molecules into its interior, passing its membrane.
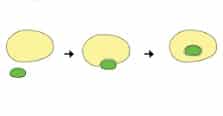 Specifically, phagocytosis consists of capturing certain particles through pseudopodia (extensions of the cytoplasm ). This process can be carried out with a defensive objective or for feeding .
Specifically, phagocytosis consists of capturing certain particles through pseudopodia (extensions of the cytoplasm ). This process can be carried out with a defensive objective or for feeding .
With pseudopods, the cell surrounds the particles and takes them inside, forming species of vesicles known as phagosomes , which when fusing with lysosomes makes degradation possible. This action allows the body's defense and also the recycling and elimination of dead tissues.
It is important to note that not all cells can develop phagocytosis. This is a property of neutrophils, macrophages and some other cell types that are classified as professional phagocytes . Other cells that can carry out phagocytosis, however, do not have the process as a significant function.
In addition to everything stated above, we cannot ignore another series of important data about phagocytosis, among which are the following:
-We can establish that its process is made up of a total of five phases: chemotaxis, adhesion, ingestion, digestion and excretion of what are waste products outside the cell in question.
-In a phagocytosis process, different receptors play an essential role. We are referring to some such as Fc receptors, complement receptors, lectins and even the so-called Toll or TLRs.
-In addition to everything indicated, we cannot overlook the fact that there are some molecules that can significantly influence phagocytosis. These are molecules such as cytokines, lipopolysaccharide or others that are associated with certain pathogens.
-It must be emphasized that phagocytosis can be accelerated if the microorganism in question is coated with what are opsonins.
Let's see how phagocytosis works in the face of an infection . The cell, upon detecting the infectious agent, emits pseudopodia that surround the microbe and engulf it, confining it to the phagosomes. These phagosomes fuse with lysosomes, which have proteins inside that allow the phagocytosed particles to be broken down.
It is important to mention that there are bacteria that, given the importance of phagocytosis for the immune system, managed to create strategies that allow them to evade this defensive process and resist the immune response. In this way, the body faces greater difficulties in eliminating infectious agents.
