Virtually all genes are shared by the bonobo, the chimpanzee and Homo sapiens, as seen when examining the human genome.
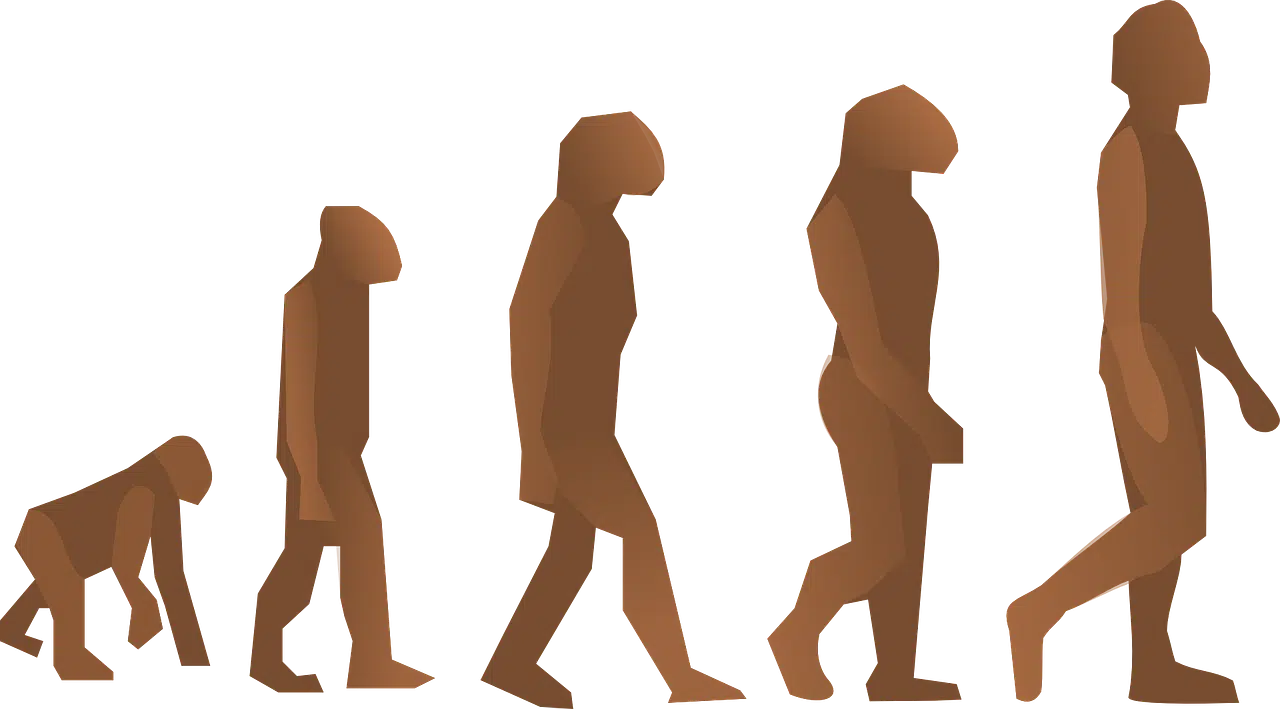
Biological evolution is a process of transformation, over multiple generations, of genetic and phenotypic traits that are transmitted to the descendants of different populations of living beings. Over time, taking a common ancestor as a starting point, a wide variety of life forms have spread on planet Earth .
Thanks to evolution, more than one species can emerge and organisms have the possibility of guaranteeing one change (or more) that favors their adaptation to a certain environment.
It is essential to be clear that, for there to be evolution , some genetic variation , that is, a mutation , must occur. Thus, then, the DNA sequence is altered and that brand new genetic material is inherited.
Importance of biological evolution
Natural selection summarizes and demonstrates the importance of biological evolution .
For many millions of seasons, at the beginning of earthly life, microscopic beings had strong competition as a result of the struggle for survival : they needed to obtain energy and food to survive. Those organisms that were better adapting to their habitat had a higher reproduction rate compared to the others. In this framework, the weakest species were condemned to extinction or forced to mutate in order to survive. The biodiversity , the species , that have been lost in a relatively short geological time and disappeared from the face of the Earth nourish the phenomenon recognized as mass extinction .
Ecology experts who know in detail what the principle of competitive exclusion is about explain that species usually fit into more than one ecological niche to minimize the degree of competition as much as possible.
It cannot be overlooked that there is enormous complexity in this class of phenomena. Chance and errors associated with sampling, for example, influence how the frequency of an allele changes between one generation and another, giving rise to so-called genetic drift . Even though there is no selective force , as a result of genetic drift, two populations that start out sharing a genetic structure are segmented into different communities whose alleles are different.
The scientific branch called evolutionary developmental biology focuses, today, on investigating the role of both genetic drift and natural selection as forces that drive evolutionary change. The neutralist theory of molecular evolution , which maintains that the greatest percentage of evolutionary changes is due to the process of fixing neutral mutations that do not immediately determine the fitness of a being, inspired this type of research.
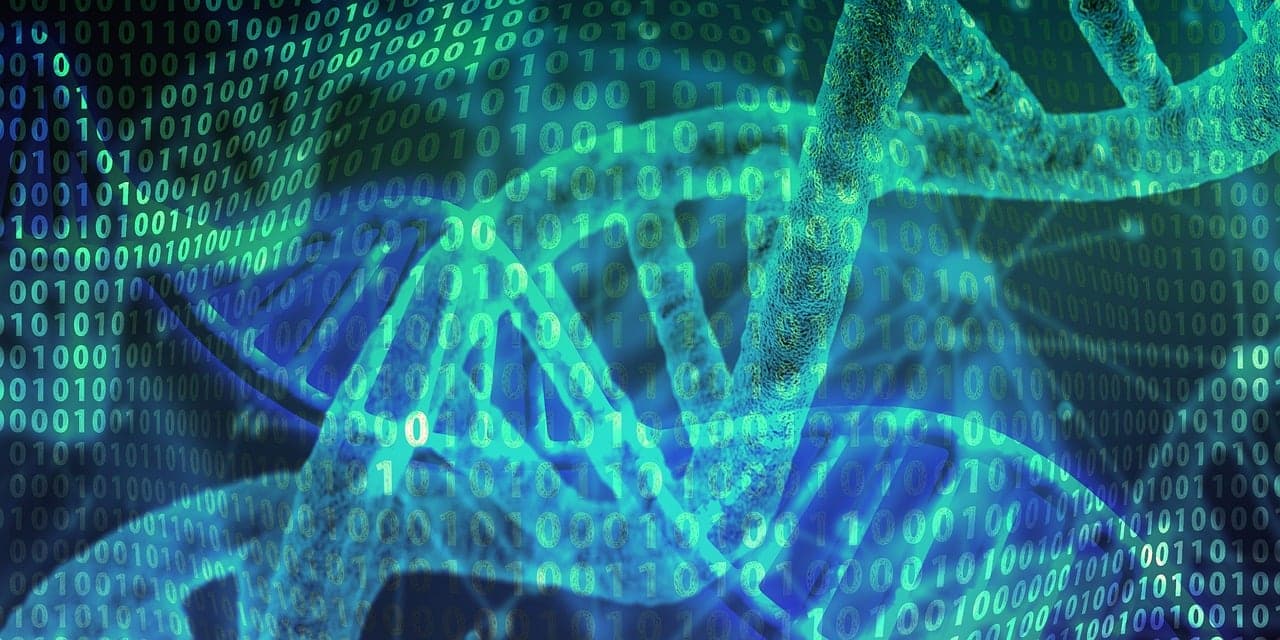

In the case of organisms, their genome is located in DNA; certain viruses, meanwhile, find it in RNA.
Evolution theory
Interest in the theory of evolution inevitably leads to the figure of Charles Darwin . This naturalist of English origin observed nature, studied and launched a work that, even today, is consulted and known on a global scale: "The origin of species" .
This scientist promoted the idea of natural selection and, in 1858, he received from a British colleague ( Alfred Russel Wallace ) who was also investigating the matter an essay independent of his with which he aspired to launch a unified publication.
Darwin 's works, which were translated into numerous languages, were not exempt from criticism and opened the game to strong debates. Even from a Christian perspective, the Darwinian postulate of evolution is not compatible with how the Bible narrates creation.
More key concepts related to biological evolution
In addition to those mentioned above, there are more key concepts related to biological evolution .
One of them is gene flow , a notion that refers to how, between one population and another, gene alleles are transferred in order to lower the level of genetic differences in local populations.
Coevolution , meanwhile, refers to a cycle focused on an interaction dynamic in which there is a selection and a response. In this sense, it is necessary to pay attention to what happens when a predator and its prey or a pathogen and a host interact, causing changes and new adaptations .
When learning about the origin of life , the evolution of man and biodiversity, one must also educate oneself about the meaning of speciation . This word, according to the theory, describes the process thanks to which, based on a first species, more species emerge.

The process of dinosaur extinction, scientific reports indicate, began long before an asteroid hit the Earth.
Evidence of evolution
There is several evidence of evolution that provides valuable information about what the oldest beings that populated the Earth were like and how species have mutated.
Paleontology , for example, is an excellent tool for understanding how organisms have progressed. The fossil record is key to being able to travel in time and reconstruct stages of evolution based on ancient organic remains . There is even fossil evidence of human evolution .
Likewise, it is essential to evaluate morphological evidence , genetic evidence , embryological evidence and molecular evidence .
If the focus of interest is understanding how organisms have spread throughout our planet, then biogeography offers useful answers in this regard.
