Stomata are openings that can be natural or created through surgery.
Stoma is a term used in medicine and botany to refer to certain openings . Before moving forward, it is important to analyze the etymological origin of the concept.
In this case, we can establish that it is a word that derives from the Latin stoma . This word, in turn, comes from a Greek word that means “ mouth .”
Concepts such as stomach , stomatology , stomatitis and stomach , among many others, have emerged from stoma.
Stoma in medicine
Medically, a slit that opens in a hollow organ or between two such structures is called a stoma. This opening can be natural or created through surgical intervention.
With an operation , organs such as the stomach , colon and urinary bladder can be transformed into artificial stomas. Colostomy , for example, is a surgical procedure that involves the creation of a stoma in the large intestine to enable the removal of excrement through drainage. In this way, the use of the rectum is avoided.
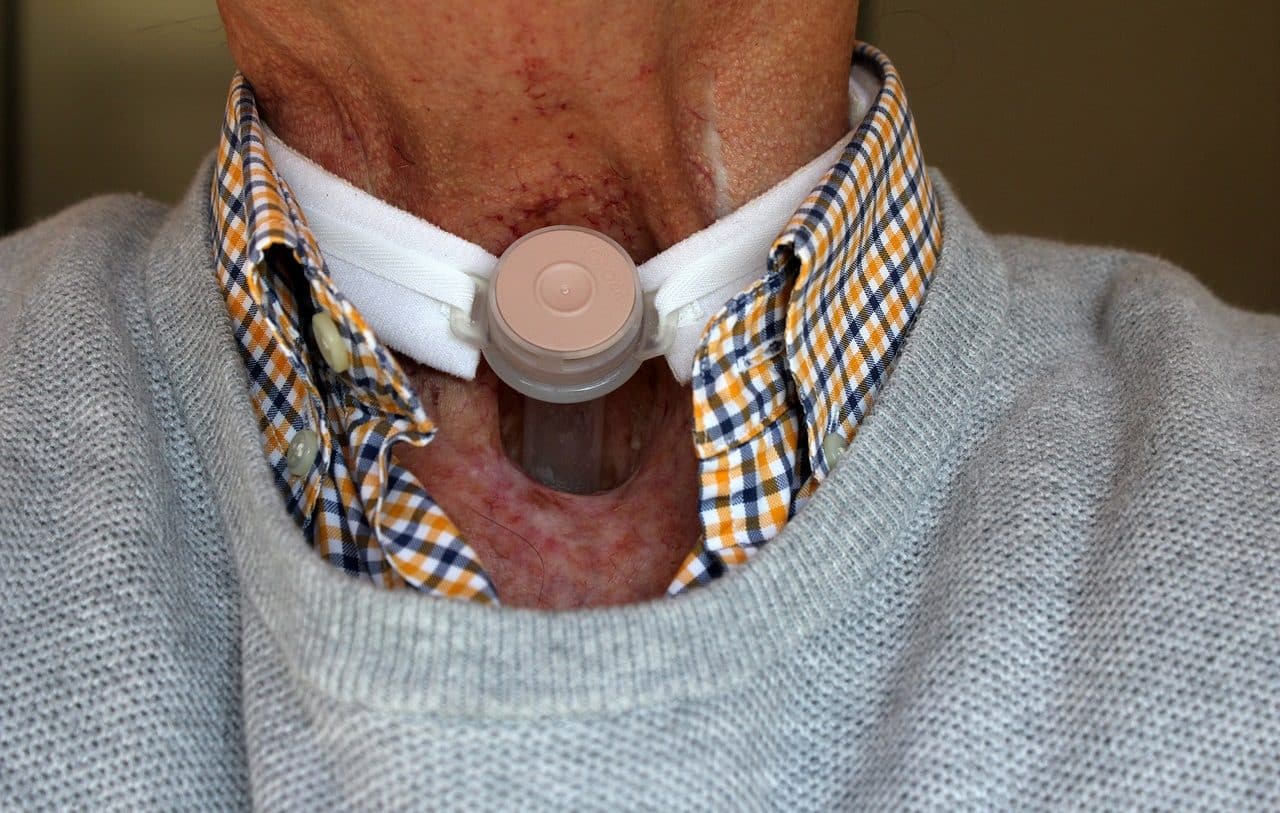
Tracheostomy also involves the development of a stoma, in this case in the trachea. By making an opening in the neck area, a tube can be inserted to extract lung secretions and provide an airway. When the tracheostomy is temporary, the hole is then closed, although there are individuals who need the stoma in question permanently and for life.
It is important to note that stomas can experience complications and cause various health disorders. Abscesses , infections , hemorrhages and fistulas are some of them.
A stoma can even become blocked and lead to ischemia or even necrosis . In all cases, it is very important that a doctor monitors the patient's evolution for the prevention and eventual treatment of these problems.

In botany, the occlusive cells that delimit an ostiole form a stoma.
Resource for urine elimination
In the same way, we cannot ignore the existence of what is known as a urinary stoma . It is an opening made in the abdominal wall so that urine can be eliminated through it. This is something that can be done in two different ways: with a system composed of a disc and bag in a single unit or with a system where both elements are independent of each other.
People who have this type of stoma need to comply with a series of recommendations for their health. We are referring to advice such as drinking between 1.5 and 2 liters of water daily; that they do not gain considerable weight, that they avoid drinking carbonated drinks (soda) and that they include both natural infusions and yogurts in their diet.
They are also recommended to maintain good hygiene, avoid wearing clothing that is too tight, and not practice contact sports that could damage their stoma.

Stomata fulfill very important functions in plants.
Stoma in botany
For botany , the stoma is a small opening found in the epidermis of plants. This hole present in leaves or organs allows the specimen to exchange fluids and gases with the external environment.
Stomata, in this sense, are specialized epidermal cells found in the green sectors of plants . Each stoma is formed by the union of two occlusive cells, which leave a pore between them. Since the size of the cells can be regulated, the size of the opening is also regulated, which may appear surrounded by cells that have another type of morphology.
It should be noted that the stomata are not found in the root . In areas that do not have chlorophyll, there may be stomata, although without functionality. On the other hand, those parasitic species that lack chlorophyll do not have stomata either.
Its operation
Stomata make possible the gas exchange of CO2 (carbon dioxide) and O2 (oxygen) that plants use in cellular respiration and photosynthesis . Likewise, the stomata allow plant transpiration .
It is interesting to mention that stomatal opening and closing are carried out depending on various environmental factors such as humidity , sunlight and the level of carbon dioxide. Calcium and potassium , among other substances, play an active role in boosting the process.
Stomatal composition
As we already indicated, each of the stomata is composed of two specialized cells ( occlusive cells ), which have a pore (the ostiole ) between them. In some cases, there are attached, subsidiary or annexed cells that are functionally associated with the occlusive cells.
The ostiole, on the other hand, leads to the substomatal chamber . This substomatic space serves to communicate the system formed by the intercellular sectors with the external environment. If the stomata are organized in a row, the chambers maintain a connection with each other.
