
Isaac Newton's research focused on light linked to the sun gave impetus to a technique called astronomical spectroscopy.
Spectroscopy is the name that identifies, within the field of Physics , the discipline that is responsible for studying the various types of spectra . Those who specialize in it focus their attention on the interaction that involves both matter and electromagnetic radiation , taking into account its generation or absorption at a certain wavelength .
In this framework, three situations are distinguished, two of which involve photons . This is what happens with the resonant emission or capture of electromagnetic radiation by matter, as well as with the elastic collision , where the propulsion of photons undergoes a single change (as a reference it is possible to mention X-rays and diffractions of neutrons and electrons ). As an example of a collision classified as inelastic (which fails to conserve kinetic energy ), it is possible to point to a technique applied in Physics and Chemistry that is called Raman spectroscopy .
The theory positions it as a tool that serves to explore how much light an object can give off, absorb or reflect.
Spectroscopy classes
The list that brings together all types of spectroscopy is very extensive.
To simplify the understanding and listing of varieties, below we will group them according to the process they have in common.
The absorption -focused set, for example, draws on differential absorption spectroscopy (DOAS) . It is a modern procedure with innovative technology useful for, among other issues, monitoring particles and gases in the atmosphere that impact air quality and climate.
Atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS) , valid for quantifying metals by establishing the concentration level of these elements, is another option, but there are still others to be described. Specialists in the subject have also found how to take advantage of the advantages of infrared absorption spectroscopy with Fourier transform in order to achieve an infrared spectrum of emission or absorption of gases, liquids or solids. This group is completed with two more alternatives: electron absorption spectroscopy and one called neutron absorption spectroscopy .
About seven modalities appear in the list that specifically refers to resonance . Here coexist, among others, nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy suitable for examining a molecular structure and for the development of thermodynamic analyzes and kinetic studies; the surface plasmon resonance spectroscopy chosen when examining modified nanomaterials and the effective electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) spectroscopy when it is intended to detect, managing a considerable thermal range, flaws in certain materials and proceed to the study of paramagnetic species, since whether transitory or stable in essence.
If we delve deeper into other categories , X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy and techniques such as acoustic impedance spectroscopy or the multitudinous versions linked to emission gain visibility. This last record is fed, to indicate a couple of procedures, by fermion emission spectroscopy and backscattered electron emission spectroscopy , without forgetting optical emission spectroscopy (OES) or W and Z emission spectroscopy . bosons .
The rainbow serves as an example of the refraction phenomenon linked to the visible spectrum (that is, to the part of the electromagnetic spectrum perceived by the eyes of human beings).
Practical applications
Spectroscopy has practical applications in ecology and the environment , to specify one possibility, because it facilitates the discovery of contaminating products in soils reserved for agriculture.
In the field of Medicine , however, a non-invasive diagnostic method called infrared spectroscopy is used to measure blood flow, identify ischemia events, etc. Similarly, impedance spectroscopy allows us to establish, in a wide range of frequencies, what the electrical response linked to certain biological tissues is like.
Nor should we overlook the great relevance it has within Chemistry , specifically to promote a chemical analysis and determine the conformation and electronic structure of a system, both molecular and atomic.
Spectroscopy is present, even, in the field of Astronomy , a framework in which we go in search of extrasolar planets through Doppler spectroscopy and in Biology , associated with analysis of metabolic issues and biomolecules.
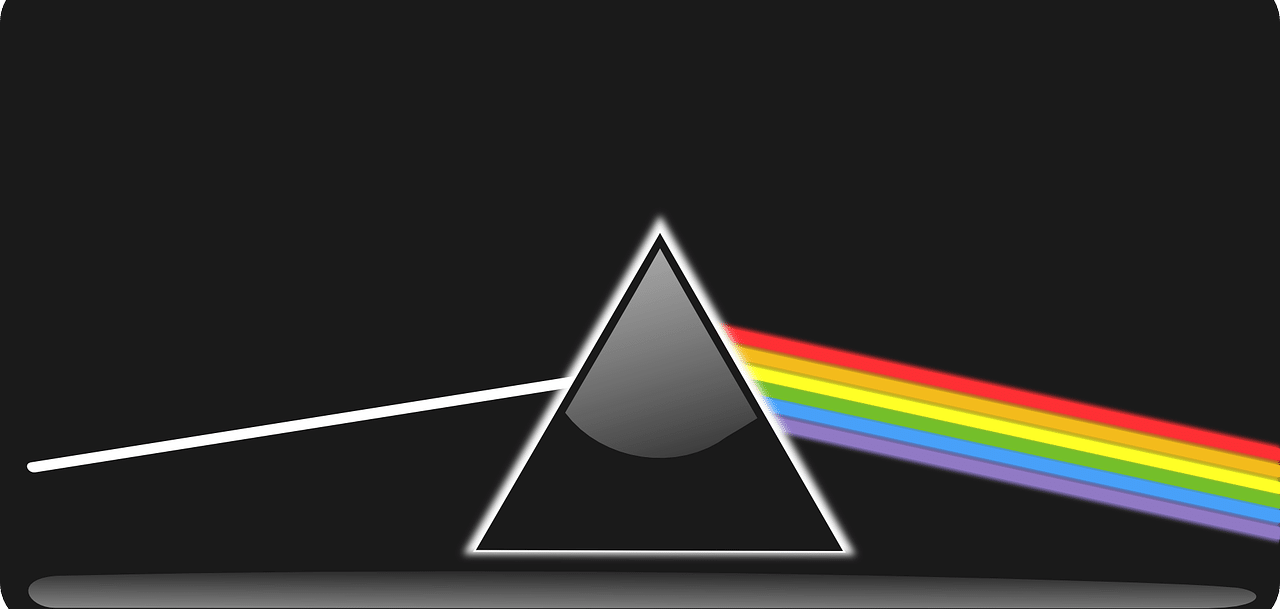
A prism, generally with the appearance of a triangle, has the ability to reflect, produce refraction and generate the decomposition of light, giving rise to the colors of the rainbow.
Concepts related to spectroscopy
It is interesting to know the meaning of different concepts related to spectroscopy to learn more about the subject.
For this reason, on this occasion we will indicate that a spectrometer , a device named equally as a spectroscope and a spectrograph , is intended for the study of the frequency spectrum typical of wave movements.
Using a diffraction grating or a prism , meanwhile, optical equipment identified as a monochromator is capable of segmenting the colors that make up light and giving each one its own space.
The expression visible spectrum , finally, refers to the fringe belonging to the electromagnetic spectrum that can be detected and appreciated by human vision.
