Radiometry is the discipline that analyzes the measurement of radiation in the electromagnetic spectrum.
The electromagnetic spectrum is the range that covers all electromagnetic waves . This is the set formed by all radiation, from those with the shortest wavelength to those with the longest wavelength.
The notion of electromagnetic spectrum can also refer to the electromagnetic radiation emitted or absorbed by a substance . This radiation, which includes an emission spectrum and an absorption spectrum , is specific and allows the identification of the element in question.
Before moving forward with the analysis of the concept, it is important to focus on the two terms that make it up. In the field of physics , the distribution of the intensity of a radiation, considering a certain magnitude , is called a spectrum . The adjective electromagnetic , meanwhile, refers to electromagnetism : the interaction established by magnetic and electric fields.
Characteristics of the electromagnetic spectrum
The electromagnetic spectrum is, in theory, infinite . However, it is usually considered to range from the Planck length (a longitudinal scale that indicates that, below it, the current models of physics do not correspond since space does not respond to classical geometry ) to the limit of the observable universe . .
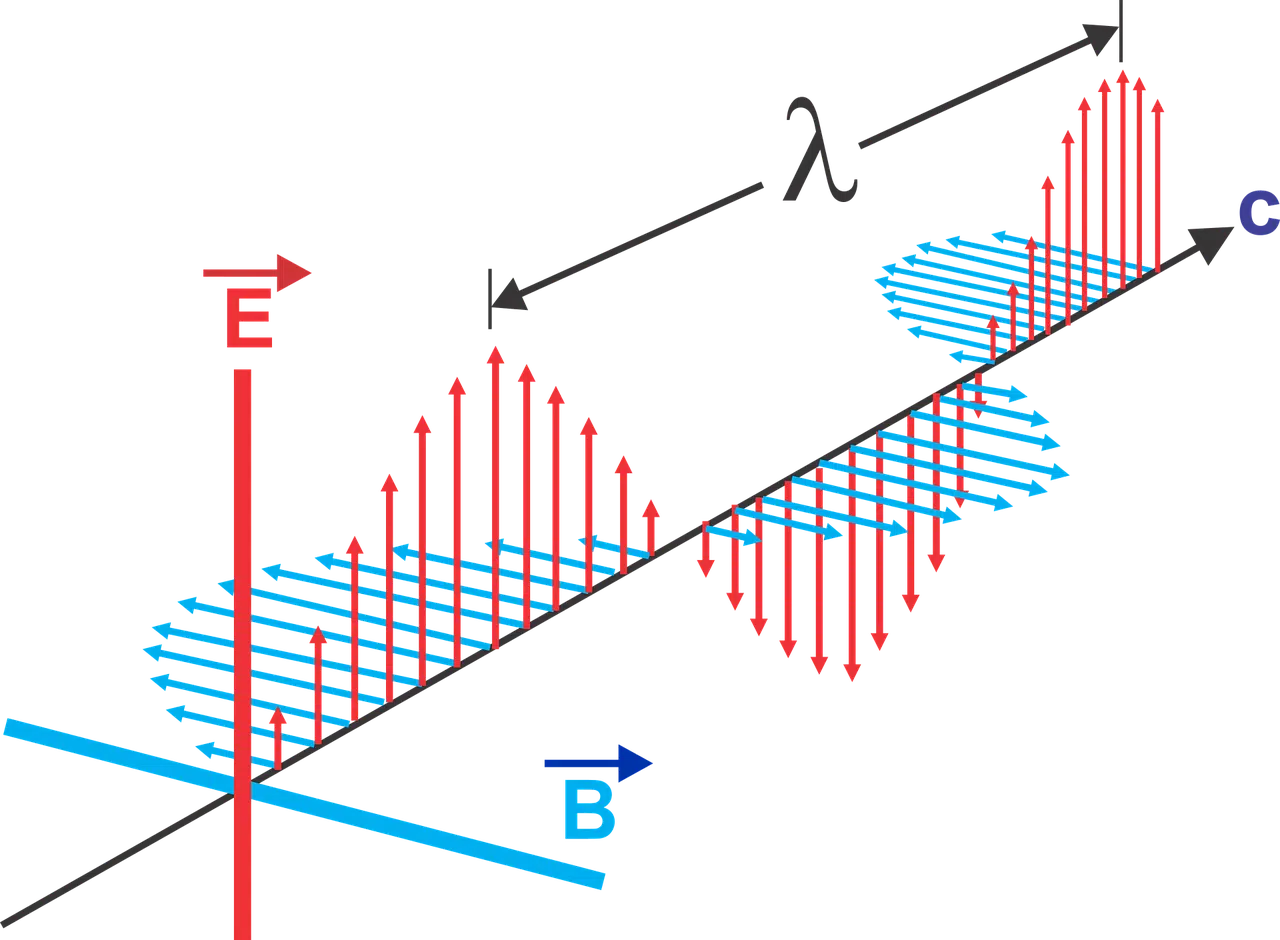
An electromagnetic wave is understood as the vibration of the magnetic and electric field that transports energy. Photons are the carrier particles of all forms of radiation of this class.
Low- frequency waves have a low amount of energy and long wavelengths. On the contrary, high frequency waves contain a lot of energy and short wavelengths.
The various electromagnetic radiations behave according to their wavelength , although there are other variables that have an impact. When interacting with specific molecules or atoms, the behavior is also associated with the energy level.

An optical spectrometer is a device that measures the properties of light in a given region of the electromagnetic spectrum.
The bands
In order to facilitate its study, the electromagnetic spectrum is segmented into bands or regions . In any case, there are waves that, due to their different uses, can be included in two bands.
The boundaries of the bands of the electromagnetic spectrum are not exactly fixed: superposition is therefore possible. What differentiates each band from the others is how the waves behave in emission , absorption and transmission and in the type of use that can be given to them.
The most common classification, in this way, is made taking into account the length of the waves . From shortest to longest length, the electromagnetic spectrum is made up of gamma rays , X-rays , ultraviolet radiation , visible light , infrared radiation , microwaves and radio waves (radiofrequency).
In the case of radio waves, we can also distinguish between extremely high frequency waves , extremely high frequency waves , superhigh frequency waves , ultrahigh frequency waves , very high frequency waves , short or high frequency waves , medium or medium frequency waves , long or low frequency waves , very low frequency waves , ultra-low frequency waves , super low frequency waves , extremely low frequency waves and tremendously low frequency waves .

Wi-Fi works with the radio frequency of the electromagnetic spectrum.
Gamma rays, X-rays and ultraviolet rays in the electromagnetic spectrum
Gamma rays occupy the shortest wavelength band in the electromagnetic spectrum. This radiation is produced in subatomic processes, in astrophysical phenomena or through the intervention of radioactive elements.
Due to their large amount of energy, these rays can deeply penetrate matter, damaging the cell nucleus. That is why gamma radiation is used for the sterilization of medical equipment and food. It is also used to carry out some nuclear medicine studies and treatments.
X-rays follow gamma rays in the electromagnetic spectrum. They can achieve the impression of a photographic film and pass through an opaque body: the higher the voltage, the lower the density and the lower the atomic number, the greater the penetration capacity.
X-rays and crystallography use X-rays. This radiation, from the transmission and absorption of X-rays, is also used to discover if structural elements have defects.
Moving upward in terms of wavelength, ultraviolet rays appear alongside X-rays in the electromagnetic spectrum. This radiation is emitted by the sun ( solar radiation ), although there are also artificial sources.
Ultraviolet rays are applied to sterilize food and water as they allow the elimination of fungi, viruses and bacteria. Fluorescent lamps also use this radiation.
It must be considered that all these types of radiation carry risks for humans . Depending on the degree of exposure, they can cause cancer and other diseases.
visible light
Visible light is that radiation that the human eye can perceive. This area of the electromagnetic spectrum, then, is known as the visible spectrum .
Although there is no precise limitation, the visible spectrum is generally considered to include waves with lengths between 380 and 750 nanometers ; However, some individuals can perceive waves with lengths between 310 and 1050 nm .
It should be noted that visible light is considered according to human vision. Birds and insects, for example, are able to see ultraviolet radiation, something that humans cannot do.
The longest wavelength regions in the electromagnetic spectrum
Infrared radiation , microwaves , and radio waves are the longest wavelength regions in the electromagnetic spectrum.
Infrared rays are applied in the operation of remote controls (also called remote controls), in fiber optics and in thermography, for example. Microwaves , for their part, are used in mobile or cell phone antennas, in Bluetooth wireless transmission and in ovens. As for radiofrequency , it is used in television and radio transmissions, in nuclear magnetic resonances, in radars and in medical and aesthetic treatments.
