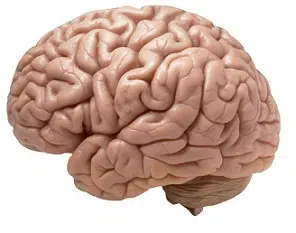
 The Greek word enkephalos derived from the scientific Latin encephalos , which in turn came to our language as encephalus . This is the name given to the group of organs that are found inside the skull and are part of the central nervous system of vertebrate animals .
The Greek word enkephalos derived from the scientific Latin encephalos , which in turn came to our language as encephalus . This is the name given to the group of organs that are found inside the skull and are part of the central nervous system of vertebrate animals .
The skull is a structure of bones in whose cavity the brain is located. The protection conferred by this bone sector is very important for life, since the brain directs most of the activities and actions essential for a human being.
The main part of the brain corresponds to the cerebrum , which is divided into lobes. This organ is responsible for controlling the nervous system and is subdivided into the forebrain or forebrain ; midbrain or midbrain ; and hindbrain or hindbrain .
These three vesicles begin to develop from the embryo 's four weeks of life, when the neural tube has closed and the neural crest has formed. Let's see below a detailed description of each of them and their respective parts. Let's start with the forebrain, in which we find the telencephalon and the diencephalon. It is the largest part of the brain, and when observing it we can notice the right and left hemispheres.
The telencephalon is subdivided into a striatum, a rhinencephalon and a cerebral cortex, in which the following lobes are found: the occipital, the parietal, the temporal and the frontal, which cover such fundamental functions of our body as language. , vision, organs of movement, hearing, smell and perception, among others. In particular, the frontal, parietal and temporal are in charge of learning, without which we could not develop and survive.
In the diencephalon we find the epithalamus, within which is the gland that produces melatonin , a hormone of great importance. There is also the thalamus, where sensations are controlled, the subthalamus, a structure that is linked to motor functions, and the hypothalamus , the center that regulates emotions and physical control, in addition to secreting the hormones oxytocin and vasopressin.
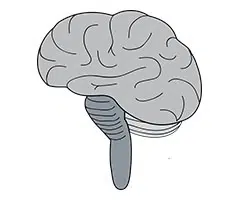 With respect to the midbrain, we can say that it has four tubercles that are related to vision (the two anterior ones) and hearing (the two posterior ones). In addition, it is responsible for filtering the data that passes between the hindbrain and the forebrain.
With respect to the midbrain, we can say that it has four tubercles that are related to vision (the two anterior ones) and hearing (the two posterior ones). In addition, it is responsible for filtering the data that passes between the hindbrain and the forebrain.
Finally comes the hindbrain, a portion found around the fourth ventricle of the brain and is formed by the myelencephalon and the metencephalon. It is located on the spinal cord and is made up of three parts: the medulla, the pons and the cerebellum.
In turn, in the metencephalon we have the cerebellum , which allows the integration of motor pathways and sensory pathways, and is responsible for controlling movement, posture and muscle energy. Returning to the myelencephalon, there we can see the medulla oblongata (also known as the medulla oblongata ), which controls some essential functions, such as breathing and blood circulation through the heart.
Since the medulla oblongata is an extension of the spinal cord , it is correct to say that it enables communication between it and the brain.
Problems in the brain can cause all kinds of disorders and even death. Body control, memory and intelligence depend on the brain, so damage to this set of organs has serious consequences.
Schizophrenia , Parkinson's disease , Alzheimer's disease and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis are some pathologies that affect the brain. In addition, there are bacteria and viruses that, by generating an infection , alter its functioning.
