 Embryo is a term that derives from the Latin word émbryon . The concept refers to the living being that is in the initial stages of its development .
Embryo is a term that derives from the Latin word émbryon . The concept refers to the living being that is in the initial stages of its development .
The idea of embryo, therefore, refers to the period that begins with fertilization and reaches the stage in which the being reaches the morphological characteristics that distinguish its species. In the case of humans, the embryo arises with conception and persists until the end of the third month of pregnancy , when it becomes known as a fetus .
Continuing with our species, it is worth remembering that conception occurs when a sperm (male gamete) manages to fertilize an egg (female gamete), forming a zygote that combines the deoxyribonucleic acid ( DNA ) of the two parents. This zygote, in its development, is called an embryo until the third month of gestation. Then it becomes a fetus until the moment of delivery , when the already gestated baby leaves the mother's womb and begins its independent life.
The natural way for the creation of an embryo is through a sexual relationship between a man and a woman: when the man deposits his semen in the woman's vagina, a sperm can fertilize an egg and thus lead to conception. In any case, there are assisted reproduction techniques that allow embryos to be created through different processes (such as artificial insemination and in vitro fertilization ).
After about thirty hours from the moment of conception , the cells of the zygote begin to go through a division process through progressive multiplication, so that many can be formed in one go, in stages in which the previous number is doubled. (two, four, eight, etc.). Once the zygote has become an embryo, a phenomenon that takes place between the first four and seven days after fertilization, it settles into the wall of the uterus.
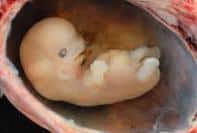
Once the embryo reaches the fourth week of its development, its extension is usually around five centimeters and it enters the wall of the uterus to begin feeding. However, the formation of all your organs and the systems you need to survive in the future, such as the brain, spinal cord and heart, do not begin until the fifth week of pregnancy.
 Some time later, when the placenta begins to form, the embryo is located in the center of the uterus and remains suspended in the fluid of the amniotic sac . Some of its most characteristic features, such as feet, hands, eyes and face, begin to form from the sixth week.
Some time later, when the placenta begins to form, the embryo is located in the center of the uterus and remains suspended in the fluid of the amniotic sac . Some of its most characteristic features, such as feet, hands, eyes and face, begin to form from the sixth week.
When the ninth week arrives, the embryo already has well-defined limbs, as well as a large part of its fundamental organs. About seven days later, the stage of embryonic development ends to give rise to that of the fetus.
Beyond human beings and animal species, the notion of embryo is also used in phanerogamous plants (to refer to the material housed in a seed that allows a future plant to develop). The embryo is made up of the radicle that goes to the micropyle, the hypocotyl (a small shoot), the cotyledons (the leaves that first appear) and the plumule (also known as gemula , and is the cauline apex).
In colloquial language, finally, the beginning of a thing that has not yet been developed is called an embryo. This can apply to a project that is just seeing the light of day and will take a long time to complete.
