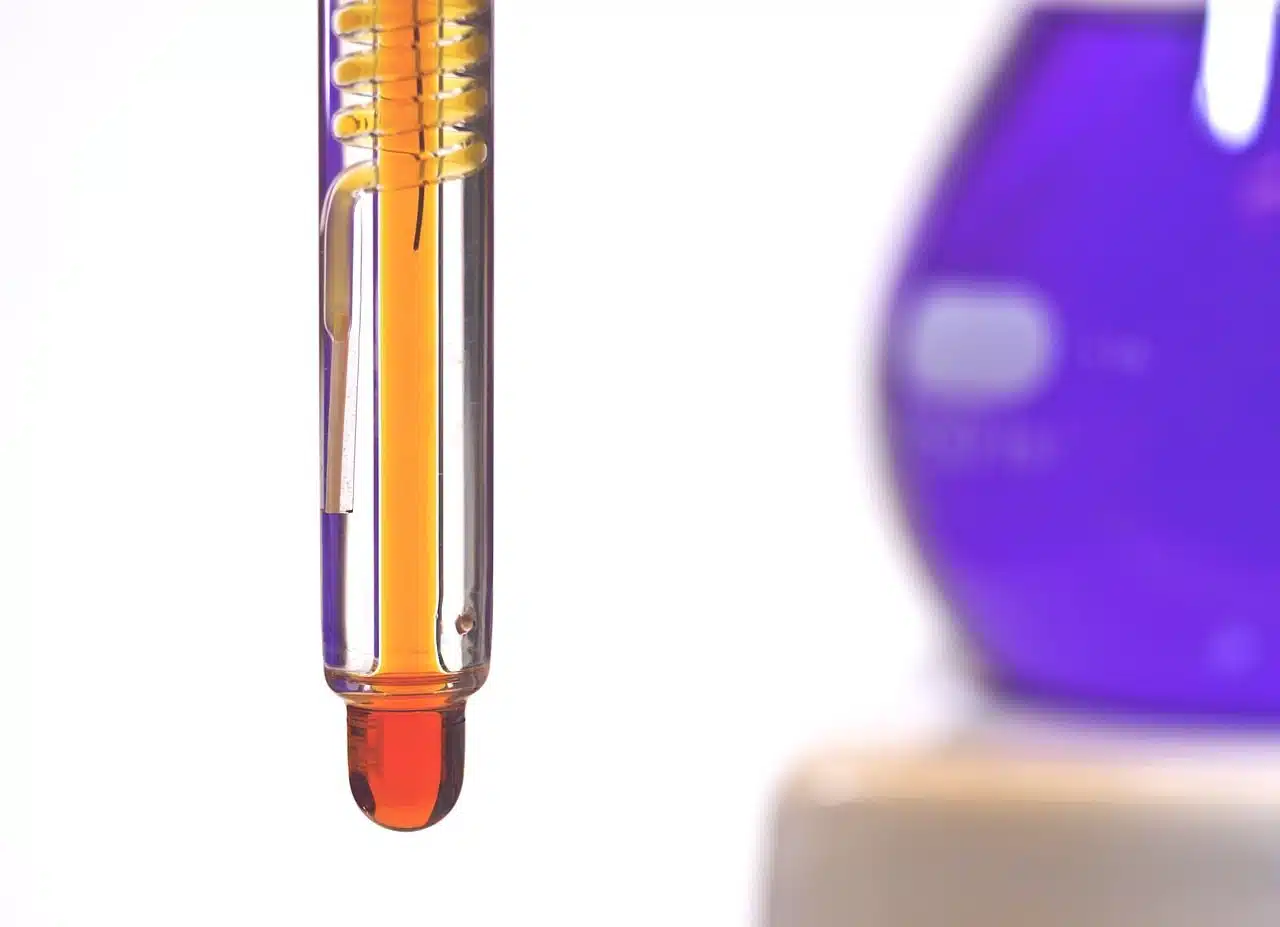
By taking advantage of water from the sea and subjecting it to a combined process of electrolysis and desalination, it is possible to generate green hydrogen.
Electrolysis is the name of a process through which, through the application of electricity , the elements of different chemical compounds are separated. Through the use of electric current, chemical experts maintain, substances in solution can be broken down into ions .
The multifaceted Englishman William Nicholson , the story goes, was analyzing how batteries worked when he accidentally discovered electrolysis . Decades later, his colleague Michael Faraday , who was especially interested in the fields of electrochemistry and electromagnetism , gave substance to what were called, in his honor, Faraday's laws of electrolysis .
These postulates are used to work and find out data about electrodes , electric charge , direct current and molar mass . In this framework, it is enriching to know that, according to Faraday's law of electrolysis positioned first, there is a directly proportional relationship between the mass corresponding to an electric charge that has been deposited on an electrode as a result of electrolysis and the amount of electrical charge ( electricity ) that has been transferred to said electrode . The second of these Faraday principles , meanwhile, refers to how, in a certain electrical charge , the mass of a certain chemical species that is deposited on an electrode corresponds directly to the equivalent weight possessed by the element in question.
When reviewing the beginnings of electrolysis and its evolution over time, one cannot fail to point out that valuable contributions to this topic were also made by the scientists Martin van Marum (who implemented the electrolysis procedure without being aware of it), William Nicholson and Anthony Carlisle (who experimented with an electric current in water), Humphry Davy , William Thomas Brande and Paul Héroult , among others.
Types of electrolysis
There is a wide range of types of electrolysis and an extensive field of applications.
It is possible to carry out an electrolysis of water (using a direct current and without joining the electrodes ) and to carry out an electrolysis of molten sodium chloride (useful to obtain gaseous chlorine and metallic sodium ), to name two alternatives as a way of reference.
Proton polymer membrane electrolysis , solid oxide electrolysis , and anion exchange membrane electrolysis are other varieties to consider.
It is worth highlighting that this phenomenon, which involves a transfer of electrons that involves an anode and a cathode, allows chemical energy to be obtained thanks to the transformation of electrical energy . It is essential to produce, for example, green hydrogen , of an ecological and sustainable nature that can be generated based on a renewable energy source and water (it has even been experimented with seawater ). The electrolysis process also serves to obtain a natural solution with disinfectant power and is used in the area of electrometallurgy in order to isolate the metal in its pure state into compounds.

By applying electricity as part of the process known as electrolysis, the elements that make up a chemical compound are separated.
Components and stages of the procedure
To fully understand what electrolysis consists of, what particularities the process has and its practical usefulness, you must first master key concepts, know the components involved and distinguish which and how the stages of the procedure are.
It is necessary, at this point, to learn about electrolytic cell , reduction potential , electrical conductivity and chemical reaction , among many other notions.
The phenomenon begins using a pair of electrodes so that, by connecting them to an electrical power source and immersing them in a solution, a direct current can be applied. Each electrode involved, the theory describes, manages to attract ions of opposite charge . Thus, then, the anions end up moving towards where the cathode is located (where a reduction reaction occurs) and the cations go towards the anode (where the oxidation reaction takes place). New substances emerge from the transfer of electrons as part of this process.
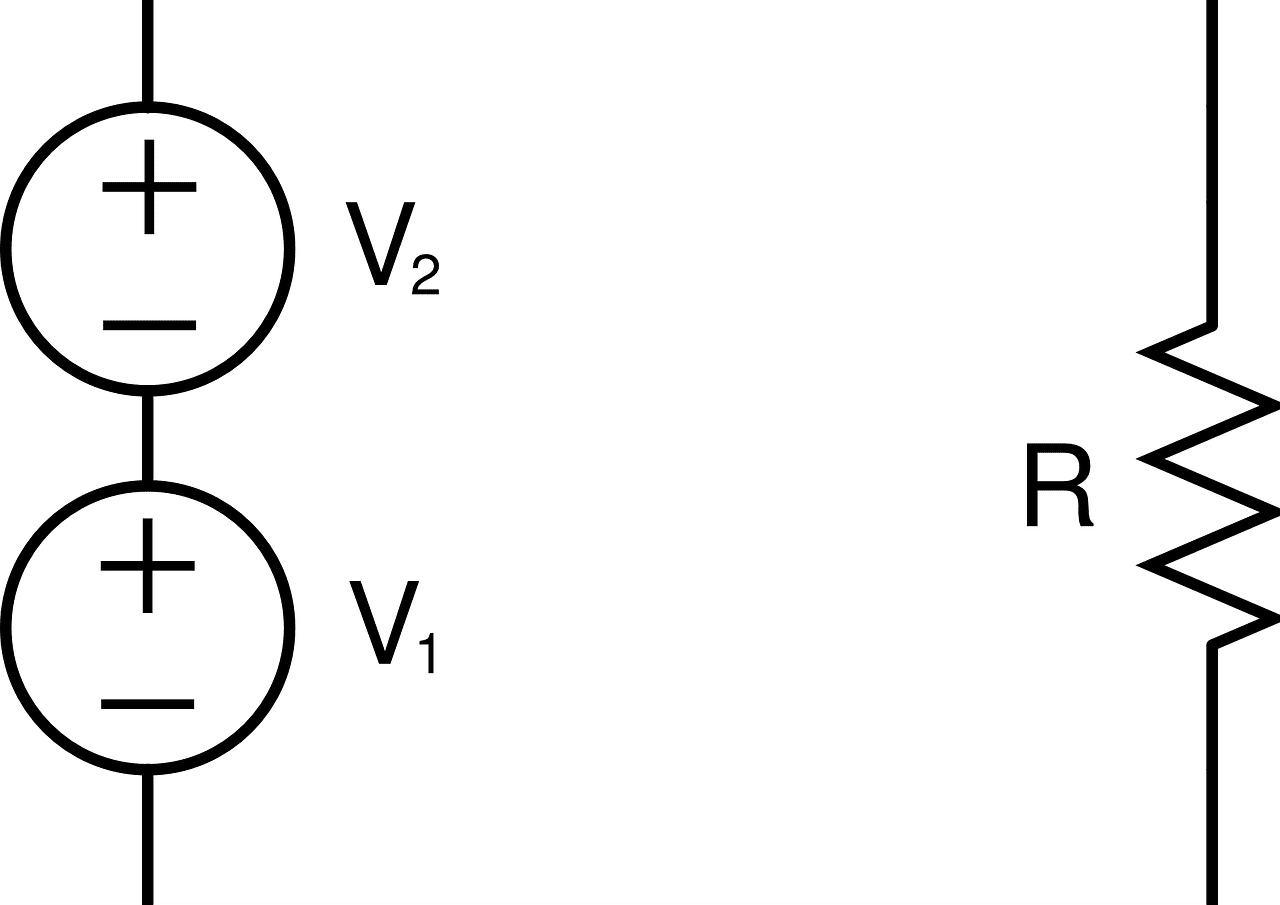
In batteries (or electrochemical cells) the production of a current of electricity occurs through a chemical reaction.
Advances and challenges in electrolysis
Scientific work, research and technological progress have allowed great advances, but there are still some pending challenges in terms of electrolysis .
It would be more convenient, for example, not to have to allocate a large amount of energy (and money) to supply the electrolyzers and for the hydrogen that can be produced through this method not to have such a high price.
These are achievements worth celebrating and taking advantage of, in any case, the generation of the aforementioned green hydrogen and the use of this process to eliminate lead and graphene from water (either in pursuit of the purification of drinking water or in the treatment of water). residuals ).
There is also a commitment and growing interest on an international scale to begin to create, through electrolysis , "green steel" , a product whose manufacturing style would mark a before and after in the field of steelmaking .
Taking into consideration the environmental impact related to this process, contemplating the opportunities that open up with this technique that contributes to sustainability and the continuous evolution of science, electrolysis will surely continue to expand its fields of application and will be increasingly used better. short and medium term.
