
The electrocardiogram and other common studies are based on electrophysiology
The scientific discipline dedicated to the analysis of electrical phenomena in people and animals is called electrophysiology . The concept is formed with the compositional element electro- (which refers to electrical or electricity) and the noun physiology (the specialty focused on the functions of living beings).
a branch of medicine
Electrophysiology, in this way, studies the electrical properties of cells . It is usually considered a branch of medicine that is oriented toward bioelectric processes.
Many times when talking about electrophysiology, cardiac electrophysiology is specifically referred to, an area of cardiology (the study of the heart). It is important to mention that the heartbeat is stimulated through electrical signals that occur in the myocardium.
The nodules (specialized cells found in the right atrium) are responsible for emitting electrical impulses. These impulses cause the atria to contract so that blood passes to the ventricles, and then they cause the ventricles to contract, with which the blood is expelled to the rest of the body. Cardiac electrophysiology, in this framework, investigates the intervention of electricity in the entire process.
Experts in cardiac electrophysiology can diagnose and treat electrical disorders of the heart , which often lead to arrhythmias , bradycardias , or tachycardias . The so-called electrophysiological studies allow us to see how the heart works at an electrical level.
classic technique
The development of an electrophysiological study consists of the introduction of catheters that are directed to the heart to record, from inside the organ , the electrical activity.
Electrodes must then be placed on different parts of the tissue to measure the flow of ions. With one whose size is measured in micrometers it is possible to treat a single cell, to study its electrical activity in particular. Of course, this invasion has an impact on the reduction of your life .
Optical electrophysiology
While through the so-called classic electrophysiology techniques it is possible to observe the electrical activity of a single point of the entire tissue, that is, they reduce a phenomenon that is distributed over a surface to a tiny space, optical techniques allow for more monitoring. broad and therefore precise. The thing is that the engineers and scientists who designed them pursued this specific objective.
To do this, it was necessary to develop molecules that could emit light according to their environment, that is, whether it was chemical or electrical. This can be seen in other concepts of similar flexibility, such as fluorescent proteins and voltage-sensitive staining . Once the compounds are introduced into the tissue (a step that is achieved through gene expression, injection or perfusion), the distribution of electrical activity can be observed and recorded, which occurs in one or two dimensions. .
Optical electrophysiology allows several different types of readings, each focused on a part of the body, and many of them are part of the most common clinical studies. The electrocardiogram, electroencephalography, electromyography and electrooculogram are four of the most common.
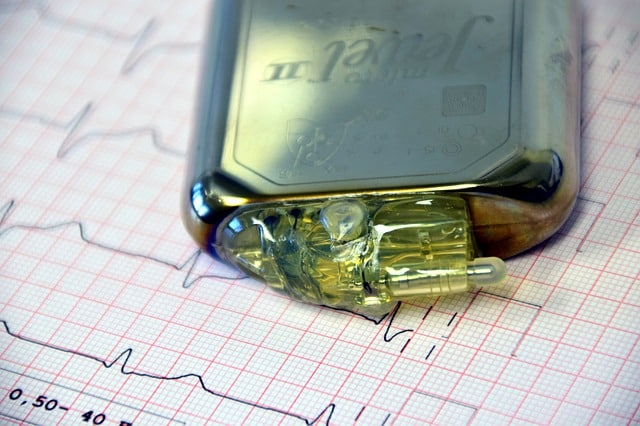
Some electrical heart problems require the use of a pacemaker.
Pacemaker
Sometimes, the indicated treatment for an electrical problem of the heart consists of the installation of a pacemaker : a device that can generate electrical impulses and thus stimulate or regulate the heart rhythm.
Throughout its history, the pacemaker has come a long way and has become very reliable. Experiments in this field began at the end of the 19th century , and millions of lives have been saved thanks to this invention. Some of its specific functions, in addition to those already mentioned, are synchronization, prevention of rhythm problems, monitoring of rhythmic alterations and improving heart pumping.
