The Metal Age was the successor to the Stone Age and was made up of the Copper Age, the Bronze Age and the Iron Age.
The Age of Metals is the name for an extensive period during which humanity discovered and used iron and copper, for example. Metallurgy played a key role during that era that unfolded after the decline of the Stone Age .
The first phase of the Metal Age was known as the Copper Age , while the second stage was called the Bronze Age . The Iron Age completed that instance that, for those in charge of locating it in years and geographical spaces, began when the mastery, treatment and use of metals evolved (in this regard, there are records of hammered metals that date back to the Neolithic ), giving space to smelting , an ancient metallurgical process that became possible thanks to the discovery of fire . The panorama of that time, as it has been reconstructed, was marked by the customs, beliefs and activities of sedentary societies that found their main means of subsistence in agriculture .
Experts associate the period that inspires the content of this article with the discovery and positioning of minerals that have been opening paths and optimizing work performance and efficiency in numerous areas. Copper , bronze and iron , in this context, served to make increasingly better metal artifacts , agricultural tools, metal shields and weapons , for example.
Metal Age Segmentation
The segmentation of the Age of Metals , as we indicated above, includes three parts. It should be noted that the advance of these eras was not simultaneous in all the communities that inhabited the Earth before the emergence of writing , hence the need to analyze each continent, town or geographical region in particular.
In general terms, it is established that with the Copper Age, the Neolithic was left behind and an era of prehistory began during which there was experimentation with foundry , ceramics were worked, interest in metallurgy and Efforts were concentrated on the development of alloys .
Over time, using an alloy of tin and copper as a resource, the Bronze Age had its moment of splendor. Particularly this period was subdivided into Ancient or Early Bronze , Full or Middle Bronze and Late or Final Bronze .
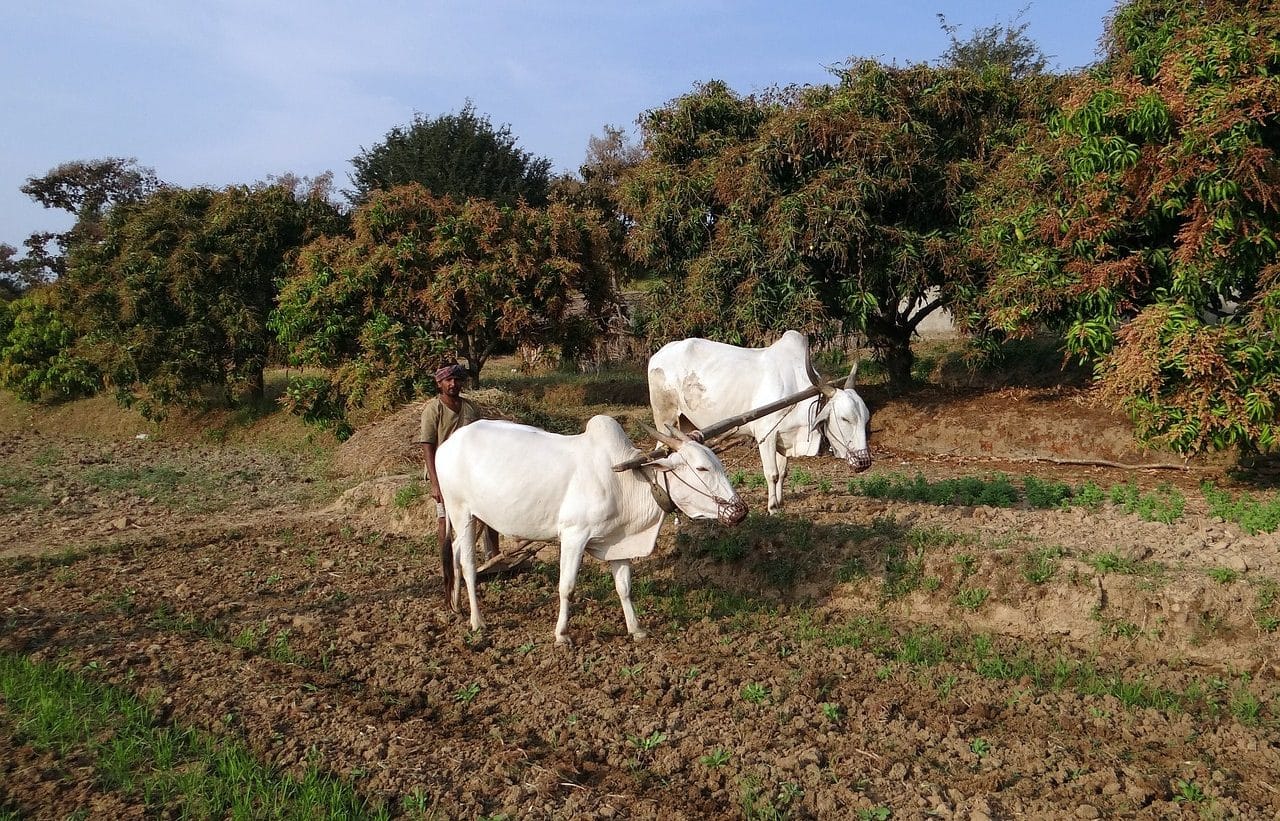

The ancient farmers began the method of plowing pulled by animals, but this practice began to be fought by those who fight for respect for all species since they are against using animals as labor force.
Finally, within the Age of Metals, the Iron Age is distinguished, which when studied reveals a series of transformations that transcended the simple fact of taking advantage of iron and obtaining benefits based on it. The culture, beliefs and organization or structure of the populations were modified on an international scale through invasions, fortifications, uprisings, military power and the implementation of artisanal techniques in the agricultural sector, for example.
Discoveries and innovations
Humanity made outstanding discoveries and valuable innovations throughout the Age of Metals that logically translated into a wide variety of improvements.
With the wheel and boats first armed with logs and perfected with a kind of sail, the field of transportation was revolutionized, while the implementation of techniques and the use of increasingly resistant materials benefited the construction industry. The architecture of those times ranged from private homes to temples and environments reserved for food storage .
Nor can we ignore the phenomenon called megalithism , a process that extended until approximately the Bronze Age . Megaliths, monuments designed with enormous pieces of stone, survived the Neolithic and reached the Age of Metals , they are the symbol of this practice that originated, among other works, tombs .
In this era, many people dedicated to agriculture adopted the method of plowing pulled by different species of animals and, with the purpose of generating environments conducive to considerable levels of harvest, optimizing time and tasks, irrigation canals were built.
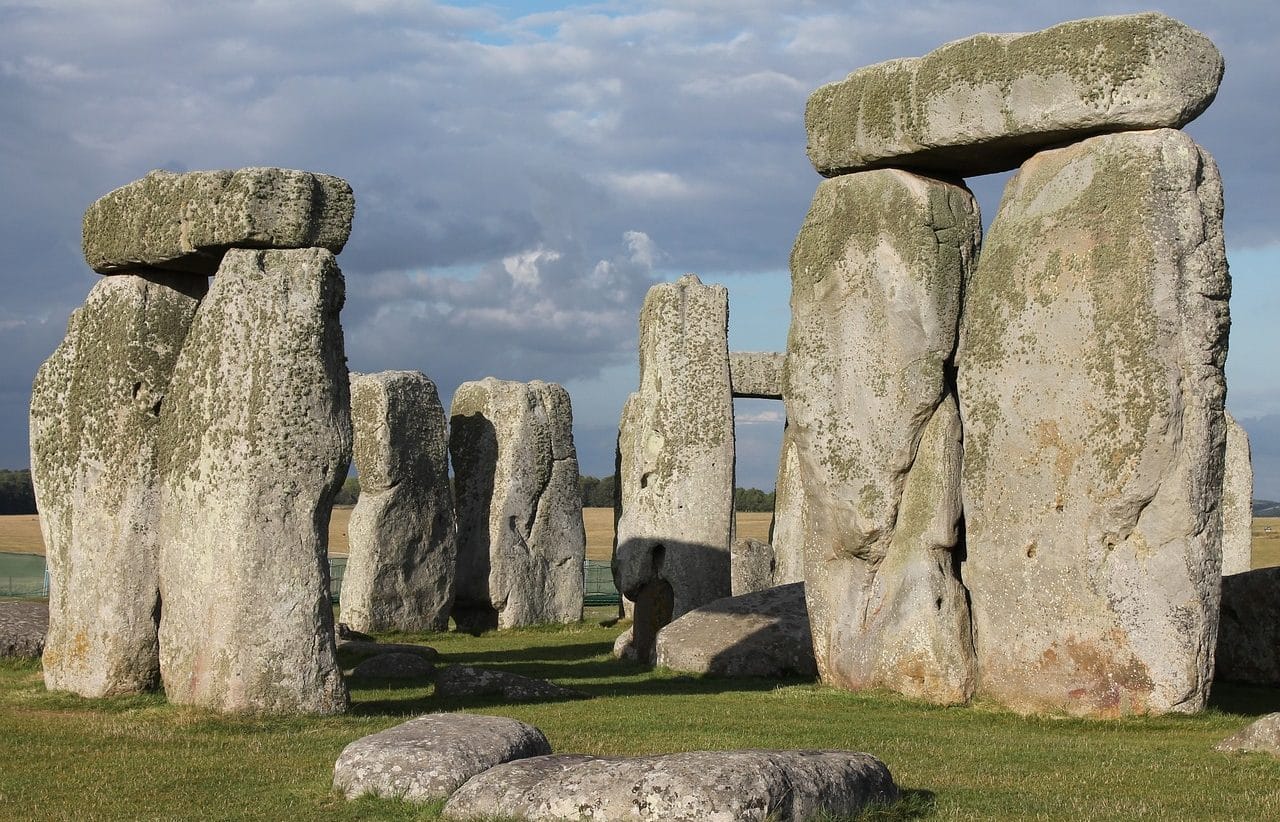

In prehistory, monuments, known as megaliths, were erected based on gigantic blocks of stone.
Current approaches to the Age of Metals
Current approaches to the Age of Metals depend exclusively on research, archaeological excavations, fossil studies and ancient history exhibitions.
Specialized bibliography, newspaper articles focused on scientific findings, and presentations by historians invite you to travel back in time to find out how prehistoric people lived, worked, conceived of life, and cultivated their faith.
With the help of archaeology, it has been possible to identify everything from the oldest house discovered to date in Athens (a construction that is estimated to date back to the Iron Age ) to the remains of a colossal door installed in Israel during the early phase. from the Bronze Age .
Explorations that took place in the Iberian Peninsula have allowed us to establish that, in the Copper Age , the leadership of certain exponents of the female gender was recognized. This conclusion arose from appreciating the characteristics of a megalithic tomb found in Seville where, in a setting of luxury and sophistication, the remains of a woman whom specialists nicknamed "the lady (or lady) of ivory" were deposited. Likewise, there were studies from that time that revealed, among other interesting information, a piece of information linked to hunting : this activity, in hunter/gatherer communities, was carried out by both men and women.
