
The knowledge economy is linked to the information society.
The knowledge economy is the set of economic activities that demand high intellectual capital and stand out for the use of information and communication technologies (ICT) . That is why its value is considered to lie in the generation and application of ideas.
Before moving forward, it is important to analyze the terms that make up the concept. Economics is the science that analyzes how, by appealing to scarce resources, effective satisfaction of material needs can be achieved. The notion also refers to the practices and goods that make up the wealth of a person or a community. Knowledge , meanwhile, is knowledge or understanding.
Characteristics of the knowledge economy
The knowledge economy is based on information for the creation of wealth through the value it adds to services and products. It is considered a paradigm that places know-how at the center.
From the knowledge economy, new sectors emerged and others were also modernized. From telecommunications to computing , through education, robotics and engineering, numerous industries have been developed and enhanced based on the exploitation of knowledge .
Governments and large companies, in this framework, usually invest large sums in research and development (R&D) to promote innovation and contribute to the growth of the knowledge economy. This is linked to the multiplier effect of this economic paradigm and the already mentioned value it adds to multiple activities and goods.
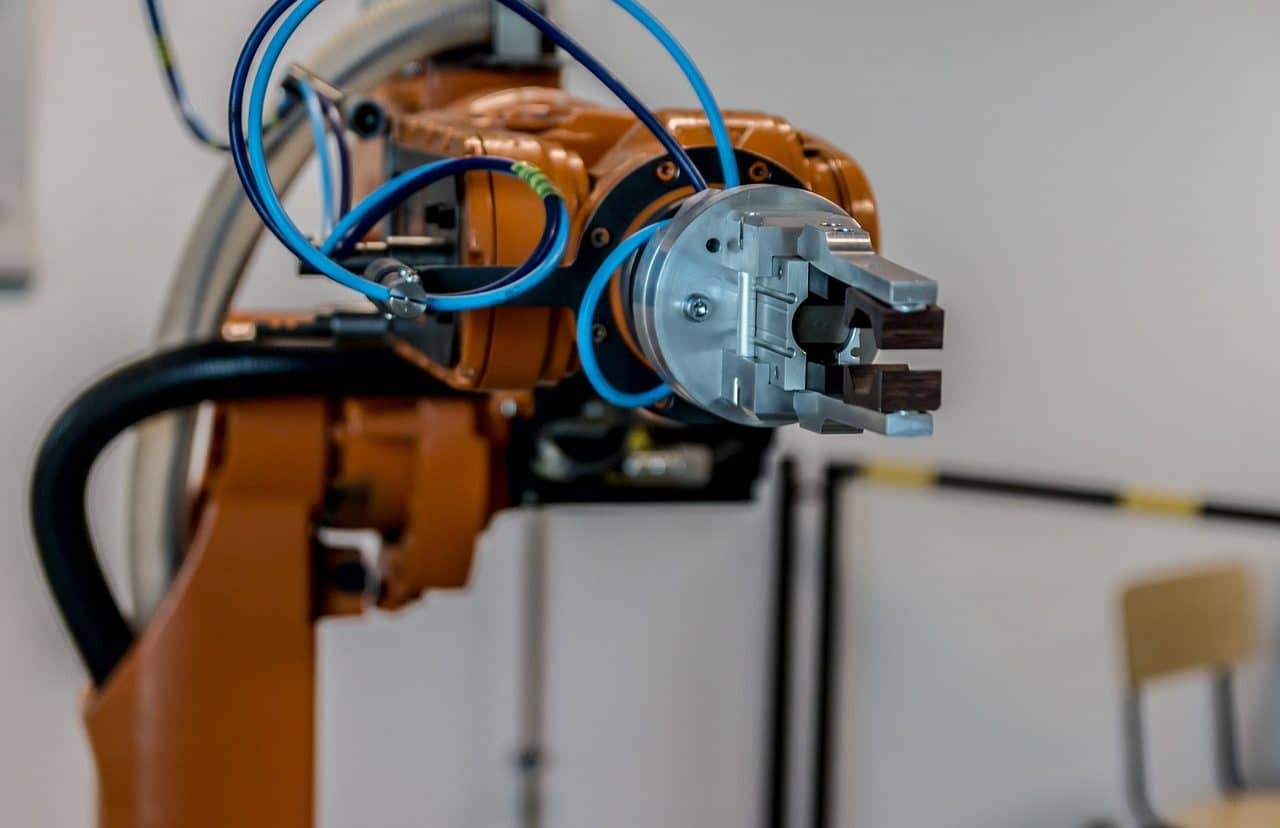
Nanotechnology, advanced robotics and technological finance (Fintech) are sectors that drive the knowledge economy.
Digitization
It is common for the knowledge economy to be associated with the digital economy : one that is based on the use of technological devices or that involves virtualization . Another associated notion is the idea of the new economy , which refers to the exploitation of knowledge, the application of technology and globalization.
It must be clarified, however, that currently the boundaries between the traditional economy, the digital economy and the new economy are blurred. The knowledge economy maintains as a distinctive characteristic the fact that it is based on ideas , although the processes and activities of all economic areas increasingly intersect.
Knowledge management is key in technological startups and technology transfer. Today's everyday realities such as e-commerce, digital marketing and teleworking or remote work can no longer be linked exclusively to the knowledge economy, which also feeds increasingly popular resources such as 3D printing, cloud computing , the Internet of Things (IoT) and artificial intelligence (AI).
It is evident that services such as digital platforms could not have emerged without the knowledge economy. Other areas, such as biotechnology , personalized medicine and electric mobility, demand specialized human capital and the use of ICT, which is also related to this model.

Public innovation policies contribute to the development of the knowledge economy.
Advantages of the knowledge economy
The advantages of the knowledge economy are numerous. Promotes continuous learning and higher education , contributing to the progress of communities.
As we already indicated, it adds value to already existing goods and services . It also allows the creation of new products and benefits, which end up being used by any economic sector and by society in general.
Their innovations, on the other hand, can contribute to sustainable development . The promotion of renewable energies and the construction of smart cities , for example, require knowledge and technologies. Through digital transformation and process automation , in turn, it can bring efficiency to all productive activities and reduce costs.
At a general level, it is usually highlighted that the knowledge economy cuts across all industries, contributing to improving productivity, increasing exports and creating quality jobs .
Social impact
It cannot be omitted to mention that, due to its own characteristics, the knowledge economy appears as a way for local development , even in towns or cities far from large urban centers and capitals. It does not require land or machinery and often generates virtual proposals that can be contracted or consumed from anywhere in the world without the need to invest in transportation and logistics. Betting on knowledge as a source of wealth is possible beyond the geographical characteristics and natural conditions of a territory.
Of course, driving the knowledge economy also brings challenges. Inequality in access to knowledge becomes more noticeable, which is why digital literacy for the entire community becomes essential. Without digital inclusion, many of the benefits mentioned are limited.
If value is generated through specialization , those who cannot train as the labor market demands suffer a social disadvantage and see their chances of progress limited. They may even be left out of the use of innovations that, in theory, become available to the entire society.
For example: if, through software development, telemedicine platforms multiply so that patients can make remote consultations and many health and social work companies begin to provide these services, those who do not have the knowledge to download an application and use it, or they do not directly have access to the Internet or cell phone (mobile), they do not have the possibility of receiving that medical care.
