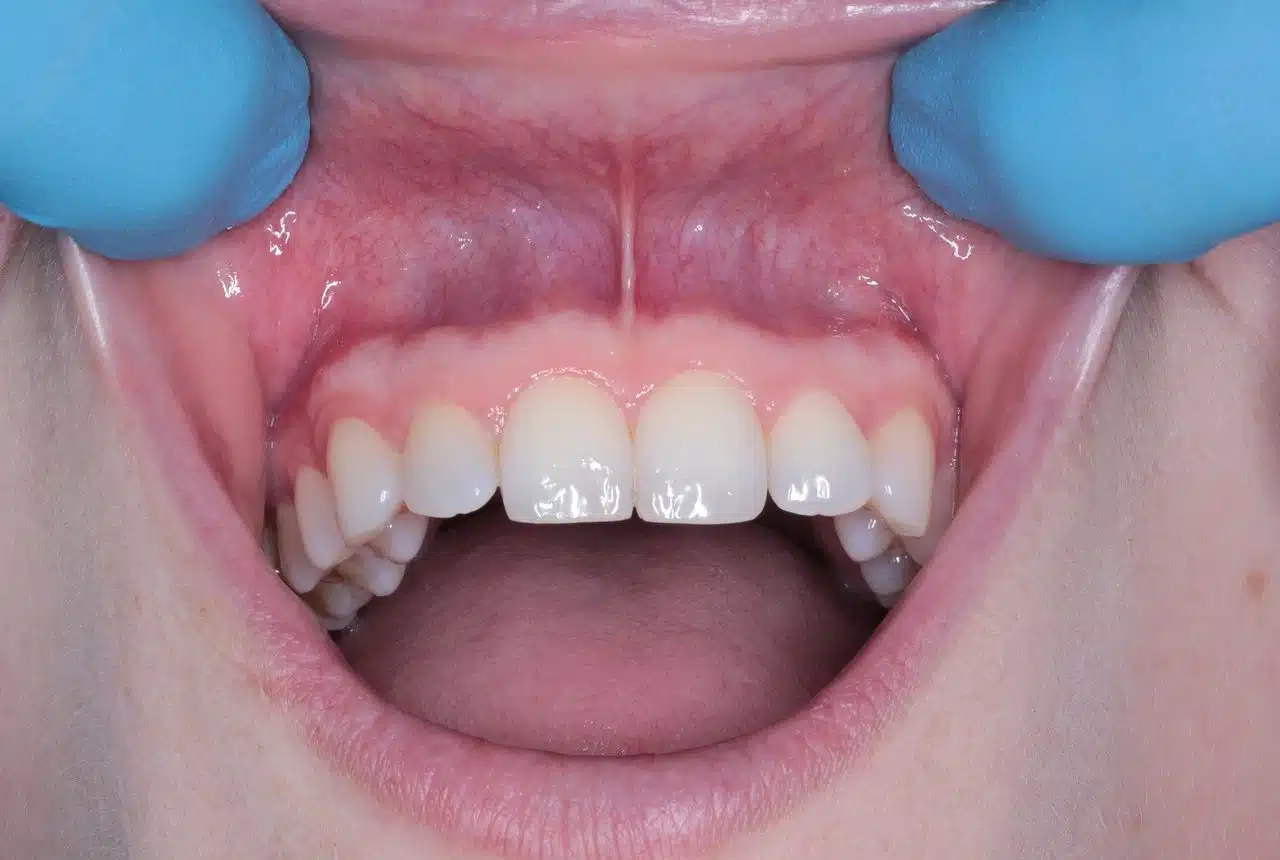
Teeth make it possible to chew food.
A tooth is a hard body found in the jaws of humans and many animals and is used to chew food or, in the case of certain animals, as a defense. The exposed part of the teeth, which is visible, is known as the crown and is protected by tooth enamel . The root of the tooth, for its part, is not visible in a healthy mouth. The union of the crown with the root is called the neck .
The teeth - from the Latin dentis - are embedded in the maxillary bones through a joint known as gomphosis . In this joint it is possible to distinguish the dental cementum and the alveolar bone , which are joined by the periodontal ligament .
Teeth composition
Composed of calcium and phosphorus , teeth are mineralized tissue structures whose development begins at an early age. First, temporary or baby teeth emerge, which fall out naturally and are replaced by permanent teeth .
Thanks to teeth, people and animals can chew food for proper digestion. The teeth can be divided into incisors (which allow cutting food ), canines (dedicated to tearing), premolars (which crush food) and molars (grind). It should be noted that teeth are also involved in oral communication.
Oral hygiene , which is carried out with a toothbrush, dental floss and other implements, is essential to keep teeth in good condition. If hygiene is not correct, it is possible to develop diseases such as dental plaque , cavities , periodontitis and gingivitis .
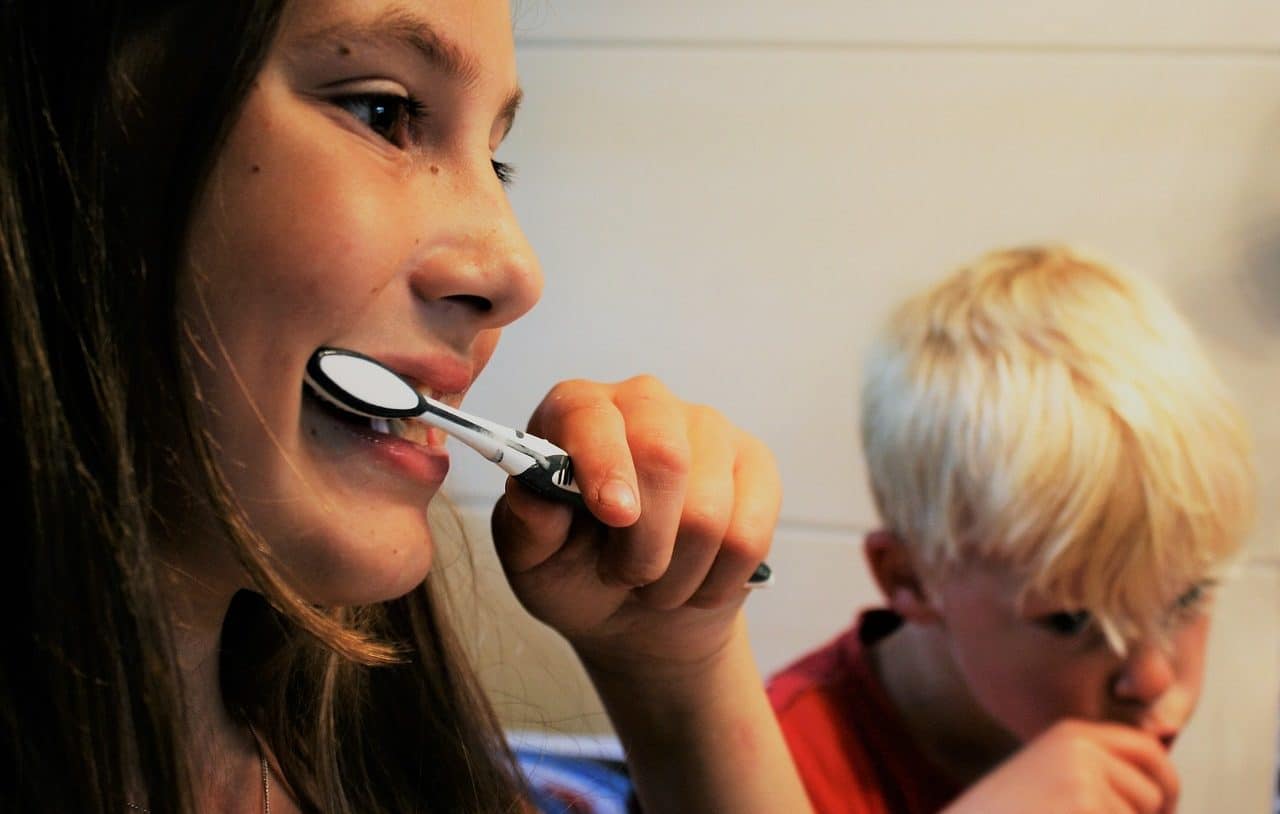

Maintaining good oral hygiene is essential for the care of your teeth.
Dental diseases
dental plate
The focus of dental plaque (or bacterial) is the surface of the teeth, gums and restorations, and it is not easy to observe, unless it is stained. It has a soft consistency and its color tends to be yellowish. It can form in a very short time and is difficult to eliminate, in addition to appearing in different forms and locations in each person. When dental plaque becomes calcified, calculus or tartar may appear.
Caries
The disease known as cavities (sometimes incorrectly called cavities) is characterized by the destruction of dental tissue due to the acids released by certain bacteria that settle on the surface of the teeth. It is important to treat cavities in time to prevent them from attacking the hard tissues, which generates serious inflammation and, in the worst case, the death of the dental pulp, which is also known as necrosis .
Gingivitis
Gingivitis is a disease, usually of bacterial origin, that causes bleeding and inflammation of the gums, due to food debris that is not properly removed during the oral hygiene process.
Periodontitis
The common name for periodontitis is pyorrhea , and it is a chronic and irreversible disease. Its normal course begins with gingivitis and later with gingival retraction and bone loss; In the worst cases, when left untreated, it can remove bone support from the teeth.
Bruxism
Nocturnal bruxism is a little-known disorder and consists of involuntary pressing and grinding of the teeth during sleep, and affects an average of 15% of the population. Since the patient is usually not aware of these actions, they are usually noticed by someone who sleeps with them, or by a dentist who discovers the inevitable destruction of dentin and enamel . In general, bruxism usually appears between 17 and 20 years of age, and its remission usually occurs around the age of 40, spontaneously. Regarding gender, it affects men and women equally.
Halitosis
Halitosis is a symptom characterized by bad breath and affects more than half of the general population. After several hours of sleep, given the lack of activity of the oral structures and the low production of saliva, the presence of halitosis is common.
