Beta decay is based on the emission of a beta particle carried out by a nuclide as a way to balance the relationship established between protons and neutrons in the atomic nucleus.
Beta decay is the name given to a process that is interpreted as a derivation of the weak interaction and is linked to the atomic nucleus . This phenomenon, in which the mass number remains stable, involves the emission of a beta particle (which can correspond to a positron or an electron ) by a nuclide . The purpose is to compensate for the proton - neutron bond.
It is interesting to know that, under conditions of instability, within the framework of what is also known as beta decay, a conversion of protons into neutrons and vice versa occurs. As a result of this disintegration , which, experts on the subject indicate, violates parity , a nucleus remains characterized by greater stability.
Nor can it be overlooked that, when listing what varieties exist in terms of beta decay , electronic capture (or electron capture ) is usually included since the processes are very similar and the aforementioned nuclear force intervenes in both. weak .
Types of beta decay
It is enriching to find out what types of beta decay exist and use theory to learn to differentiate between them.
One of the categories is defined as beta minus (or negative beta ) decay. In this context, a neutron ends up converted into a proton , thus creating both an antineutrino and an electron . The latter has a negative charge and appears when one of the neutron quarks becomes a proton quark .
When a proton transforms into a neutron , however, it is called beta plus (or positive beta ) decay. The fruits of this mutation are an electron neutrino and a positron , which is why this phenomenon is also described as beta radioactivity and positron emission .
Sometimes two beta decays occur simultaneously, leading an unstable isotope of a nuclide to undergo a double beta decay . When deepening the notions about the particularities of beta decay and the profile of beta particles, it is advisable to complement the information by knowing in detail about radioisotopes , as the unstable atoms that exhibit an excessive amount of nuclear energy have been called.
Depending on what type of beta decay occurs, a neutron can transform into a proton and vice versa.
History
When reviewing the origins and evolution of beta decay , which continues to be important to science today, the figure of Enrico Fermi takes center stage. This prestigious physicist born in Italy who became a naturalized American was inspired by the contributions of his colleague Wolfgang Pauli about the supposed existence of an invisible particle of neutral essence (which made it possible to justify the conservation of energy ) to promote the concept of the neutrino . He carried out several tests until announcing, in 1934, the discovery of radioactivity incited by neutrons .
Months earlier, as appears from the records, he launched a theory that served as an explanation for beta decay . Within the framework of particle physics, this ancient contribution is identified as the interaction or Fermi constant . This content accounts for a direct interaction between two pairs of fermions at a vertex, very useful to represent the weak interaction .
Applications of beta decay
Beta decay is used in a wide variety of areas and is tested in numerous experimental projects. When analyzing its practical applications, its importance within nuclear medicine , cosmology , astrophysics and technological research, for example, is noted.
Understanding what beta decay consists of and how it is carried out is necessary to, to specify a possibility, understand processes that are triggered within a nuclear reactor , regardless of whether it is on or has been turned off. It should be noted that, in the desire to seek stability, there are radioactive elements produced in a nuclear power plant through a reaction called nuclear fission that undergo beta decay . It has been estimated that for each nuclear fission it is possible to count six episodes of beta decay .
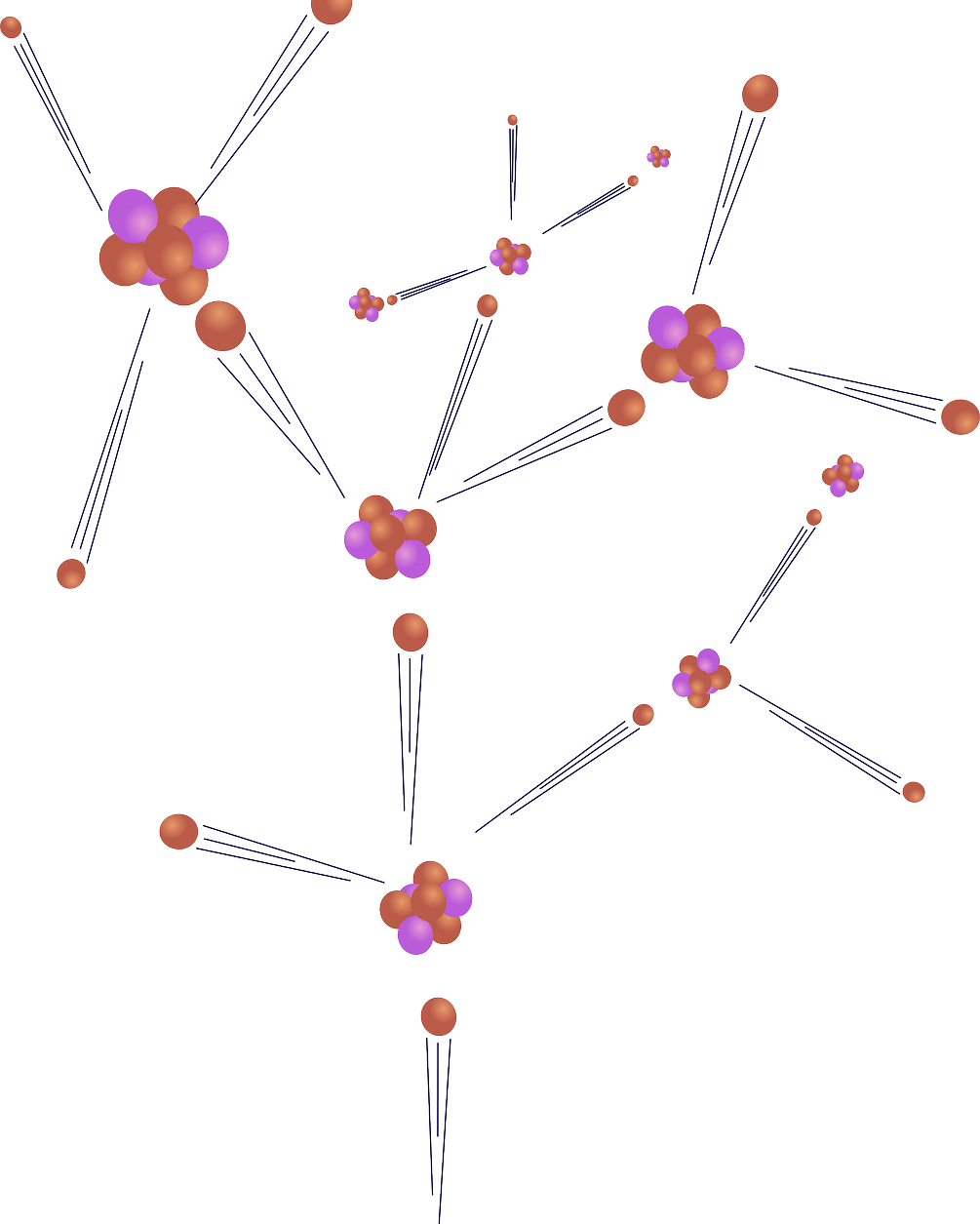
According to physics experts, there are approximately six beta decays for every nuclear fission that takes place.
It is worth noting, to add more data on this matter, that beta radiation born from beta decay is key to making medical diagnoses by performing (and interpreting results) a positron emission tomography (PET) .
When radiotherapy is indicated for the treatment of cancer or when carrying out quality control tests and determining the thickness of a certain product, beta particles also come into play.
The reverse version of beta decay , to add another reference, is used for the "hunting" or detection of high-energy neutrinos .
Another fact to take into account: beta decay is observed even in the so-called R-process (also classified as thermal or neutron capture ) that occurs within the framework of supernova nucleosynthesis and generates isotopes characterized by their richness in neutrons and their great weight.
