The derivative of the derivative of a function is known as the second derivative.
Derived is a term from the Latin derivātus that can be used as a noun or as an adjective. In the first case, it is a notion of mathematics and specifically differential calculus that names the limit value of the link between the increase in the value of a function and the increase of the independent variable .
The derivative, therefore, represents how a function is modified as its input also registers alterations. In the cases of real value functions of a single variable , the derivative represents, at a certain point, the value of the slope of the tangent line to the graph of the function at that point.
Its origin
The birth and use of derivatives in the mathematical field, although they have their origin in Ancient Greece , we can establish that they appear as such thanks to two very important historical figures: the English mathematician Isaac Newton and the German logician Gottfried Leibniz .
And they started from the theories and concepts established by their predecessors over time to carry out their own applications and methods. Thus, for example, Newton discovered algorithms, proceeded to undertake the restructuring of the calculation bases and created his own method to calculate tangents .
Types of derivative
There are many types of derivatives according to their characteristics. It is possible to talk about partial derivative , directional derivative , functional derivative , implicit derivative , covariant derivative , exterior derivative , logarithmic derivative , exponential derivative , gateaux derivative and Lie derivative , to mention some possibilities.
Differential geometry and vector calculus are some of the areas that use different kinds of derivatives. It is interesting to mention that the value adopted by the derivative of a function at a certain point is susceptible to geometric interpretation , because it corresponds to the slope of the tangent line in the graphical representation.
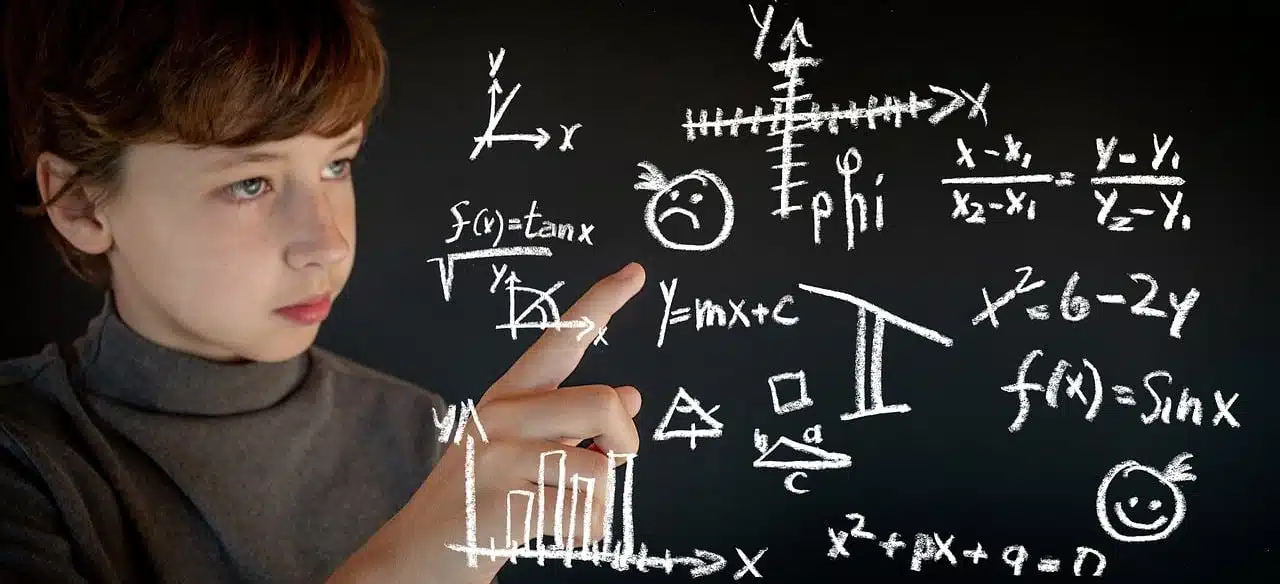

The multivariable generalization of a derivative is called a gradient.
The study of movement
Derivatives are important when studying motion . It should be noted that movement, in the field of physics, is the modification of the position of an object with the passage of time, taking into account a reference system.
In this way, when the position of the body in relation to time is represented by a function, the speed of the element in question for the various moments is the derivative of the function .
Examples of derivative
Take the case of a family driving from their home to a beach tourist destination 400 kilometers away . They complete the journey in 5 hours since they left at 4:30 p.m. and arrived at 9:30 p.m. , traveling therefore at an average speed of 80 kilometers per hour .
It should be considered, however, that in some sections they moved at a lower speed, while in others, at a higher speed. In this framework, the average speed between 4:30 p.m. and 6:30 p.m. was 70 km/h .
The derivative, in short, is the speed of the car at each moment. The calculation of the instantaneous speed (that is, at a specific moment; for example, at 17:03 ) can be done based on the average speed in time intervals that are increasingly smaller around the indicated time.

The derivative of a trigonometric function reflects how a function of this kind changes in relation to an independent variable.
A kind of word
For grammar , a derived word is one that is formed through a derivation. This is a word formation procedure based on the indication of semantically linked concepts with others to which affixes are added. For example: messaging and messenger are two words derived from the word message . In the same sense, maritime, marine, tide, sailor, swell and tidal wave are words derived from sea .
In this sense, we can establish that there are two types of words in general terms. Thus, on the one hand there are the so-called primitives , which are those that do not come from any other; and on the other hand we come across the derivatives which, as their name indicates, are those that are formed from others by adding prefixes or suffixes of various kinds.
In this way, in addition to the examples already mentioned, we can mention the case of bread . This is a primitive word, while those derived from it include baker and bakery .
On the other hand, among the most frequent prefixes used to create derived words we find bi- , which can be translated as "two" , and equi- , which is synonymous with equality. Regarding suffixes, among the most used are -itis (which is equivalent to an inflammation) and -azo (which is an augmentative ).
Derived in chemistry and finance
At a chemical level, a derivative is a product that is obtained through another . Thus it can be said that molasses is a liquid product derived from sugar cane , or that gasoline is a mixture of hydrocarbons derived from petroleum .
In finance , on the other hand, a derivative instrument (also known as a financial derivative ) is a financial-type product that has a value based on the price of a different resource (called, in this context, an underlying asset ).
