
A radio wave allows the wireless transmission of Morse code.
Morse code is a system based on the use of dots and dashes to represent numbers and letters . This is a resource that was used especially decades ago, especially in communication via telegraph .
Its name comes from the American artist and inventor Samuel Morse ( 1791 – 1872 ). Morse teamed up with Alfred Vail ( 1807 – 1859 ) to develop a telegraphy system that served to transmit messages using electrical pulses under a cipher created by himself.
The so-called Morse telegraph , in this framework, was based on a pencil that drew lines according to electrical flow. The character encoding , meanwhile, was carried out with the combination of dots, lines and spaces to give rise to the Morse alphabet .
History of morse code
The history of Morse code has its origins in the early 20th century , when electrical signaling systems began to be developed using various techniques.
In 1820 , the Danish Hans Christian Ørsted ( 1777 – 1851 ) detected the link between electricity and magnetism, discovering electromagnetism . Five years later, the Englishman William Sturgeon ( 1783 – 1850 ) created the first electromagnet . Thus the foundations were laid for electromagnetic telegraphy , with pulses of electric current that traveled through cables to a receiver that had an electromagnet.
By 1833 , Morse had already devised an electric telegraph , which he presented two years later. In 1837 , meanwhile, he postulated the first of his codes intended for the transmission of natural language via electrical pulses and silences.
It can be said that the application of Morse code in telegraphy began in 1844 , when Morse and Vail tested a device that, by receiving electric currents, made holes in a paper tape.
In the first instance, Morse had planned to transmit numbers, which could be associated with words thanks to a code book. It was Vail who included the letters and added special characters. In this context, the types of marks known as dits and dahs (equivalent to dots and dashes or dashes) emerged.

Naval communications can be developed with Morse code.
Your advantages
Morse code and the telegraph were the first systems that made real-time communication possible over great distances . Until then, messages were transmitted according to the speed of the messenger since a person had to transport them on foot, on horseback, by train or by boat.
In this way, news could take weeks or months to reach a place. Thanks to the telegraph and Morse code, that time could be reduced to seconds.
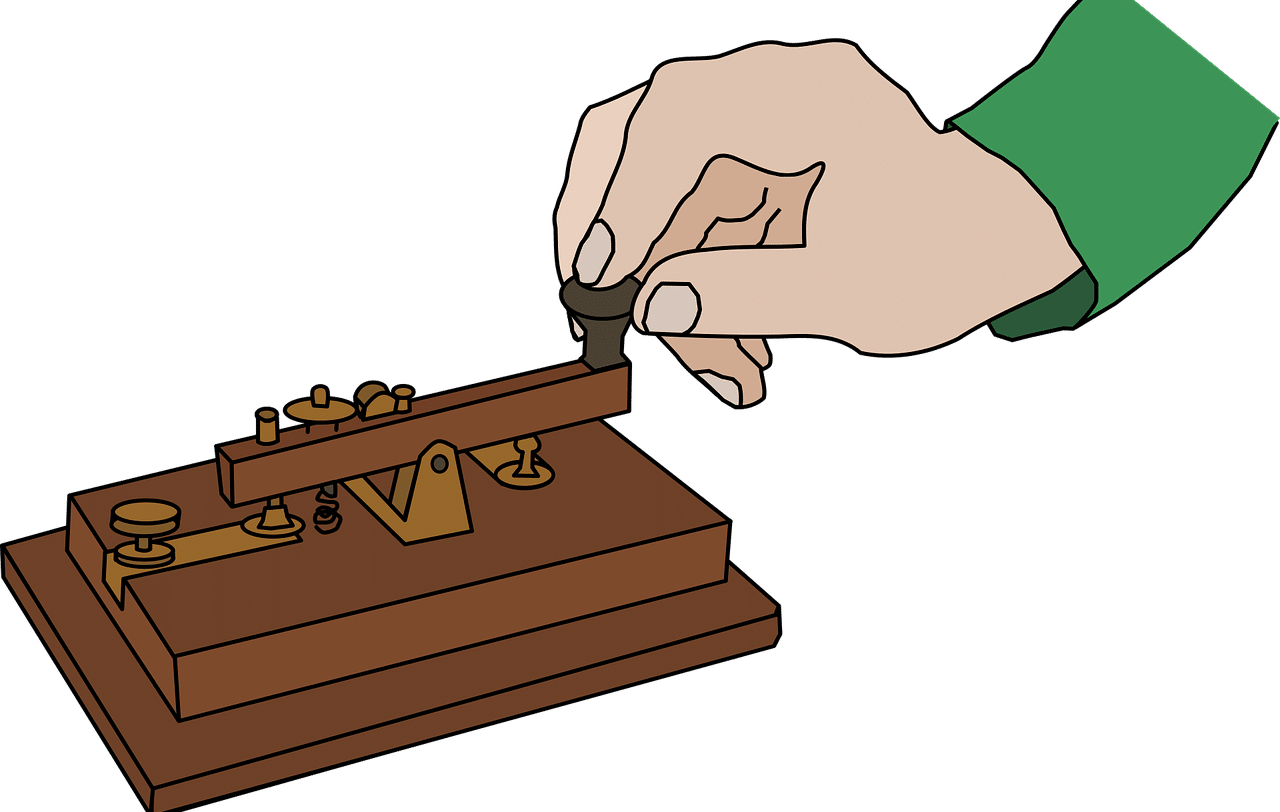
The telegraph , in short, is a machine that is used to send electrical pulses of different durations through a cable . Having the ability to send short pulses ( dots ) and long pulses ( dashes ), Morse and Vail created the code to transmit messages with words and phrases.
The telegraph message, therefore, is transmitted by sending the pulses over the transmission lines. The communication protocol implies that a minimum pulse is used to represent a point: in this case, the telegraph knob is pressed once. To represent a line, you need to press three times as long as on the point.
The time that is equivalent to three points allows you to mark the separation between each letter. If you want to separate words, the time is equivalent to three lines. Thus, the receiver is in a position to separate the letters, develop the words and interpret the integral message.
There are software and applications on the Internet that are used to translate Morse code.
Using morse code
In 1843 , the United States Congress decided to build a 60 km telegraph line to link Baltimore and Washington . The following year the first message was transmitted between those points, which began with a phrase from the Old Testament .
From then on, progress was made with the laying of power lines, generally using the light poles already used by the railroad. In this way, telegraphs were installed in most train stations .
The use of Morse code continued to expand: in the 1860s , transcontinental lines were installed. With the outbreak of the American Civil War , meanwhile, the importance of the telegraph to transmit emergency communications was demonstrated, something that was ratified with the First World War .
Beyond the telegraph
The use of Morse code goes beyond the telegraph, an instrument that is practically no longer used due to technological advances. Currently the Morse code is transmitted by radio waves , boats take advantage of it with light signals and it can even be applied by hitting .
Suppose there is an accident in a mine and a group of workers are trapped in a tunnel without communication instruments. Hoping to be found, they begin banging on the ceiling with a stick, sending distress signals (such as SOS ) with Morse code. The intention is that someone heard the knocks and interpreted them to understand the message.
