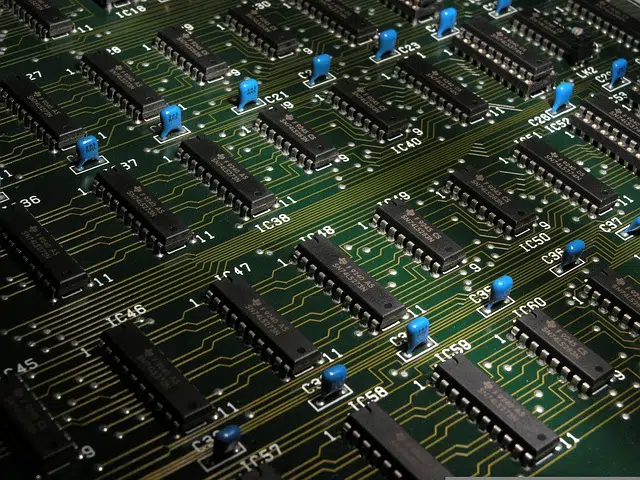
An integrated circuit combines miniaturized elements on the same support.
Circuit , originating from the Latin circuitus , is a concept with various uses and meanings. The term refers to the route in a closed curve, the route that ends at the starting point or the land located within a perimeter.
Integrated , for its part, comes from the verb integrate (to complete a whole with the missing parts, to make something become part of a whole, to constitute a whole).
In electronics , an integrated circuit is a combination of circuit elements that are miniaturized and that are part of the same chip or support . The notion is therefore also used as a synonym for chip or microchip .
Components of an integrated circuit
The integrated circuit is made with a semiconductor material , on which electronic circuits are manufactured through photolithography. These circuits, which occupy a few millimeters, are protected by an encapsulation with metallic conductors that allow the connection to be established between said chip of semiconductor material and the printed circuit.
There are several types of integrated circuits. Among the most advanced and popular, microprocessors can be mentioned, which are used to control everything from computers to mobile phones and household appliances .
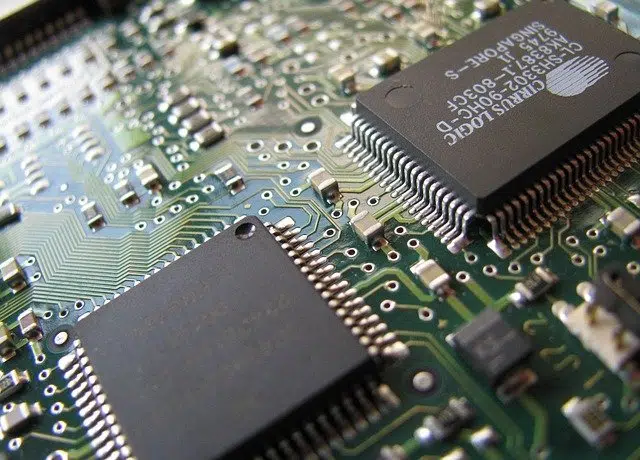
Integrated circuit is often used synonymously with microchip or chip.
Classification according to type
Integrated circuits can be classified in various ways. It is possible to talk about monolithic circuits (made of a single single crystal, usually silicon), thin-film hybrid circuits (with components that exceed monolithic technology) and thick- film hybrid circuits (without capsules, with deposited resistors). by screen printing and laser cutting).
Another classification is made according to the number of components and the level of integration. Integrated circuits, in this case, are known by their acronym in English: SSI ( Small Scale Integration ), MSI ( Medium Scale Integration ), etc.
History of the integrated circuit
Many interfaced microelectronic devices, especially transistors and diodes, as well as passive components such as capacitors and resistors , take advantage of integrated circuit technology, whose history dates back to the late 1950s, when an engineer named Jack St. Clair Kilby developed the first prototype for the Texas Instruments company.
Until then, electronic equipment usually consisted of vacuum tubes (also called electronic or thermionic valves, among other names), a component used to switch, modify or amplify an electrical signal by controlling the movement of electrons with the help of certain devices. gases or in a space with very low pressure. However, thanks to Kilby's work, the active and passive components began to be located on the same metal surface whose dimensions were dozens of times smaller than those of a single vacuum tube.
Its evolution
The first integrated circuit developed by Kilby was manufactured on a square germanium die; Each side measured 6 millimeters and was made up of a capacitor, three resistors and a transistor . The debut was a complete success, which allowed this revolutionary engineer to continue researching and improving his invention. It is worth mentioning that the name "chip" derives from the homonymous English term used to refer to chips, among other things.
But the transition from vacuum tubes to semiconductors was not a coincidence, but was supported by a series of experiments that demonstrated the usefulness of the latter to replace the former in terms of functionality, occupying a fraction of their size. This great advance, which makes the reality that precedes it seem absurd, gained strength in a short time, thanks to the fact that integrated circuits began to be mass produced and the world was able to verify that in addition to their obvious advantage over tubes , were reliable and easy to make complex.
Today, we find this technology in the microprocessors of devices as diverse as computers and mobile phones, and also in digital memories, which use a chip instead of mechanical parts.
