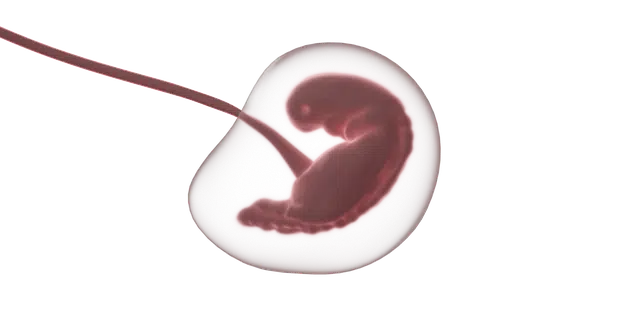
The zygote arises from the union of the sperm and the egg.
The Greek word zygoûn (which translates as "unite" ) evolved into zygōtós ( "united" ), which in turn came into our language as zygote or zygote . The cell that results from the fusion of the female gamete with the male gamete in the process of sexual reproduction that plants and animals develop is called a zygote.
From the term in question, others that are equally important have emerged, such as the following:
– Heterozygous , which is used to refer to that cell that is formed from the union of two gametes that have different constitutions.
– Homozygous , which is used to refer to a cell that is created from the union of two gametes of identical constitution.
Emergence of the zygote
Also called an egg , the zygote arises when the sperm joins the egg . When their respective nuclei fuse, the nucleus of the zygote arises, which has two complete sets of chromosomes (one from each gamete). The organelles and cytoplasm, for their part, come from the egg cell .
Once the zygote is formed, its segmentation occurs, which includes successive mitosis to give rise to the blastomeres (embryonic cells), which in turn give rise to the morula and then the blastula . In the continuity of embryonic development, the blastula becomes a gastrula and then a neurula . In this sequence the zygote heads from the fallopian tube towards the uterus .
The various phases of segmentation are known as blastulation , gastrulation , and organogenesis . When embryonic development concludes, the zygote is called the fetus .

It can be said that the zygote is a phase of prenatal development.
Classification according to type
According to the location and level of yolk (the substances that allow nutrition of the embryo), zygotes can be classified as centrolecitic (with great abundance of yolk); telolecytic ; mesolecitic or heterolecitic ; and oligolecitic or isolecitic (with little yolk).
It is important to keep in mind that it is possible to differentiate two large poles in the zygote: the animal or germinative pole , which houses the nucleus and metabolic activity, and the vegetative pole where the aforementioned yolk accumulates.
Differences between zygote, embryo and fetus
It must be stated that it is very common to confuse the terms zygote, embryo and fetus. And they are commonly used to refer to the future baby that is on the way during pregnancy . However, it must be clear that they mention it but in the different phases of what would be its prenatal development:
– Zygote is the cell that arises when the sperm and the egg fuse their nuclei during fertilization. It usually has 46 chromosomes and its size is identical to that of the aforementioned egg.
– Embryo is the one that is produced from the first day after fertilization until the eighth week of gestation.
– Fetus . In this case we can state that it is considered that the end of the embryonic stage and the beginning of the fetal stage takes place from week 8 of pregnancy. At this point the embryo is considered to be a fetus. This will make it grow while its vital organs develop and it will acquire the appearance of a baby until it is born, which usually happens between weeks 38 and 40 of pregnancy, as a general rule.
