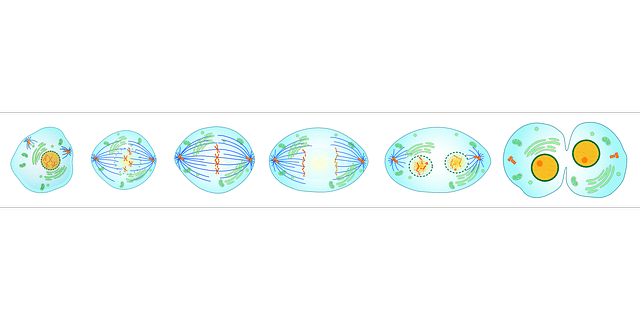
Karyokinesis is the process that leads to the division of the cell nucleus.
The etymology of cariokinesis refers us to two words from the Greek language: káryon (which can be translated as "nucleus" ) and kínēsis (a notion that refers to "movement" ). The concept is used in the context of biology to refer to the process that causes the nucleus of a cell to divide .
Karyokinesis is part of mitosis : cell division that, after the duplication of genetic information, generates new cells that have all the chromosomes.
Karyokinesis process
Also called amphiastral mitosis or astral mitosis , karyokinesis occurs at the beginning of mitosis . In order for the genetic material found in the mother cell to be distributed equally between two daughter cells, its nucleus must divide.
Once karyokinesis has taken place and there are two separate nuclei, cytokinesis takes place: the cytoplasm separates and two daughter cells are formed. When mitosis is completed, two cells have been produced that are genetically identical. Asexual reproduction, the growth of a living being and the repair of tissues are carried out thanks to mitosis.
In addition to everything stated above, we have to establish another series of relevant data on karyokinesis. In this way, for example, we can state that it can be of two types. Thus, firstly, it can be symmetrical, which is a bipartition or binary fission , and secondly it can be asymmetrical. This can also respond to the name budding.
Karyokinesis is part of mitosis and meiosis.
Various phases
In the same way, it is really important to know that karyokinesis or cell division is carried out through a total of five phases:
– Prophase that consists of chromosome condensation, the disappearance of the so-called nuclear envelope and the formation of the mitotic spindle.
– Prometaphase , which is the movement of chromosomes. Where? Therefore it is known as the mitotic spindle.
– Metaphase , which is characterized by being the moment of karyokinesis in which the chromosomes are in the so-called equatorial plane. But not only that, it must be established that they are linked by the centrometers to the mitotic use.
– Anaphase , which is the stage that occurs when the division of the aforementioned centrometers occurs. Specifically, what happens in this phase is that what the copies of the different chromosomes do is move towards the opposite poles of the cell.
– Telophase , which will allow the obtaining of two daughter cells. It is composed of cytokinesis, a chromosome-type decondensation, the reappearance of what is known as the nuclear turn and, finally, the disappearance of the mitotic spindle.
Other considerations about karyokinesis
It should be noted that karyokinesis also develops in meiosis , which is another type of cell division . In this case, the resulting cells have half the chromosomes.
It can be said, in short, that karyokinesis involves a distribution or repartition of the nuclear material of a cell, which develops within the framework of cell division.
