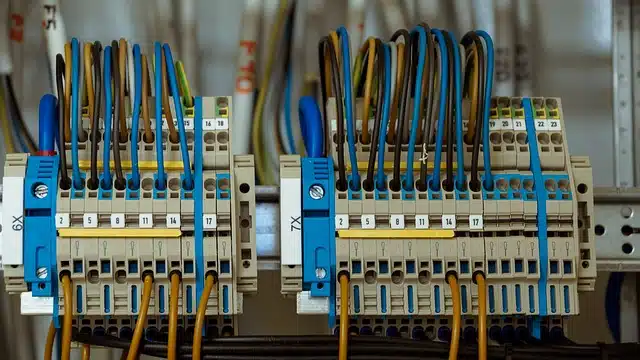
Structured cabling allows the transmission of signals in an enclosure.
The system of cables , connectors , conduits and devices that allow establishing a telecommunications infrastructure in a building is known as structured cabling . The installation and characteristics of the system must meet certain standards to be part of the structured cabling status.
In this way, the adherence of structured cabling to a standard allows this type of system to offer installation flexibility and independence from suppliers and protocols, in addition to providing ample growth capacity and being easy to manage.
In these cases, the laying is usually carried out with twisted pair copper cable (for IEEE 802.3 type networks), although fiber optic cable or coaxial cable can also be used.
Utility of structured cabling
What structured cabling allows is to transport, within a building or enclosure, the signals that come from a sender to its corresponding receiver. It is, therefore, a physical network that can combine UTP cables , connection blocks and adapters, among other elements.
By supporting various telecommunications devices, structured cabling allows it to be installed or modified without the need to have prior knowledge about the products that will be used on it.
When laying, the extension of the cabling, traffic segmentation, the possible appearance of electromagnetic interference and the eventual need to install virtual local networks must be taken into account.

Structured cabling is made with UTP cables and other elements.
Its components
Among the main elements of the structural cabling system are the horizontal cable (which runs horizontally between the floor and the ceiling), the vertical cable , trunk or backbone (which interconnects various rooms) and the telecommunications room (with the telecommunications equipment ).
Another concept related to structured cabling is the grounding and bridging system ; It is a fundamental component in a modern cabinet. The objective of this resource is to divert to ground any improper supply of electrical current to the devices within reach of users, which occurs as a result of an error in the insulation of the active conductors.
It is worth mentioning that the plans do not always indicate the existence of grounding (also known as ground wire , ground well or ground connection , among other names it receives), and may be unique for the circuits or branches that are in contact with trays, pass boxes or ducts. The installation of safety ground cables is carried out underground.
Electrical capacity and speed of structured cabling
On the other hand, there is capacitance , also called electrical capacity (the property of a body to conserve an electric charge), which can cause distortions in the signal transmitted by a cable. The capacitance increases the longer the cable and the thinner the insulation layer. To measure capacitance, a cable tester can be used, which can help determine if the cable has been stretched or bent.
Depending on the category of a network , its speed varies considerably; Observing the seven included between 1 and 6A, said value is: less than 512 kbit/s; 4 Mbit/s; 10 Mbit/s; 16 Mbit/s; 100 Mbit/s; 1 Gbit/s; 10 Gbit/s. Some of them have very specific uses, or known limits: 1 is used in telephone communications and its low speed does not make it suitable for transmitting data; 3 is used for 10BaseT networks (an ethernet configuration, a local network standard); 4 is used for Token Ring networks (an architecture created by IBM).
It is worth mentioning that there are always portions of the transmission lines that are subject to background noise coming from the transmitter, the rest of the lines or from external sources. This noise , in turn, mixes with the signal and generates slight distortion.
