
Biosecurity aims to preserve health from pollution and other threats.
Biosafety is a notion that is not part of the dictionary prepared by the Royal Spanish Academy ( RAE ). In its broadest sense, biosecurity consists of protecting living conditions from the action of biological, chemical or physical agents.
The concept, in this way, refers to guaranteeing that biological resources do not suffer damage due to the actions of external actors. Its purpose is to minimize risks and prevent negative impacts.
It can be said that biosecurity consists of preserving the state of living beings : animals (including humans), plants or a habitat in general. This protects health from contamination, epidemics, biological attacks or other threats.
Biosafety in the work environment
Biosafety is often associated with risk control in a work environment . In health centers (hospitals, sanatoriums, clinics, etc.) and laboratories, people often work with infectious agents : this is why guaranteeing biosafety is essential for the well-being of employees and also patients. In this framework, hospital biosafety is also discussed, with the use of gloves and face masks, proper waste disposal, and disinfection of environments being important.
Suppose a doctor must treat a patient who is bleeding. To avoid possible infections, you must wear gloves : this way you do not come into direct contact with blood . The patient, on the other hand, must be treated in a clean environment so that pathogens do not enter through their wound. The gauze and cotton used in the task should also be disposed of in the appropriate place to take care of biosecurity.
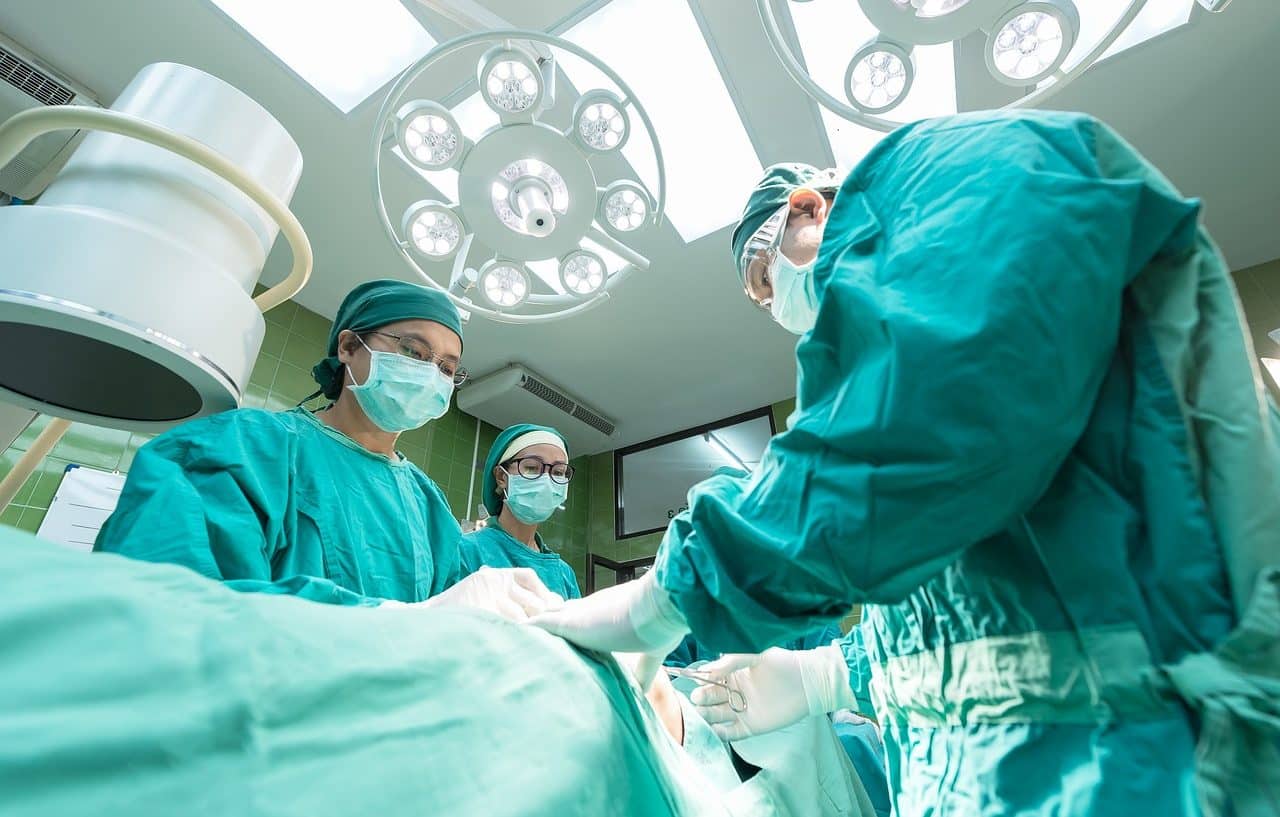
Preserving biosafety is essential in an operating room.
Different levels
According to the degree of lethality of each disease, it is possible to recognize four levels of biosafety : in the first, infectious agents cannot cause diseases in a healthy adult; In the second are those that can make an adult sick and, in addition, cause an infection of various types; the third level covers exotic agents that can be transmitted by aerosols and cause serious or fatal diseases; and the last level is occupied by the most dangerous, capable of being transmitted by air or even by routes that have not been identified by medicine.
It should be noted that biosafety does not consist of a simple decision or a resource that is used on a certain day to avoid an isolated case of contamination; It is a set of practices, devices and facilities that constantly and actively aim towards greater protection of living beings that are exposed to a series of well-defined risks, which must be previously identified.
Principles of biosafety
Universality
Any measure must take into account all people involved in the activity on which biosecurity is to be applied, regardless of whether they have the necessary antibodies to protect themselves from the potential threat or if they have any disease. Everyone must respect the precautions dictated by the organization to avoid exposing their skin and mucous membranes to any situation that could lead to contagion or infection.
Use of barriers
It is about preventing, by all possible means, blood and other body fluids from coming into direct contact with potentially contaminating substances. For this purpose, barriers are used, which can be gloves or masks, among many other examples. It is important to note that many times this measure simply reduces the chances of contamination but does not eliminate them completely.
Disposal of contaminated material
It is important to have adequate means to remove material that has been exposed to the source of contamination. At this point we talk about a series of specific procedures and devices that allow the safe deposit and disposal of any object that may be risky for users.
