Benzene is an aromatic hydrocarbon.
Benzene is an aromatic hydrocarbon that has six carbon atoms and has a ring structure. It is a flammable, colorless liquid that is used as a reagent and solvent .
Before entering fully into the definition of the term, it is necessary to discover its etymological origin. In this case it must be stated that it is the sum of two clearly delimited components:
- The noun benzoe derived from Arabic and was the name given to Javanese incense .
- The suffix -ene , which is the ending used within the field of chemistry to name hydrocarbons.
Characteristics of benzene
It should be remembered that a hydrocarbon is an organic compound that combines carbon and hydrogen atoms. Its molecular form, therefore, is based on the bonding of carbon atoms and hydrogen atoms in chains that can be branched or linear and closed or open.
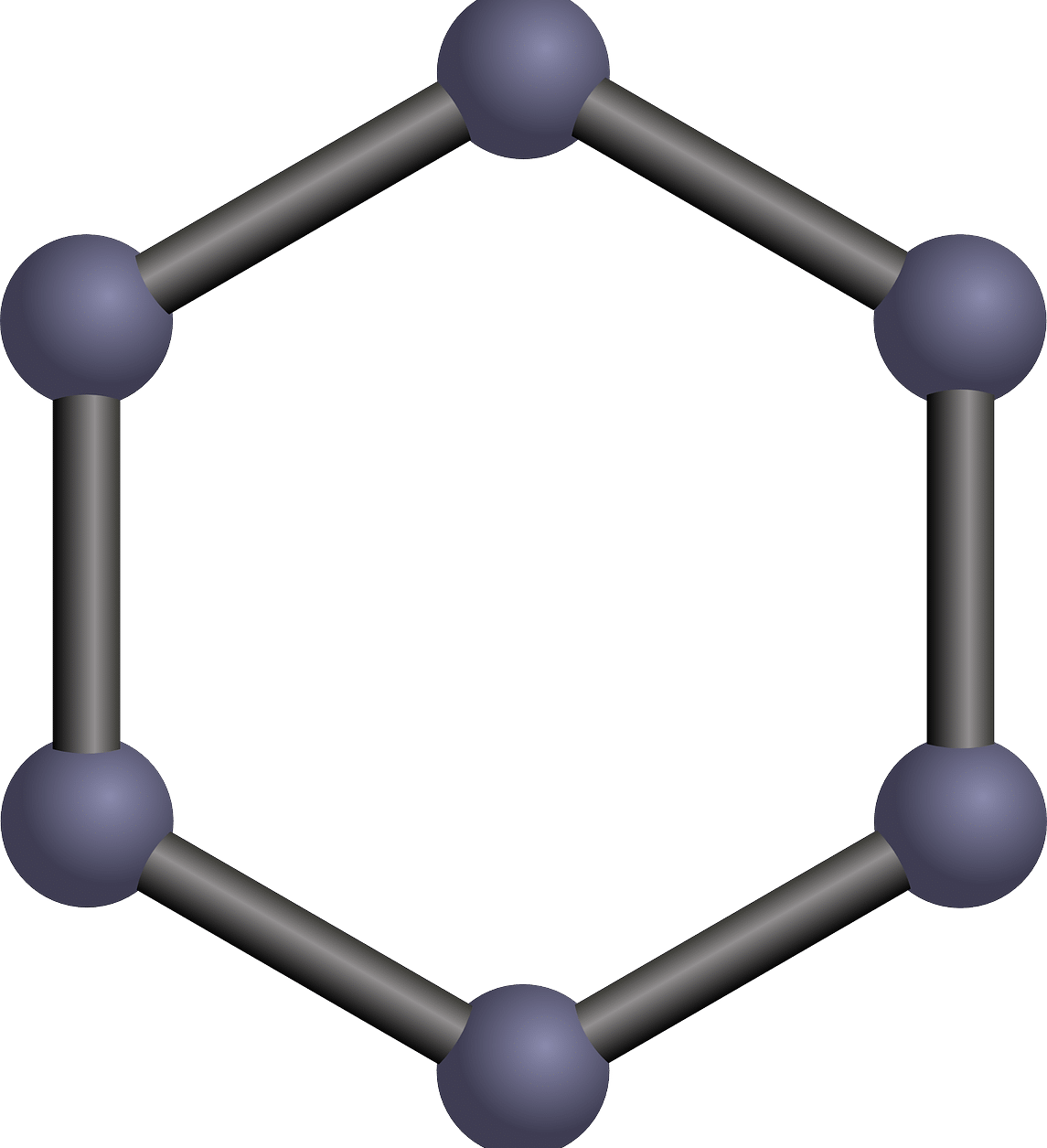
Benzene has six carbon atoms and six hydrogen atoms that make up a hexagon . At the vertices of this figure the carbon atoms appear, with three single bonds and three double bonds that are located in alternate positions.
History of its discovery
The discoverer of benzene was the British chemist and physicist Michael Faraday (1791-1867), when he managed to isolate lighting gas in 1825 and detected this molecule . The German August Kekulé (1829-1896), for his part, was the one who first represented benzene with three double bonds.
Later, the American Linus Pauling (1901-1994) postulated mesomerism or resonance of benzene: a tool that allows the representation of a molecular structure through the linear combination of theoretical structures that do not coincide with real structures.

The production of nylon requires the use of benzene.
Uses of benzene
Benzene is one of the most used chemicals in the world. It is used to make nylon, resins , plastics, lubricants, rubber, detergents and dyes. Benzene is even used to produce pesticides and certain medications.
Naturally, benzene is found in crude oil and is produced in forest fires . Finally, cigarette smoke and gasoline also contain benzene.
Other data of interest
In addition to all the characteristics mentioned about benzene, we can present others that are equally relevant and of interest:
- Boils at 80.1º C.
- It melts at 5.4º C.
- It has a strong smell.
- It is lighter than water.
- It is insoluble in water, but very soluble in solvents such as ether and ethanol or cyclohexane, for example.
- It is toxic.
- It has a bitter, burnt taste.
- It is considered one of the most relevant pollutants that can exist in indoor spaces. And it can be released by decorative elements, carpets, furniture made with conglomerate, vinyl, wood coverings, cleaning products and even paints.
