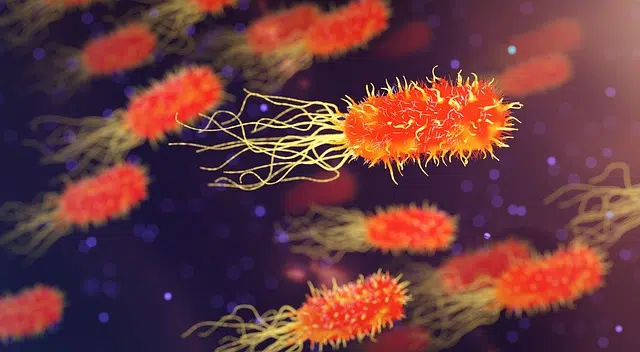
Bacteria are microorganisms that can cause diseases.
The word bacteria comes from a Greek term that means "rod." It is a prokaryotic unicellular microorganism that can cause diseases , fermentations or putrefaction in living beings or organic matter.
Because they are prokaryotic cells, they lack a nucleus or internal organelles. On the other hand, although the term comes from rod, bacteria can be shaped like a rod , sphere or helix .
Classification of bacteria according to their shape
Bacteria can be classified into various groups based on different criteria. So, for example, if we start from what its form is, we find the fact that there are four clearly delimited types:
Bacilli . They are bacteria that are defined by being elongated and because they can be curved or straight. In the same way, we must emphasize the fact that they may or may not have flagella.
Leptothrix . Large ones are those that fall under this name and their main identifying feature is that they can present filaments called septate.
Spirits . In this case, bacteria that have a helical curved appearance are included under this category.
Coconuts . The bacteria that receive this name are those that have a rounded shape and can occur singly, in pairs or in the form of a clustered chain.

To see bacteria, you need a microscope.
Other types
In addition to everything stated above, we also have to highlight the fact that bacteria can also be classified based on their respiration. In this case, we could make two large groups: the aerobes , which are those that make use of oxygen, and the anaerobes , which do not use that but other elements such as carbonate, for example.
Thirdly, we can determine that bacteria can also be classified taking into account their need for growth. A fact that would lead to finding two types of bacteria: heterotrophic (parasitic, putrefactive, symbiotic...) and autotrophic (photosynthesizing, chemosynthesizing...).
Bacteria can live in any habitat; Some species even survive in outer space. These characteristics make bacteria the most abundant organism in the world: 40 million bacterial cells can coexist in just one gram of soil .
Beneficial bacteria
The human body houses about ten bacterial cells for every human cell. The immune system allows most bacteria to be harmless or even beneficial (they help digestion, for example). However, certain bacteria can cause serious diseases such as tuberculosis , leprosy , and cholera .
Bacteria help in the production of cheese, butter and yogurt, play important roles in the manufacture of certain medications and collaborate in the treatment of wastewater . They are also used for tanning leather and curing tobacco.
Scientific study
The discipline responsible for the study of bacteria is known as bacteriology . It is a branch of microbiology , the science dedicated to studying microorganisms. Bacteriology and microbiology belong to the field of biology .
These scientific fields have advanced thanks to technological advances, although it is estimated that we know only 1% of the microbes in the biosphere.
