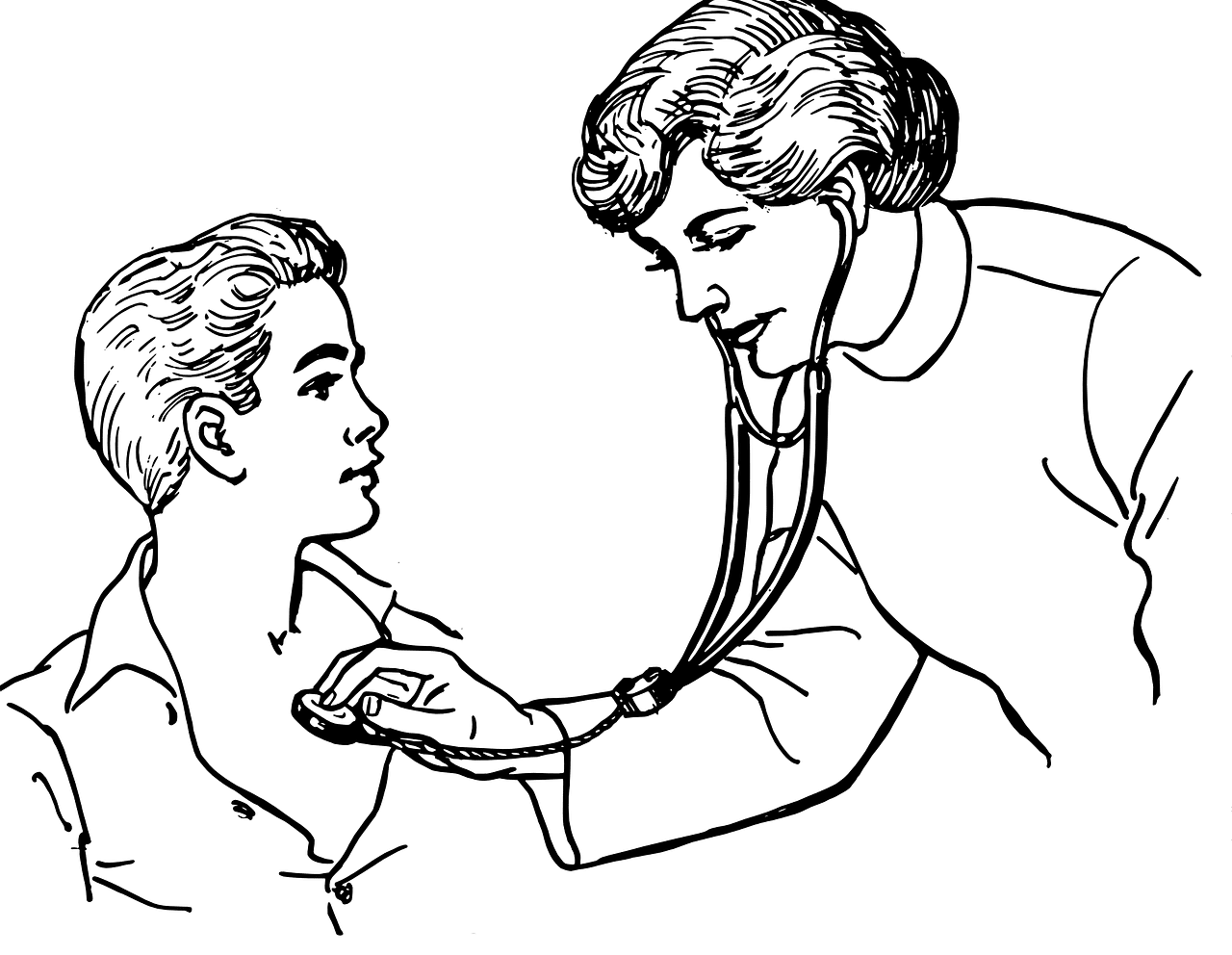
Auscultation consists of listening to the sounds produced by the organs to detect possible pathologies.
Auscultation is the act and result of auscultation . This verb can be used with reference to the medical practice that consists of listening to the sounds generated by the organs in the chest or belly to analyze them and detect possible pathologies. Auscultation is also to inquire about the state of something or the thoughts of an individual regarding a certain topic .
It can be said that auscultation involves exploring the patient's body by listening, either with instruments or directly, to the sounds that are produced in the rib cage or abdomen. These noises can be caused by the contraction of the heart or by air passing through the lungs , for example.
Historical evolution
In ancient times, to perform auscultation, the doctor used to put his ear close to the patient's body to hear the sounds directly. Also, on occasions, he resorted to a kind of tube to hear more clearly.
Currently auscultation is carried out with an instrument called a stethoscope or stethoscope , which has a membrane connected to headphones. The stethoscope optimizes acoustics so that the doctor receives sounds better.
Auscultation is usually performed with a stethoscope.
Types of auscultation
These changes throughout the history of medicine are reflected in the fundamental classification of auscultation:
- Immediate : the doctor places his ear on the patient's body to hear the noises without the help of any instrument. As mentioned above, this is an old method and is practically no longer used.
- Using a trumpet : a tube similar to that of a trumpet is used, the widest part of which rests on the patient's body while at the other end the doctor perceives the noises. In the past, this type of auscultation was used to monitor the condition of the fetus, but currently ultrasound is sufficient.
- Mediate : consists of the use of the stethoscope, and is the most widespread worldwide since it is more precise and versatile than the previous ones.
Cardiac auscultation , which is performed at different points in the chest, allows the professional to detect murmurs, which are symptoms of a possible problem with the heart valves. To carry out this evaluation, the doctor asks the patient to inhale air, hold it, and then exhale it.
Other types of auscultation are digestive auscultation , lung auscultation , and obstetric auscultation (which consists of listening to the fetal heartbeat with a Doppler ultrasound).
Digestive evaluation
Digestive auscultation consists of applying the bell of the stethoscope to each of the quadrants of the abdomen to listen to the movements of the intestines.
Depending on factors such as the intensity and frequency of the noises that the professional perceives using this technique, they can determine if the patient's condition is normal or if they have some pathology.
Lung auscultation
To evaluate the air flow through the tracheobronchial tree, lung auscultation combined with percussion is carried out; Together, they also allow the doctor to study the patient 's pleural space. The fundamental objectives of this technique are the following three:
- Listen to the noises generated by breathing.
- Perceive the so-called adventitious or added noises (they are those that overlap with those of normal breathing and are always signs of chronic or acute pathology ).
- If the doctor believes that the patient has some abnormality, then he also tries to listen to the voice noises that reach the chest wall.
- For evaluation , the patient can stand or sit; The doctor places the stethoscope on both sides of the spine, on the front of the chest and on the sides, while instructing the former to breathe in or out.
