Black holes are part of the object of study of quantum physics.
A black hole is an area of space with highly dense matter . Due to this enormous condensation of matter, it has a great force of gravity and produces a distortion in space-time .
It should be considered that black holes are neither holes nor empty : on the contrary, they contain more matter in less space than any other astronomical object or space. Its gravitational field is so strong that light cannot escape; Likewise, black holes attract matter that is in their vicinity.
Formation of a black hole
The formation of black holes is linked to the explosion of giant or massive stars when they reach their final stage. This stellar explosion is referred to as a supernova .
It must be considered that nuclear fusion reactions occur in stars, fusing hydrogen and helium in their cores. These processes lead to part of its mass being converted into energy and giving it its characteristic shine.
When the hydrogen runs out, the star dies, beginning the collapse of its core. Depending on its mass, the star can then become a white dwarf or cause a gravitational collapse, generating the supernova that occurs with giant stars.
Black holes, in this framework, arise from the condensation of the inert remains of a giant star . Since there is no force slowing down gravity , the black hole shrinks to zero volume and becomes infinitely dense. At that point, the light from the original star cannot escape the gravitational force.

After a supernova, the stellar core can become a black hole or a neutron star .
The contribution of Albert Einstein
Albert Einstein made important contributions related to the understanding of black holes. The scientist described this spatial region in his field equations .
These Einstein field equations, which are part of the theory of general relativity , explain gravity as an effect of the curvature of space-time , caused in turn by energy and matter.
According to what Einstein warned, this curvature of space-time generates a space-time singularity that is surrounded by a closed surface, called the event horizon (or event horizon ). This event horizon, meanwhile, establishes a separation between the region in question and the rest of the universe ; Likewise, it means that, upon entering it, the particles cannot leave. Einstein , in this way, anticipated the existence of black holes.
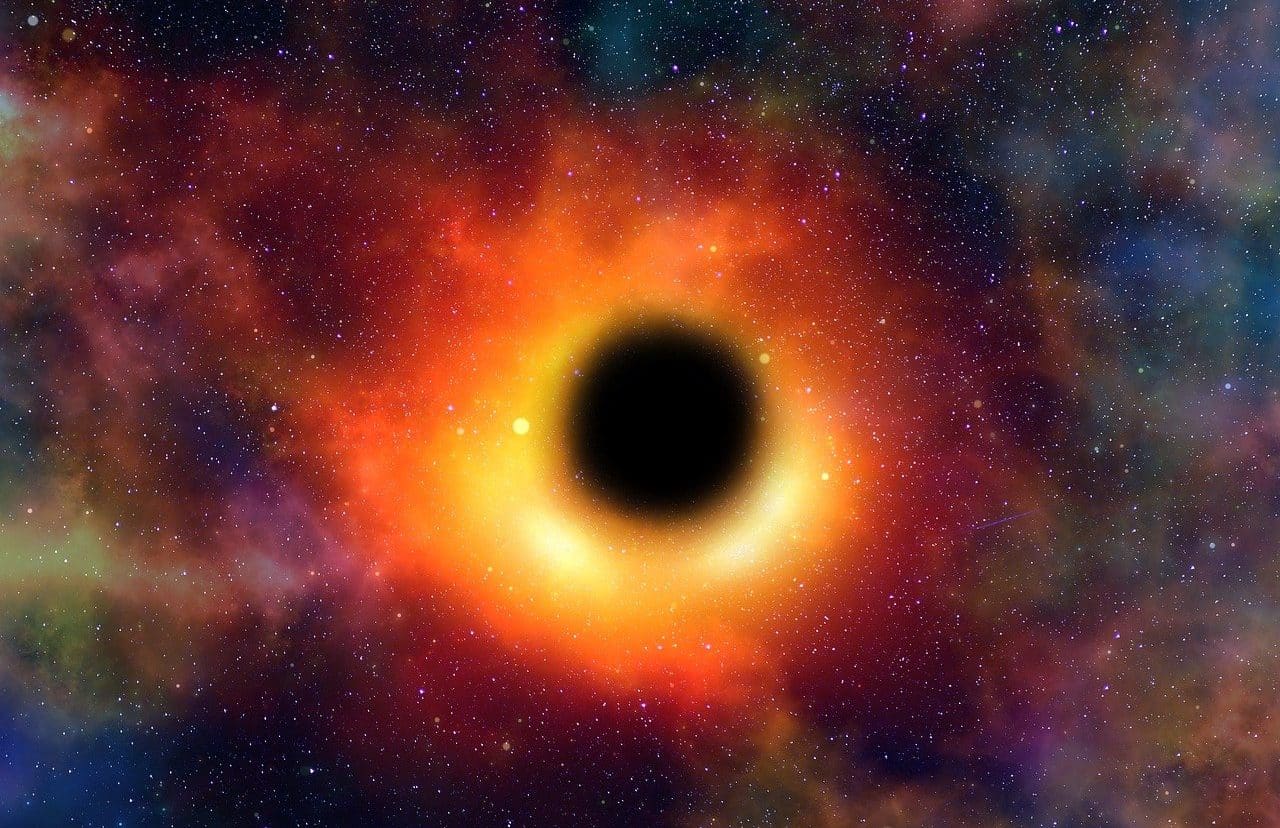

An accretion disk, made up of dust and gas, rotates around a black hole.
Radiation and black holes
As we already indicated, the high concentration of mass in a black hole gives rise to a gravitational field from which neither the particles nor the radiation can escape. However, black holes can emit a type of radiation, which was conjectured in the '70s by Stephen Hawking .
Known as Hawking radiation , it theoretically occurs in the vicinity of the black hole's event horizon. This is a quantum phenomenon that would imply a reduction in the rotational energy and mass of black holes, which means that, if the black hole does not manage to add mass through another means, it will end up shrinking until it disappears.
Classification according to type
Black holes can be classified in different ways. Depending on its angular momentum and its charge, it is possible to distinguish between the Kerr-Newman black hole (has a charge and rotates), the Kerr black hole (has no charge but rotates), the Reissner-Nordström black hole (has of charge and does not rotate) and the Schwarzschild black hole (lacks charge and does not rotate).
In terms of mass, a distinction is made between the mini black hole (or micro black hole ), the stellar black hole , the intermediate black hole and the supermassive black hole .
We must also name other types of black holes that are hypothetical. A primordial black hole would be one whose formation is linked to the extreme density that existed after the explosion detailed by the Big Bang theory , when the expansion of the universe began, and not due to stellar collapse. These primordial black holes would be the dark matter in galaxies.
A white hole , on the other hand, would allow Einstein 's field equations to be solved, although due to the conditions it requires it is estimated that its existence is not possible. The difference with a black hole is that this type of region would not absorb energy or matter, but would allow their escape. Another possible solution to the aforementioned equations is called a wormhole , a structure with a multiply connected topology that would function as a kind of bridge or tunnel to move in space and time .
Black holes in fiction
While astrophysics and astronomy in general advance little by little with the existing knowledge about black holes, these regions of the cosmos often appear in the field of fiction.
Movies and series such as "Interstellar" , "Star Trek" and "Doctor Who" have linked plots to black holes, associating them with the possibility of time travel , the theory of the multiverse and even their artificial creation to use them for specific purposes. destructive.
